
Concept explainers
(a)
To plot:
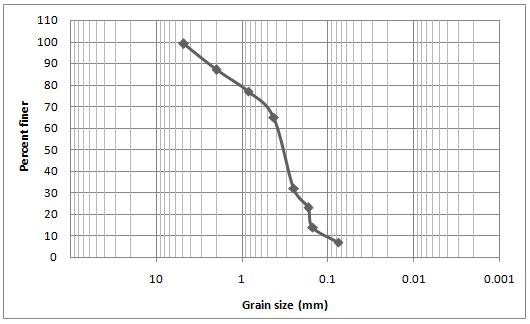
Grain size distribution curve.
Answer to Problem 19P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Sieve No. | Sieve No. | Percent finer |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Pan | Pan | -- |
Concept used:
Plot the grain size distribution curve between the sieve number (mm) and the percent finer. The sieve number (mm) is plotted in x -axis and percent finer in y -axis.
Calculation:
Conclusion:
The grain distribution curve is plotted.
(b)
The values of
Answer to Problem 19P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Sieve No. | Sieve No. | Percent finer |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Pan | Pan | -- |
Concept used:
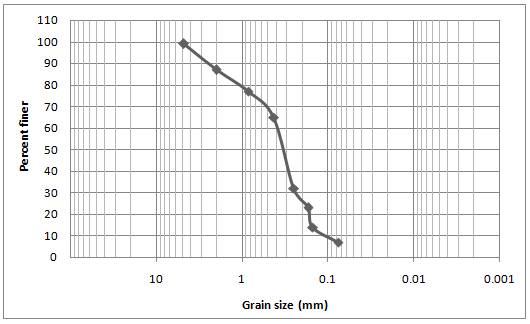
Plot the grain size distribution curve between the sieve number (mm) and the percent finer. The sieve number (mm) is plotted in x -axis and percent finer in y -axis. Then the corresponding values of
Calculation:
Conclusion:
The values of
(c)
The value of uniformity coefficient
Answer to Problem 19P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Sieve No. | Sieve No. | Percent finer |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Pan | Pan | -- |
Concept used:
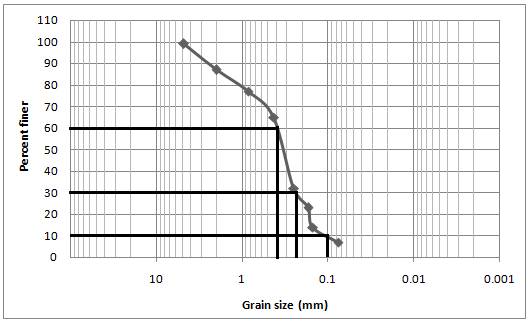
Calculation:
Conclusion:
The value of coefficient of uniformityis
(d)
The value of coefficient of gradation
Answer to Problem 19P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Sieve No. | Sieve No. | Percent finer |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Pan | Pan | -- |
Concept used:
Calculation:
Conclusion:
The value of coefficient of uniformity is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Traffic and Highway Engineering - With Mindtap
- F U₁ ΕΙ ΕΙ H F₁₂ U₂ ΕΙ EI H F ΕΙ ΕΙ H Undeformed Configuration 3 Deformed Configurationarrow_forwardCivil engineering quantities question Answer the question and at the end put notes on how a BOQ is constructed.arrow_forwardPlanning is underway for the construction of a new railway section between Stockholm and Uppsala as part of the "Fyra spår Uppsala" project. Your task is to carry out a preliminary slope stability analysis for a planned road underpass beneath the new railway. The analysis concerns the eastern slope at the underpass. The designed clay slope has a depth of 12.5 meters and a width of 27.0 meters. According to geotechnical investigations, the soil consists of homogeneous, overconsolidated clay with a saturated unit weight of 15 kN/m³ and an undrained shear strength of 35 kPa. The groundwater table is at ground level (0.0 m). According to Figure 1, the most critical slip surface is circular, with the center of rotation (point O) located 4.0 meters above the current ground surface (0.0 m). The slip surface intersects the ground at the toe of the slope and 6.0 meters east of the slope crest. Questions to Answer Calculate the factor of safety (F) against rotational failure using an undrained…arrow_forward
- Question 6. Water enters a reach of rectangular channel where y₁ = 0.5 m, b = 7.5 m, and Q = 20 m³/s (Figure P10.39). It is desired that a hydraulic jump occur upstream (location 2) of the sill and on the sill critical conditions exist (loca- tion 3). Other than across the jump, losses can be neglected. Determine the following: (a) Depths at locations 2 and 3 (b) Required height of the sill, h (c) Resultant force acting on the sill (d) Sketch the water surface and energy grade line. (e) Describe the nature and character of the jump. 1 2 3. harrow_forwardQuestion 5. This figure shows a cross section of an aqueduct that carries water at 50 m³/s. The value of Manning's n is 0.02. Find the bottom slope. 45° 4.0 m 7.0 m-arrow_forwardQuestion 4. A rectangular, unfinished concrete channel of 30-ft width is laid on a slope of 7 ft/mi. Determine the flow depth and Froude number of the flow if the flowrate is 350 ft³/s.arrow_forward
- Question 3. A lake discharges into a steep channel. At the channel entrance the lake is 4 m above the channel bottom. Neglecting losses, find the discharge for the following geometries: (a) Rectangular section, b = 4 m (b) Trapezoidal section, b = 3 m, angle = 60° (c) Circular section, d = 3.5 m.arrow_forwardQuestion 7. A popular sharp-crested weir for use in low-flow situations is the V-notch weir, as shown below. When these weirs are designed, the equation for determining the flowrate by neglecting the velocity head of the upstream flow can be written as Q = CH", where C is a coefficient of discharge and is a function of the notch angle (0) and n is a weir constant. The constants C and n must be determined experimentally for a given weir. In logarithmic form, the weir equation is log Q = n log H + log C. Assume we have a flume in the lab where we can experimentally explore the relationship between Q and H for this weir by adjusting the flowrates. Develop an appropriate experiment to determine n and C' (the weir discharge coefficient) for the weir used. Write the experimental procedure steps and measurement readings that are needed to determine these coefficients empirically. Hint: Please refer to your lab manual. Draw down Nappe H V notch weir Weir plate sharp-crested weirarrow_forwardPlease solve the question by hand with a detailed explanation of the steps.arrow_forward
- Please solve the question by hand with a detailed explanation of the steps.arrow_forwardGiven the properties of the wide flange: Property Value d = 530 mm bf = 210 mm tw = 18 mm tf = 16 mm Compute the value of rt defined as the radius of gyration of compression flange plus 1/3 of the compression web area about y-axis.correct answer: (50.52 mm)arrow_forwardUsing a relevant image such as a 3D architectural rendering of a warehouse landscape in Edmond.arrow_forward
 Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning




