
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781337553278
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
thumb_up100%
Chapter 17, Problem 4P
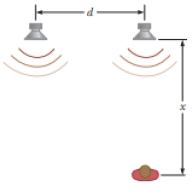
Why is the following situation impossible? Two identical loudspeakers are driven by the same oscillator at frequency 200 Hz. They are located on the ground a distance d = 4.00 m from each other. Starting far from the speakers, a man walks straight toward the right-hand speaker as shown in Figure P17.4. After passing through three minima in sound intensity, he walks to the next maximum and stops. Ignore any sound reflection from the ground.
Figure P17.4
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
pls help on these
pls help on these
20. Two small conducting spheres are placed on top of insulating pads. The 3.7 × 10-10 C sphere is fixed whie
the 3.0 × 107 C sphere, initially at rest, is free to move. The mass of each sphere is 0.09 kg. If the spheres
are initially 0.10 m apart, how fast will the sphere be moving when they are 1.5 m apart?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.1QQCh. 17.2 - Consider the waves in Figure 17.8 to be waves on a...Ch. 17.4 - When a standing wave is set up on a string fixed...Ch. 17.6 - Prob. 17.4QQCh. 17.6 - Balboa Park in San Diego has an outdoor organ....Ch. 17 - Two waves on one string are described by the wave...Ch. 17 - Two pulses of different amplitudes approach each...Ch. 17 - Two wave pulses A and B are moving in opposite...Ch. 17 - Why is the following situation impossible? Two...Ch. 17 - Two pulses traveling on the same string are...
Ch. 17 - Two identical loudspeakers 10.0 m apart are driven...Ch. 17 - Two sinusoidal waves on a string are defined by...Ch. 17 - Verify by direct substitution that the wave...Ch. 17 - Prob. 9PCh. 17 - A standing wave is described by the wave function...Ch. 17 - Prob. 11PCh. 17 - A taut string has a length of 2.60 m and is fixed...Ch. 17 - A string that is 30.0 cm long and has a mass per...Ch. 17 - In the arrangement shown in Figure P17.14, an...Ch. 17 - Review. A sphere of mass M = 1.00 kg is supported...Ch. 17 - Review. A sphere of mass M is supported by a...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17PCh. 17 - Review. A solid copper object hangs at the bottom...Ch. 17 - The Bay of Fundy, Nova Scotia, has the highest...Ch. 17 - Prob. 20PCh. 17 - The fundamental frequency of an open organ pipe...Ch. 17 - Ever since seeing Figure 16.22 in the previous...Ch. 17 - An air column in a glass tube is open at one end...Ch. 17 - A shower stall has dimensions 86.0 cm 86.0 cm ...Ch. 17 - Prob. 25PCh. 17 - Prob. 26PCh. 17 - As shown in Figure P17.27, water is pumped into a...Ch. 17 - As shown in Figure P17.27, water is pumped into a...Ch. 17 - Prob. 29PCh. 17 - Why is the following situation impossible? A...Ch. 17 - Review. A student holds a tuning fork oscillating...Ch. 17 - Prob. 32PCh. 17 - Suppose a flutist plays a 523-Hz C note with first...Ch. 17 - Two strings are vibrating at the same frequency of...Ch. 17 - Prob. 35APCh. 17 - A 2.00-m-long wire having a mass of 0.100 kg is...Ch. 17 - Prob. 37APCh. 17 - You are working as an assistant to a landscape...Ch. 17 - Review. Consider the apparatus shown in Figure...Ch. 17 - Review. For the arrangement shown in Figure...Ch. 17 - Review. A loudspeaker at the front of a room and...Ch. 17 - Two speakers are driven by the same oscillator of...Ch. 17 - A standing wave is set up in a string of variable...Ch. 17 - Review. The top end of a yo-yo string is held...Ch. 17 - Prob. 45APCh. 17 - Prob. 46APCh. 17 - Review. A 12.0-kg object hangs in equilibrium from...Ch. 17 - Review. An object of mass m hangs in equilibrium...Ch. 17 - Two waves are described by the wave functions...Ch. 17 - Prob. 50CP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- pls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forward19. Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain above sea level, has a peak of 8849 m above sea level. Assume that sea level defines the height of Earth's surface. (re = 6.38 × 106 m, ME = 5.98 × 1024 kg, G = 6.67 × 10 -11 Nm²/kg²) a. Calculate the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point at the peak of Mount Everest. b. What is the ratio of the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point 644416m below the surface of the Earth to a point at the top of Mount Everest? C. A tourist watching the sunrise on top of Mount Everest observes a satellite orbiting Earth at an altitude 3580 km above his position. Determine the speed of the satellite.arrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forward
- pls help on allarrow_forward6. As the distance between two charges decreases, the magnitude of the electric potential energy of the two-charge system: a) Always increases b) Always decreases c) Increases if the charges have the same sign, decreases if they have the opposite signs d) Increases if the charges have the opposite sign, decreases if they have the same sign 7. To analyze the motion of an elastic collision between two charged particles we use conservation of & a) Energy, Velocity b) Momentum, Force c) Mass, Momentum d) Energy, Momentum e) Kinetic Energy, Potential Energyarrow_forwardpls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forward
- pls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forward17. Two charges, one of charge +2.5 × 10-5 C and the other of charge +3.7 × 10-6 C, are 25.0 cm apart. The +2.5 × 10−5 C charge is to the left of the +3.7 × 10−6 C charge. a. Draw a diagram showing the point charges and label a point Y that is 20.0 cm to the left of the +3.7 × 10-6 C charge, on the line connecting the charges. (Field lines do not need to be drawn.) b. Calculate the net electric field at point Y.arrow_forward3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
What Are Sound Wave Properties? | Physics in Motion; Author: GPB Education;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GW6_U553sK8;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY