
Concept explainers
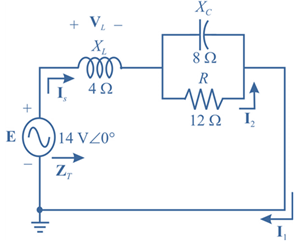
For theseries-parallel network in Fig.17.38.
a. Calculate ZT.
b. Determine Is.
c. Determine I1.
d. Find I2.
e. Find VL..
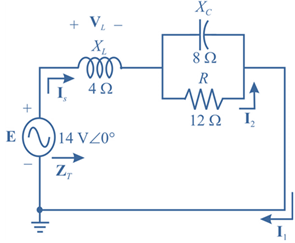
Fig.17.38
(a)
Total impedance
Answer to Problem 1P
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given circuit is:

Calculation:
Let us modify the circuit as below to calculate the total impedance.
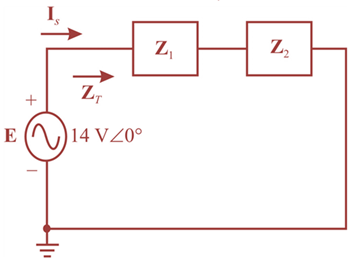
In the modified diagram,
Impedance
Impedance
Therefore, total impedance will be:
Putting the values for the total impedance:
(b)
The current
Answer to Problem 1P
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given circuit is:
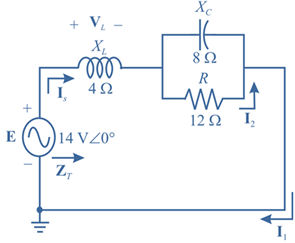
Calculation:
Let us modify the circuit as below to calculate the total impedance.
In the modified diagram,
Impedance
Impedance
Current
(c)
The current
Answer to Problem 1P
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given circuit is:
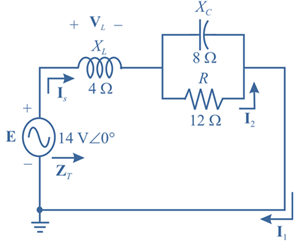
Calculation:
Let us modify the circuit as below to calculate the total impedance.
In the modified diagram,
Impedance
Impedance
Current
We can see from the circuit that,
(d)
The current
Answer to Problem 1P
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given circuit is:
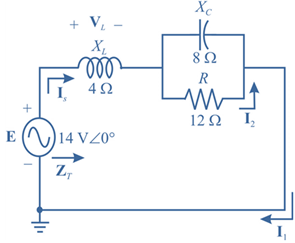
Calculation:
Let us modify the circuit as below to calculate the total impedance.
In the modified diagram,
Impedance
Impedance
Current
(e)
Voltage
Answer to Problem 1P
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given circuit is:
Calculation:
Let us modify the circuit as below to calculate the total impedance.
In the modified diagram,
Impedance
Impedance
Voltage
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
- Chose the correct answer: 1- A squirrel cage induction motor is not selected when (A) initial cost is the main consideration (B) maintenance cost is to be kept low (C) higher starting torque is the main consideration (D) all above considerations are involved 2- The torque of an induction motor is .............. (A) directly proportional to slip (B) inversely proportional to slip... (C) proportional to the square of the slip (D) none of the above 3- Insertion of resistance in the stator of an induction motor. (A) increases the load torque (B) decreases the starting torque (C) increases the starting torque (D) none of above tool to slip 10 or of the above 4- Increase in the length of air-gap in the induction motor results in the increasing of its (A) air-gap flux (B) magnetizing current (C) speed (D) power factor 5- In cumulatively cascade method for speed controlling, if PA is the number of poles of main motor and PB is the number of poles of auxiliary motor. Then the speed of the set…arrow_forwardChose the correct answer: 1- The resultant flux in stator winding of three-phase induction motor is equal to (A) Maximum value of flux due to any phase (B) Twice of the maximum value of flux due to any phase. (C) 0.5 times the maximum value of flux due to any phase (D) 1.5 times the maximum value of flux due to any phase 2- Which one of the following starters cannot be used for 3-phase, star - connected, slip-ring induction motor? (A) Auto-transformer starter (B) Star-delta starter (C) Direct-on-line starter (D) Rotor resistance starter 3- The crawling in the induction motor is caused by.............. (A) low voltage supply (B) high loads (D) improper design of the machine (C) harmonics developed in the motor 4- The 'cogging' of an induction motor can be avoided by........... (A) good ventilation (B) using DOL starter (C) star-connecting of stator winding (D) having number of rotor slots more or less than the number of stator slots 5- The method which can be used for the speed control…arrow_forwardManual solution only, no Al usedarrow_forward
- Choose the correct answer: 1- The stator core of a 3- phase induction motor is laminated in order to reduce the Eddy current loss ) Weight of the stator (B) Hysteresis loss (C) Both eddy current and hysteresis loss - In cumulatively cascade method for speed controlling of a 3-phase induction motor, if PA is the number of poles of main motor and P, is the number of poles of auxiliary motor. Then the speed of the motor B is given by Ⓐ120f/ PA + PB CO (B) 120f/PA-Ps (C) 120f/PA (D) 120f/ Ps 3-Direct online starter is used for 3- phase induction motors having capacity COOOO ⑭Ⓐ Less than 5 h.p. (B) Less than 10 h.p. (C) Greater than 10 h.p. (D) For any capacity motor 4-Crawling of a 3- phase induction motor is a phenomena mainly associated with (B) 5th harmonics Ⓒ) 7 th harmonics (D) 2nd harmonics (A) 3rd harmonics 5-Cogging in a 3- phase induction motor is caused --------- (Ⓐ) If the number of stator slots are equal to number of rotor slots (B) If the motor is running at fraction of its…arrow_forwardChoose the correct answer: 1-We avoid line starting of induction motor and use starter because... (A) It will run in reverse direction (B) It will pick up very high speed and may go out of step Motor takes five to seven times its full load current (D) Starting torque is very high 2-DOL starting of induction motors is usually restricted to........... A Low horsepower motors (D) High speed motors (B) Variable speed motors (C) High horsepower motors 3- The method which can be used for the speed control of induction motor from stator side is......... (A) V/f control (B) Controlling number of stator poles to control Ns (C) Adding rheostats in stator circuit All of these 4-In cumulatively cascade method for speed controlling, if PA is the number of poles of main motor and PB is the number of poles of auxiliary motor. Then the speed of the rotor B is given by 120f/PA + PB (B) 120f/PA-PB (C) 120f/PA 5-The crawling in the induction motor is caused by.............. (A) low voltage supply (B)…arrow_forwardFor the picture attached below the parameters are the following: f1 = 400 Hz m(t) = sin(2 fmt), where fm = 300 Hz. Assume ideal LPFs with a cut-o frequency of f1. What would be the value of frequency f2 be so that the carrier frequency is 2.5kHz? What modification of this system is required to generate USSB (at the same carrier frequency)? ( Note: this does not involbe changing the oscillator frequencies)arrow_forward
- Determine (analytically) the signals at points A-Garrow_forwardSolve without using alarrow_forwardA Si step junction maintained at room temperature under equilibrium conditions has a p-side doping of NA 2X1015/cm³ and an n-side doping of ND=1015/cm³. Compare a) Vbi b) Xp, Xn, and W c) ɛ at x=0 d) V at x=0 Make sketches that are roughly to scale of the charge density, electric field, and electrostatic potential as a function of position.arrow_forward
 Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...Electrical EngineeringISBN:9781305632134Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. SarmaPublisher:Cengage Learning
Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...Electrical EngineeringISBN:9781305632134Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. SarmaPublisher:Cengage Learning Electricity for Refrigeration, Heating, and Air C...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337399128Author:Russell E. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Electricity for Refrigeration, Heating, and Air C...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337399128Author:Russell E. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning

