
(a)
Interpretation:
Bond-line structure of the molecules should be drawn for the given IUPAC names.
Concept introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the parent chain.
Suffix denotes the presence of
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with Cyclo.
The structure of a molecule can be drawn by analyzing the presence of prefix, suffix and root word in the given IUPAC name.
In bond-line structure the carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms which are attached to that carbon atom are not to show, they are drawn as line segments. For acyclic carbon chains it draws as in a zig-zag fashion and for cyclic chains of carbon it draws as a cyclic polygon. For representing a heteroatom attached to the carbon, use a labelled line segment.
(a)
Answer to Problem 32PP
Answer
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
To analyze the presence of prefix suffix and root name in the given IUPAC name and draw the bond- line structure of the molecule (a).
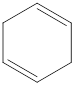
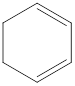
The given IUPAC name is 1,4-Cyclohexadiene.

The given IUPAC Name is 1, 4-Cyclohexadiene. In the IUPAC name 1,4 represents the position of substituents or functional group in the molecule. But no substituents presented in the name, so the 1,4 positions are locating the function groups.
The root word cyclohex indicates the molecule contains 6 carbons and the cyclo indicates the molecule is cyclic. The suffix ‘diene’ denotes the molecule is alkene and the number ‘1,4’just before the root name represent the positions of double bonds.
Therefore the bond- line structure of the molecule (a) is shown below.
(b)
Interpretation:
Bond-line structure of the molecules should be drawn for the given IUPAC names.
Concept introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the parent chain.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc. The position of this fictional group is represented just before the root name.
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with Cyclo.
The structure of a molecule can be drawn by analyzing the presence of prefix, suffix and root word in the given IUPAC name.
In bond-line structure the carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms which are attached to that carbon atom are not to show, they are drawn as line segments. For acyclic carbon chains it draws as in a zig-zag fashion and for cyclic chains of carbon it draws as a cyclic polygon. For representing a heteroatom attached to the carbon, use a labelled line segment.
(b)
Answer to Problem 32PP
Answer
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
To analyze the presence of prefix suffix and root name in the given IUPAC name and draw the bond- line structure of the molecule (b).
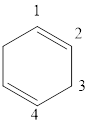
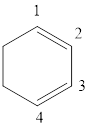
The given IUPAC name is 1, 3-Cyclohexadiene.

The given IUPAC Name is 1, 3-Cyclohexadiene. In the IUPAC name 1,3 represents the position of substituents or functional group in the molecule. But no substituents presented in the name, so the 1, 3 positions are locating the function groups.
The root word cyclohex, indicates the molecule contains 6 carbons and the cyclo indicates the molecule is cyclic, the suffix ‘diene’ denotes the molecule is alkene and the number ‘1,3’just before the root name represent the positions of double bonds.
Therefore the bond- line structure of the molecule (b) is shown below.
(c)
Interpretation:
Bond-line structure of the molecules should be drawn for the given IUPAC names.
Concept introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the parent chain.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc. The position of this fictional group is represented just before the root name.
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with Cyclo.
The structure of a molecule can be drawn by analyzing the presence of prefix, suffix and root word in the given IUPAC name.
In bond-line structure the carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms which are attached to that carbon atom are not to show, they are drawn as line segments. For acyclic carbon chains it draws as in a zig-zag fashion and for cyclic chains of carbon it draws as a cyclic polygon. For representing a heteroatom attached to the carbon, use a labelled line segment.
(c)
Answer to Problem 32PP
Answer
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
To analyze the presence of prefix suffix and root name in the given IUPAC name and draw the bond- line structure of the molecule (c).
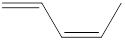
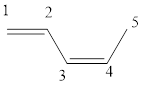
The given IUPAC name is (z)-1, 3-Pentadiene.

The given IUPAC Name is (z)-1, 3-Pentadiene.
In the IUPAC name 1, 3 represent the position of substituents or functional groups in the molecule. In the IUPAC name 1, 3 represent the position of substituents or functional group in the molecule. But no substituents presented in the name, so the 1,3 positions are locating the function groups.
The word pent indicates the molecule contains 5 carbons. The suffix ‘diene’ denotes the molecule is alkene and the number ‘1, 3’ just before the root name represents the positions of double bonds. The prefix ‘z’ is a stereo-descriptor for the double bond, which indicates the non-similar groups are attached to double bond on same sides.
Hence the bond- line structure for the given IUPAC name is
(d)
Interpretation:
Bond-line structure of the molecules should be drawn for the given IUPAC names.
Concept introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the parent chain.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc. The position of this fictional group is represented just before the root name.
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with Cyclo.
The structure of a molecule can be drawn by analyzing the presence of prefix, suffix and root word in the given IUPAC name.
In bond-line structure the carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms which are attached to that carbon atom are not to show, they are drawn as line segments. For acyclic carbon chains it draws as in a zig-zag fashion and for cyclic chains of carbon it draws as a cyclic polygon. For representing a heteroatom attached to the carbon, use a labelled line segment.
(d)
Answer to Problem 32PP
Answer
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
To analyze the presence of prefix suffix and root name in the given IUPAC name and draw the bond- line structure of the molecule (d).
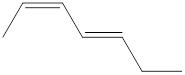
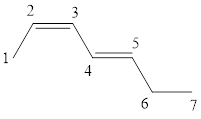
The given IUPAC name is (2Z, 4E)-Hepta-2,4-diene.

The given IUPAC Name is (2Z, 4E)-Hepta-2,4-diene.
The word Hepta indicates the molecule contains 7 carbons. The suffix ‘diene’ denotes the molecule is alkene and the number ‘2, 4’ just before the root name represents the positions of double bonds. The prefix ‘2Z,4E’ is the stereo-descriptor for the double bonds, which indicates the non-similar groups attached to 2-positioned double bond are on same sides and the non-similar groups attached to 4-positioned double bond are on opposite sides.
Hence the bond- line structure for the given IUPAC name is
(e)
Interpretation:
Bond-line structure of the molecules should be drawn for the given IUPAC names.
Concept introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the parent chain.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc. The position of this fictional group is represented just before the root name.
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with Cyclo.
The structure of a molecule can be drawn by analyzing the presence of prefix, suffix and root word in the given IUPAC name.
In bond-line structure the carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms which are attached to that carbon atom are not to show, they are drawn as line segments. For acyclic carbon chains it draws as in a zig-zag fashion and for cyclic chains of carbon it draws as a cyclic polygon. For representing a heteroatom attached to the carbon, use a labelled line segment.
(e)
Answer to Problem 32PP
Answer
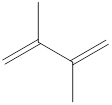
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
To analyze the presence of prefix suffix and root name in the given IUPAC name and draw the bond- line structure of the molecule (e).
The given IUPAC name is 2, 3–Dimethyl-1, 3-butadiene.

The given IUPAC Name is 2, 3–Dimethyl-1, 3-butadiene.
In the IUPAC name 2, 3 represent the position of substituents in the molecule. Dimethyl is the prefix that indicates the presence of two methyl groups in the molecule.
The word but indicates the molecule contains 4 carbons. The suffix diene denotes the molecule is alkene and the number ‘2, 3’ just before the root name represents the positions of double bonds.
Hence the bond- line structure for the given IUPAC name is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- A student proposes the transformation below in one step of an organic synthesis. There may be one or more reactants missing from the left-hand side, but there are no products missing from the right-hand side. There may also be catalysts, small inorganic reagents, and other important reaction conditions missing from the arrow. • Is the student's transformation possible? If not, check the box under the drawing area. . If the student's transformation is possible, then complete the reaction by adding any missing reactants to the left-hand side, and adding required catalysts, inorganic reagents, or other important reaction conditions above and below the arrow. • You do not need to balance the reaction, but be sure every important organic reactant or product is shown. + T X O O лет-ле HO OH HO OH This transformation can't be done in one step.arrow_forwardDetermine the structures of the missing organic molecules in the following reaction: X+H₂O H* H+ Y OH OH Note: Molecules that share the same letter have the exact same structure. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic molecules X and Y. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X Sarrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction. If there aren't any products, because nothing will happen, check the box under the drawing area instead. No reaction. HO. O :☐ + G Na O.H Click and drag to start drawing a structure. XS xs H₂Oarrow_forward
- What are the angles a and b in the actual molecule of which this is a Lewis structure? H H C H- a -H b H Note for advanced students: give the ideal angles, and don't worry about small differences from the ideal groups may have slightly different sizes. a = b = 0 °arrow_forwardWhat are the angles a and b in the actual molecule of which this is a Lewis structure? :0: HCOH a Note for advanced students: give the ideal angles, and don't worry about small differences from the ideal that might be caused by the fact that different electron groups may have slightly different sizes. a = 0 b=0° Sarrow_forwardDetermine the structures of the missing organic molecules in the following reaction: + H₂O +H OH O OH +H OH X Note: Molecules that share the same letter have the exact same structure. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the missing organic molecule X. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
- Identify the missing organic reactant in the following reaction: x + x O OH H* + ☑- X H+ O O Х Note: This chemical equation only focuses on the important organic molecules in the reaction. Additional inorganic or small-molecule reactants or products (like H₂O) are not shown. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the missing organic reactant X. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Carrow_forwardCH3O OH OH O hemiacetal O acetal O neither O 0 O hemiacetal acetal neither OH hemiacetal O acetal O neither CH2 O-CH2-CH3 CH3-C-OH O hemiacetal O acetal CH3-CH2-CH2-0-c-O-CH2-CH2-CH3 O neither HO-CH2 ? 000 Ar Barrow_forwardWhat would be the best choices for the missing reagents 1 and 3 in this synthesis? 1. PPh3 2 2. n-BuLi 3 Draw the missing reagents in the drawing area below. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. • Do not draw the missing reagent 2. If you draw 1 correctly, we'll know what it is. • Note: if one of your reagents needs to contain a halogen, use bromine. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
- Predict the products of this organic reaction: NaBH3CN + NH2 ? H+ Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ×arrow_forwardPredict the organic products that form in the reaction below: + OH +H H+ ➤ ☑ X - Y Note: You may assume you have an excess of either reactant if the reaction requires more than one of those molecules to form the products. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic products X and Y. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Garrow_forwardPredict the organic products that form in the reaction below: OH H+ H+ + ☑ Y Note: You may assume you have an excess of either reactant if the reaction requires more than one of those molecules to form the products. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic products X and Y. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ✓ marrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





