
Concept explainers
Labor Mix and Yield Variances
Matt’s Eat ’N Run has two categories of direct labor: unskilled, which costs $10 per hour, and skilled, which costs $20 per hour. Management has established standards per “equivalent friendly meal,” which has been defined as a typical meal consisting of a hamburger, a drink, and french fries. Standards have been set as follows:
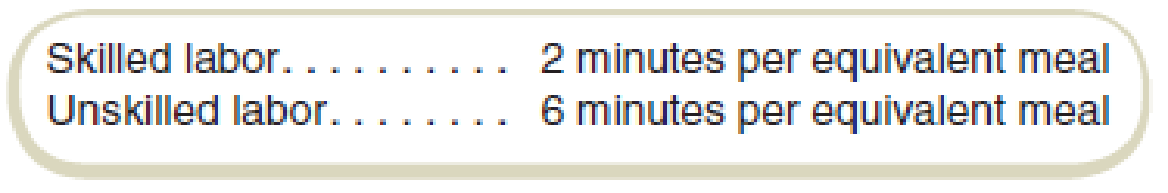
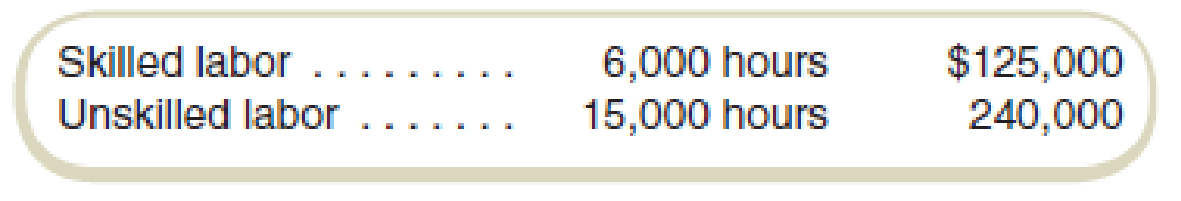
For the year, Matt’s sold 180,000 equivalent friendly meals and incurred the following labor costs:
Required
- a. Compute labor price and efficiency variances.
- b. Compute labor mix and yield variances.
a.
Compute materials price and Materials efficiency variances.
Answer to Problem 32E
The value of materials price variance is $5,000 U and ,materials efficiency variance is $0 for skilled labor, and for unskilled labor, the materials price variance is $90,000 U and materials efficiency variance is $30,000 F.
Explanation of Solution
Materials price variance:
Materials price variance is resultant materials price that has been computed or derived at the end of the accounting period for which the computations are being done.
Materials efficiency variance:
Materials efficiency variance is the resultant Materials efficiency that has been computed or derived at the end of the accounting period for which the computations are being done.
Compute the materials price variance:
| Particulars | Skilled labor | Unskilled labor |
| Materials variance: | ||
| Actual | $125,000 | $240,000 |
| Standard | $120,000 | $150,000 |
|
Materials variance | $5,000 U | $90,000 U |
Table: (1)
Compute the Materials efficiency variance:
| Particulars | Skilled labor | Unskilled labor |
|
Materials mix variance: | ||
| Actual | $120,000 | $150,000 |
| Standard | $105,000 | $157,500 |
|
Materials mix variance | $15,000U | $7,500F |
| Materials yield variance: | ||
| Actual | $105,000 | $157,500 |
| Standard | $120,000 | $180,000 |
|
Materials yield variance | $15,000F | $22,500F |
|
Materials efficiency variance | $0 | $30,000F |
Table: (2)
| Measure | Skilled labor | Unskilled labor |
| AQ | 6,000 | 15,000 |
| SP | $20.00 | $10.00 |
| ASQ | 5,250(1) | 15,750(2) |
| SQ | 6,000(3) | 18,000(4) |
Table: (3)
Thus, the value of materials price variance is $5,000 U and materials efficiency variance is $0 for skilled labor and for unskilled labor, the materials price variance is $90,000U and materials efficiency variance is $30,000F.
Working note 1:
Compute the ASQ for Skilled labor:
Working note 2:
Compute the ASQ for unskilled labor:
Working note 3:
Compute the SQ of Skilled labor:
Working note 4:
Compute the SQ of Unskilled labor:
b.
Compute materials mix and materials yield variances.
Answer to Problem 32E
The value of materials mix and materials yield variances of skilled labor is $15,000 U and $15,000 F respectively, and the value of materials mix and materials yield variances of unskilled labor $7,500 and $22,500 respectively.
Explanation of Solution
Materials mix variance:
Materials mix variance is the resultant market Materials mix that has been computed or derived at the end of the accounting period for which the computations are being done for two or more than two products.
Materials yield variance:
Materials yield variance is the resultant difference between the costs of finished goods expected from a specific amount of raw material that has been computed or derived at the end of the accounting period for which the computations are being done.
Compute the materials mix variance and materials yield variance for skilled labor and unskilled labor:
| Particulars | Skilled labor | Unskilled labor |
|
Materials mix variance: | ||
| Actual | $120,000 | $150,000 |
| Standard | $105,000 | $157,500 |
|
Materials mix variance | $15,000 U | $7,500 F |
| Materials yield variance: | ||
| Actual | $105,000 | $157,500 |
| Standard | $120,000 | $180,000 |
|
Materials yield variance | $15,000 F | $22,500 F |
|
Materials efficiency variance | $0 | $30,000 F |
Table: (4)
| Measure | Skilled labor | Unskilled labor |
| AQ | 6,000 | 15,000 |
| SP | $20.00 | $10.00 |
| ASQ | 5,250(1) | 15,750(2) |
| SQ | 6,000(3) | 18,000(4) |
Table: (5)
Thus, the value of materials mix and materials yield variances of skilled labor are $15,000 U and $15,000 F respectively, and the value of materials mix and materials yield variances of unskilled labor $7,500 and $22,500 respectively.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Fundamentals Of Cost Accounting (6th Edition)
- The underapplication of overhead will result in Group of answer choices understatement of net income. overstatement of cost of goods sold. understatement of cost of goods sold. overvalued finished goods inventory.arrow_forwardchoose best answer financial accountingarrow_forwardWhat is the couple marriage penalty or benefit?arrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning  Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





