
A
To calculate: The expected profit based on the given expectation is to be determined.
Introduction:
The expected profit can be defined as the probability to get the certain profit times the profit on business.
Degree of leverage is used to measure the change that will occur in operating income of the company when there is any change in sales.
A
Answer to Problem 17PS
The expected profit is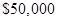
Explanation of Solution
The following formula will be used for the calculation of the expected profit −
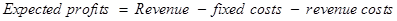 Equ (1)
Equ (1)
Given that −
Revenue = $120,000
Fixed costs = $30,000
Revenue costs 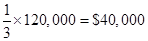
Put the given values in Equ (1) −
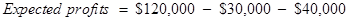
Expected profit 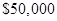
B
To calculate: the degree of operating leverage based on the estimate of the fixed cost and expected profits.
Introduction:
The expected profit can be defined as the probability to get the certain profit times the profit on business.
Degree of leverage is used to measure the change that will occur in operating income of the company when there is any change in sales.
B
Answer to Problem 17PS
The degree of operating leverage is 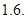
Explanation of Solution
The following formula will be used for the calculation of the degree of the operating leverage −
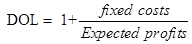 Equ (2)
Equ (2)
Given that −
Fixed costs = $30,000
Expected profits = $50,000
Put the given values is Equ (2)
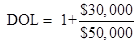
DOL = 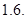 Or
Or
The degree of operating leverage = 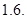
C
To calculate: the decrease in profits when sales are below 10% expectation.
Introduction:
The expected profit can be defined as the probability to get the certain profit times the profit on business.
Degree of leverage is used to measure the change that will occur in operating income of the company when there is any change in sales.
C
Answer to Problem 17PS
The decrease in profits is 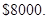
Explanation of Solution
The following formula will be used for the calculation of the expected profit −
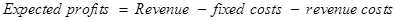 Equ (3)
Equ (3)
Given that −
DOL = 1.6
Given that −
Revenue = $120,000
Fixed costs = $30,000
Revenue costs 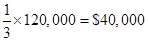
Decrement in sales = 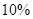
Put the given values in Equ (3)
The calculation of the profit after the decrement in sale can be given as −
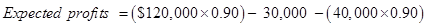
Expected profit after the decrement in sale = 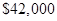
From the part (a), expected profit before decrement in sale 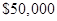
Then the decrease in profit = 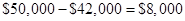
D
To calculate: It is to be proved that the percentage decrease in profits equal to the DOL times 10% drop in sales.
Introduction:
The expected profit can be defined as the probability to get the certain profit times the profit on business.
Degree of leverage is used to measure the change that will occur in operating income of the company when there is any change in sales.
D
Answer to Problem 17PS
The percentage decrease in profit is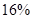
Explanation of Solution
The following formula will be used for the calculation of the percentage decrease −
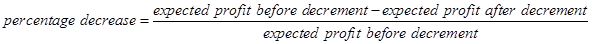 Equ (4)
Equ (4)
Put the calculated values in Equ (4)
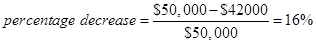
The percentage decrease = 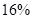 which prove that the decrease in profits equal to the DOL times
which prove that the decrease in profits equal to the DOL times  drop in sales.
drop in sales.
E
To calculate: The largest percentage shortfall in sales relative to the original expectation.
Introduction:
The expected profit can be defined as the probability to get the certain profit times the profit on business.
Degree of leverage is used to measure the change that will occur in operating income of the company when there is any change in sales.
E
Answer to Problem 17PS
The decrease in sales is 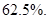
Explanation of Solution
The following formula will be used for the calculation of the decrease in sales −
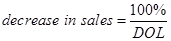 Equ (5)
Equ (5)
Given that −
DOL = 1.6
Put the given value in Equ (5)
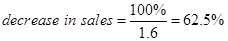
The decrease in sales = 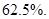
F
To calculate: The break-even sales at this point are to be determined.
Introduction:
The expected profit can be defined as the probability to get the certain profit times the profit on business.
Degree of leverage is used to measure the change that will occur in operating income of the company when there is any change in sales.
The break-even point can be defined as the point at which total cost and total revenue are equal to each other or even to each other.
F
Answer to Problem 17PS
The break-even sale is
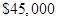
Explanation of Solution
From the above the revenue which decreases by 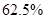 and which is
and which is 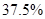 of the original revenue.
of the original revenue.
The following formula will be used for the calculation of the break-even sales −
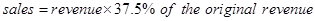 Equ (6)
Equ (6)
Put the given value in above Equ
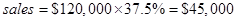
Then the break-even sales = $45,000
G
To calculate: The profit at break-even level of sales to prove that the part (f) is correct.
Introduction:
The expected profit can be defined as the probability to get the certain profit times the profit on business.
Degree of leverage is used to measure the change that will occur in operating income of the company when there is any change in sales.
The break-even point can be defined as the point at which total cost and total revenue are equal to each other or even to each other.
G
Answer to Problem 17PS
The expected profit at break-even level is $0.
Explanation of Solution
The following formula will be used for the calculation of the expected profit at the break-even level −
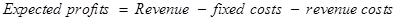 Equ (7)
Equ (7)
Given that −
Revenue = $45,000
Fixed costs = $30,000
Revenue costs 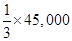
Put the given values is above Equ (7) −
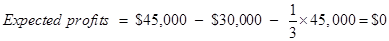
The expected profit = $0, this shows that the answer of the part (f) is correct.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
EBK INVESTMENTS
- (Do not use Excel) I like to see the work of how to solve the problem. The investment banking firm of Doots Incorporated. will use a dividend valuation model to appraise the shares of the Straight Fence Corporation. Dividends (D1) at the end of the current year will be $2.70. The growth rate (g) is 7 percent and the discount rate (Ke) is 13 percent. a. What should be the price of the stock to the public? b. If there is a 8 percent total underwriting spread on the stock, how much will the issuing corporation receive? c. If the issuing corporation requires a net price of $38.30 (proceeds to the corporation) and there is a 7 percent underwriting spread, what should be the price of the stock to the public? (Round to two places to the right of the decimal point.)arrow_forwardCalifornia Homes Associates is about to go public. The investment banking firm of Dillon and Associates is attempting to price the issue. The building industry generally trades at a 25 percent discount below the P/E ratio on the Standard & Poor’s 500 Stock Index. Assume that index currently has a P/E ratio of 30. The firm can be compared to the building industry as follows: CA Homes Building Industry Growth rate in earnings per share ............... 16% 13% Consistency of performance ...................... Increased earnings Increased earnings 3 out of 5 years 2 out of 5 years Debt to total assets.................................... 64%…arrow_forwardWhat is the Biblical perspective on the Capital Markets, and what is the relationship between them? How do they research the Biblical perspective on the Capital Markets? Could you help explain how research will fulfill this requirement and integrate a Christian worldview?arrow_forward
- Nina buys a new utility sports vehicle for 32,000 dollars. She trades in her old truck and received 10,000 dollars, which she uses as a down payment. She finances the balance at 8% APR over 36 months. Before making her 24th payment, she decides to pay off the loan. How much interest will Nina save by paying off the loan early.arrow_forwardGeneral Problems: Market volatility and bubbles. How can the problem of: Insider trading and market manipulation, Lack of transparency and information asymmetry, Inequality in access to capital, and Systemic risk from interconnected financial institutions be solved? How can practice or issue be improved?arrow_forwardIf submitted image is blurr then please comment i will write values. i will give unhelpful please.arrow_forward
- What are capital markets, and what is the purpose of capital markets? What is the foundation of the study on capital markets coping methods and increasing self-understanding? What are the general problems of capital markets to be addressed, and what are the consequences arising from the capital market?arrow_forwardMeticulous Drill & Reamer (MD&R) specializes in drilling and boring precise holes in hard metals (e.g., steel alloys, tungsten carbide, and titanium). The company recently contracted to drill holes with 3-centimeter diameters in large carbon-steel alloy disks, and it will have to purchase a special drill to complete this job. MD&R has eliminated all but two of the drills it has been considering: Davis Drills' T2005 and Worth Industrial Tools' AZ100. These producers have each agreed to allow MD&R to use a T2005 and an AZ100 for one week to determine which drill it will purchase. During the one-week trial, MD&R uses each of these drills to drill 31 holes with a target diameter of 3 centimeters in one large carbon-steel alloy disk, then measures the diameter of each hole and records the results. MD&R's results are provided in the table that follows and are available in the DATAfile named MeticulousDrills, Hole Diameter T2005 AZ100 3.06 2.91 3.04 3.31 3.13 2.82 3.01 3.01 2.95 2.94 3.02…arrow_forwardI mistakenly submitted blurr image please comment i will write values. please dont Solve with incorrect values otherwise unhelpful.arrow_forward
- hello tutor:If submitted image is blurr then please comment i will write values. i will give unhelpful please.arrow_forwardLara Fredericks is interested in two mutually exclusive investments. Both investments cover the same time horizon of 5 years. The cost of the first investment is $9900, and Lara expects equal and consecutive year-end payments of $3400. The second investment promises equal and consecutive payments of $4100 with an initial outlay of $12500 required. The current required return on the first investment is 8.4 %, and the second carries a required return of 10.4 %.a. What is the net present value of the first investment?b. What is the net present value of the second investment?c. Being mutually exclusive, which investment should Lara choose? d. Which investment is relatively more risky? Explain.arrow_forwardWhat are some of the characteristics of a firm with a long operating cycle?arrow_forward
