
Brandy Dees recently bought Nievo Enterprises, a company that manufactures ice skates. Brandy decided to assume management responsibilities for the company and appointed herself president shortly after the purchase was completed. When she bought the company, Brandy’s investigation revealed that with the exception of the blades, all parts of the skates are produced internally. The investigation also revealed that Nievo once produced the blades internally and still owned the equipment. The equipment was in good condition and was stored in a local warehouse. Nievo’s former owner had decided three years earlier to purchase the blades from external suppliers.
Brandy Dees is seriously considering making the blades instead of buying them from external suppliers. The blades are purchased in sets of two and cost $8 per set. Currently, 100,000 sets of blades are purchased annually.
Skates are produced in batches, according to shoe size. Production equipment must be reconfigured for each batch. The blades could be produced using an available area within the plant. Prime costs will average $5.00 per set. There is enough equipment to set up three lines of production, each capable of producing 80,000 sets of blades. A supervisor would need to be hired for each line. Each supervisor would be paid a salary of $40,000. Additionally, it would cost $1.50 per machine hour for power, oil, and other operating expenses. Since three types of blades would be produced, additional demands would be made on the setup activity. Other
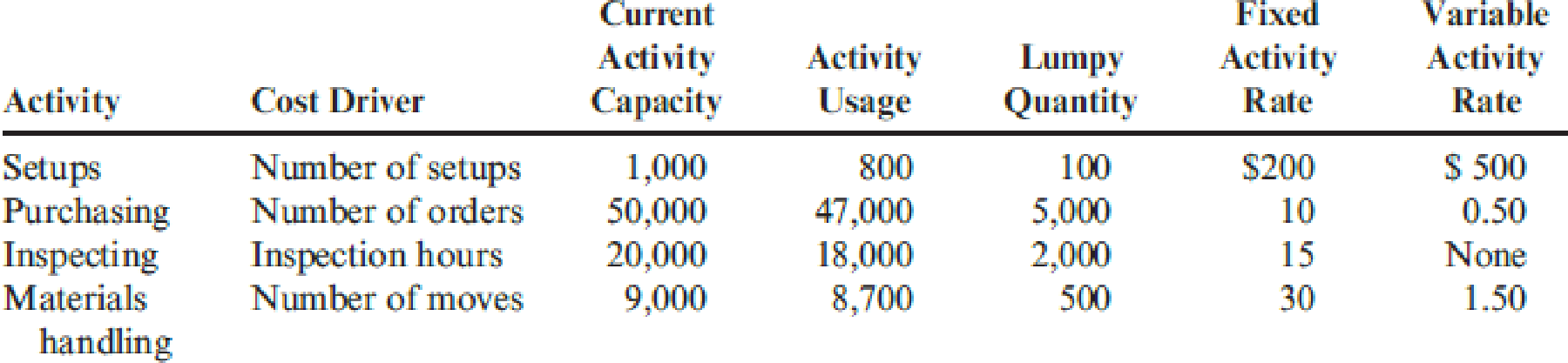
The demands that the production of blades places on the overhead activities are as follows:

If the blades are made, the purchase of the blades from outside suppliers will cease. Therefore, purchase orders will decrease by 6,500 (the number associated with their purchase). Similarly, the moves for the handling of incoming blades will decrease by 400. Any unused activity capacity is viewed as permanent.
Required:
- 1. Should Nievo make or buy the blades?
- 2. Explain how the ABC resource usage model helped in the analysis. Also, comment on how a conventional approach would have differed.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 17 Solutions
EBK CORNERSTONES OF COST MANAGEMENT
- Need help with accounting questionarrow_forwardCheck my work The finance director for the City of Green Falls printed the General Fund Revenues and Appropriations Ledgers shown below for the year just ended. REVENUES LEDGER Ref. Account Description Est. Revenues Dr(Cr) Revenues Balance Cr(Dr) Dr(Cr) Estimated Revenues-Taxes-Real Property 102 Budget Authorization 6,452,400 6,452,400 103 Accrued Revenue 104 Previous Deferral 109 Deferral 6,455,000 345,000 (308,000) (2,600) (347,600) (39,600) 110 Budget Amendment 111 Closing entry 40,000 (6,492,400) 400 (6,492,000) 112 Closing entry (6,492,000) Estimated Revenues-Taxes-Sales 102 Budget Authorization. 103 Received in Cash 110 Budget Amendment 111 Closing Entry 112 Closing Entry 736,250 (25,000) (711,250) 710,600 736,250 25,650 650 (710,600) (710,600) e Q Search ་ PRE a 1 < 2/arrow_forwardPrecision Tools Inc. has the following information related to its direct materials usage: Standard Quantity: 120,000 units Actual Quantity: 140,000 units Standard Price: $2.50 per unit Actual Price: $2.80 per unit A. Calculate the materials price variance and state whether it is favorable or unfavorable. B. Calculate the materials usage variance and state whether it is favorable or unfavorable.arrow_forward
- Job Costing: The warehouse supervisor at Alpha Electronics implements a strict cycle counting process where system accuracy must stay above 99%. Daily variances between 1-2% require immediate recount, while those exceeding 2% trigger supervisor review and investigation. During today's audit of electronic components, the system showed 2,400 items, but physical count revealed only 2,356 items present in the warehouse. The supervisor needs to determine the variance percentage before deciding on next steps.??arrow_forwardCan you please provide answer this financial accounting question?arrow_forwardSolve this Accounting problemarrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningBusiness Its Legal Ethical & Global EnvironmentAccountingISBN:9781305224414Author:JENNINGSPublisher:Cengage
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningBusiness Its Legal Ethical & Global EnvironmentAccountingISBN:9781305224414Author:JENNINGSPublisher:Cengage Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT





