
Concept explainers
Diagram the following galvanic cell, indicating the directionof flow of electrons in the external circuit and themotion of ions in the salt bridge.
Write a balanced equation for the overall reaction in thiscell.
Interpretation:
The given galvanic cell needs to be drawn and a balanced equation for the overall reaction in the cell is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
A galvanic cell is also known as a voltaic cell. It is an electrochemical cell where oxidation-reduction reactions take place and result in the generation of an electric current. In a simple galvanic cell, there are two electrodes: cathode and anode. Each of the electrodes is immersed in their respective metal ions solutions. Thus, there are two compartments of the cell. Both compartments of the cell are connected by a salt bridge which helps in the movement of ions between the compartments of the cell.
Answer to Problem 1P
Diagram of galvanic cell:
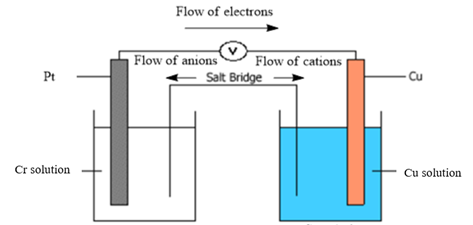
Balanced overall cell reaction:
Explanation of Solution
The given cell notation is as follows:
In a cell notation, oxidation is written always before reduction. Thus, in the given case,
Here, platinum is an inert electrode that is the source or sink for electrons. It does not play any chemical role in the electrode reaction.
Since oxidation takes place at the anode and reduction at the cathode, the anodic and cathodic reactions (half-reactions) of the cell can be represented as follows:
At the anode, oxidation takes place as follows:
At the cathode, reduction takes place as follows:
From the above two half-reactions, the overall cell reaction can be obtained as follows:
Thus, the balanced overall cell reaction is as follows:
Now, in a typical galvanic cell, the flow of anions (negatively charged ions) takes place from cathode to anode, and the flow of cations (positively charged ions) takes place from anode to cathode through a salt bridge. Also, in the external circuit, the movement of electrons takes place from anode to cathode. The diagram of the given galvanic cell can be represented as follows:
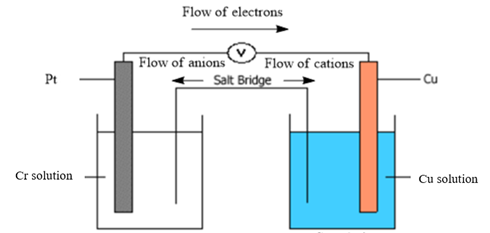
Thus, the diagram of the galvanic cell and the balanced overall cell reaction is as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Principles of Modern Chemistry
- Explain the importance of having a sampling plan with respect to food analysis. Explain the importance of having a sampling plan with respect to food analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forwardPlease predict the products for each of the following reactions. Clearly show the regiochemistry (Markovnikov vs anti-Markovnikov) and stereochemistry (syn- vs anti- or both). If a mixture of enantiomers is formed, please draw all the enantiomers. cold KMnO4, NaOH 2. DMS 1. 03 CH3OH Br2 1. 03 2. (CH3)2S H₂ Pd or Pt (catalyst) HBr 18 19 20 1 HBr ROOR (peroxide) H₂O H₂SO4 HCI HI 17 16 6 15 MCPBA 1. BH3 THF 2. H₂O2, NaOH 1. OsO4 2. H₂O₂ 110 CH3CO₂H (peroxyacid) 1. MCPBA 2. H₂O* Br2 H₂O BH3 THF B12 EtOH Pd or Ni (catalyst) D₂ (deuterium) Bra A B C D H OH H OH OH H OH α α α OH H OH OH фон d H "Harrow_forwardBriefly indicate the models that describe the structure of the interface: Helmholtz-Perrin, Gouy-Chapman, Stern and Grahame models.arrow_forward
- Using Benzene as starting materid show how each of the Following molecules Contel Ve syntheswed CHI 9. b -50311 с CHY 503H Ночто d. อ •NOV e 11-0-650 NO2arrow_forwardThe molecule PYRIDINE, 6th electrons and is therefore aromatre and is Assigned the Following structure contering Since aromatk moleculoy undergo electrophilic anomatic substitution, Pyridine shodd undergo The Following reaction + HNO3 12504 a. write all of the possible Mononitration Products that could Result From this reaction 18. Bared upon the reaction mechanison determime which of these producty would be the major Product of the hegetionarrow_forwarda. Explain Why electron withdrawing groups tend to be meta-Directors. Your answer Should lyclude all apropriate. Resonance contributing Structures fo. Explain why -ll is an outho -tura drccton even though chlorine has a very High Electronegativityarrow_forward
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





