
(a)
The total marginal benefit (MBT).
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The total marginal benefit (MB) is the sum total of individual marginal benefits. There are two consumers of mosquito abatement, such as D and L, where the marginal benefit of consumer D is MBD=100−Q and the marginal benefit of consumer L is MBL=60−Q. Therefore, the total marginal benefit can be calculated as follows:
MBT=MBD+MBL=100−Q+60−Q=160−2Q
Therefore, the total marginal benefit is MBT=160−2Q.
Marginal benefit: Marginal benefit can be defined as the additional utility derived from the additional consumption of one or more unit of goods and services.
(b)
The optimal level of mosquito abatement.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The optimal level of mosquito abatement is determined at the point where the total marginal benefit is equal to the marginal cost (MC).
The total marginal benefit is MBT=160−2Q.
The total marginal cost is given as MC=2Q.
Now, set the two expressions to get the value of optimal quantity:
160−2Q=2Q160=4QQ=1604=40
Therefore, the optimal level of mosquito abatement is 40.
Marginal benefit: Marginal benefit can be defined as the additional utility derived from the additional consumption of one or more unit of goods and services.
Marginal cost (MC): Marginal benefit refers to the amount of additional cost incurred in the process of increasing one more unit of output.
(c)
The individual total benefit at the optimal level of mosquito abatement.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Figure 1 illustrates the MB, MC, and the optimal quantity of the mosquito abatement of consumer D as follows:
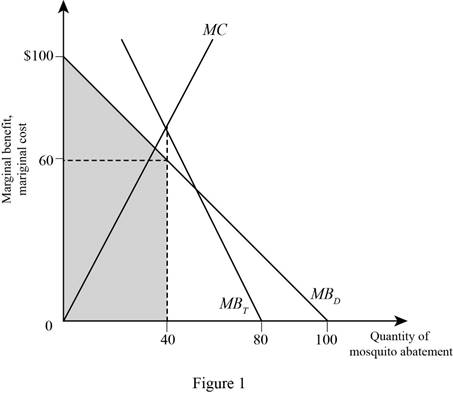
In Figure1, the vertical axis shows the MB and MC of the mosquito abatement and the horizontal axis shows the quantity of mosquito abatement, where the interaction between the total marginal benefit with MC curve determines the optimal quantity of mosquito abatement.
The MB of consumer D can be calculated by substituting the respective value in the MB function of D as follows:
MBD=(100−40)=60
Therefore, 60 is the MB of consumer D.
The MB of consumer L can be calculated by substituting the respective value in the MB function of L as follows:
MBL=(60−40)=20
Therefore, 20 is the MB of consumer D.
Therefore, the total benefit is 80(60+20).
Now, the total benefit (TB) for consumer D can be calculated using the formula given below:
TB=Optimal quantity×MBD+12×Optimal quantity×(MBD−MBL) (1)
Now, substitute the respective values in Equation (1) to get the value of total benefit of consumer D.
TB=40×60+12×40×(60−20)=3,200
Therefore, the total benefit of consumer D is 3,200.
Figure 2 illustrates the MB, MC, and the optimal quantity of the mosquito abatement of consumer L as follows:
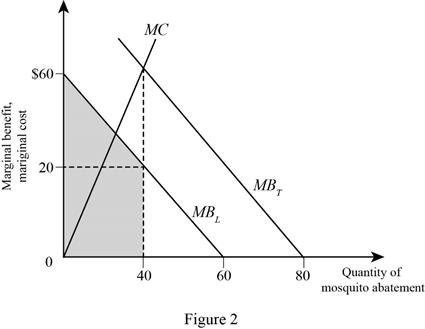
In Figure2, the vertical axis measures the MB and MC of the mosquito abatement and the horizontal axis measures the quantity of mosquito abatement, where the interaction between the total marginal benefit with MC curve determines the optimal quantity of mosquito abatement.
The total benefit (TB) for consumer L can be calculated using the formula given below:
TB=Optimal quantity×MBL+12×Optimal quantity×(MBD−MBL) (2)
Now, substitute the respective values in Equation (2) to get the value of total benefit of consumer L.
TB=40×20+12×40×(60−20)=1,600
Therefore, the total benefit of consumer L is 1,600.
Marginal benefit: Marginal benefit can be defined as the additional utility derived from the additional consumption of one or more unit of goods and services.
Marginal cost (MC): Marginal benefit refers to the amount of additional cost incurred in the process of increasing one more unit of output.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Microeconomics
- Price P 1. Explain the distinction between outputs and outcomes in social service delivery 2. Discuss the Rawlsian theory of justice and briefly comment on its relevance to the political economy of South Africa. [2] [7] 3. Redistributive expenditure can take the form of direct cash transfers (grants) and/or in- kind subsidies. With references to the graphs below, discuss the merits of these two transfer types in the presence and absence of a positive externality. [6] 9 Quantity (a) P, MC, MB MSB MPB+MEB MPB P-MC MEB Quantity (6) MCarrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardIf 17 Ps are needed and no on-hand inventory exists fot any of thr items, how many Cs will be needed?arrow_forward
- Exercise 5Consider the demand and supply functions for the notebooks market.QD=10,000−100pQS=900pa. Make a table with the corresponding supply and demand schedule.b. Draw the corresponding graph.c. Is it possible to find the price and quantity of equilibrium with the graph method? d. Find the price and quantity of equilibrium by solving the system of equations.arrow_forward1. Consider the market supply curve which passes through the intercept and from which the marketequilibrium data is known, this is, the price and quantity of equilibrium PE=50 and QE=2000.a. Considering those two points, find the equation of the supply. b. Draw a graph for this equation. 2. Considering the previous supply line, determine if the following demand function corresponds to themarket demand equilibrium stated above. QD=.3000-2p.arrow_forwardSupply and demand functions show different relationship between the price and quantities suppliedand demanded. Explain the reason for that relation and provide one reference with your answer.arrow_forward
- 13:53 APP 簸洛瞭對照 Vo 56 5G 48% 48% atheva.cc/index/index/index.html The Most Trusted, Secure, Fast, Reliable Cryptocurrency Exchange Get started with the easiest and most secure platform to buy, sell, trade, and earn Cryptocurrency Balance:0.00 Recharge Withdraw Message About us BTC/USDT ETH/USDT EOS/USDT 83241.12 1841.50 83241.12 +1.00% +0.08% +1.00% Operating norms Symbol Latest price 24hFluctuation B BTC/USDT 83241.12 +1.00% ETH/USDT 1841.50 +0.08% B BTC/USD illı 83241.12 +1.00% Home Markets Trade Record Mine О <arrow_forwardThe production function of a firm is described by the following equation Q=10,000L-3L2 where Lstands for the units of labour.a) Draw a graph for this equation. Use the quantity produced in the y-axis, and the units of labour inthe x-axis. b) What is the maximum production level? c) How many units of labour are needed at that point?arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





