
A
To calculate: The expected profit based on the given expectation is to be determined.
Introduction:
The expected profit can be defined as the probability to get the certain profit times the profit on business.
Degree of leverage is used to measure the change that will occur in operating income of the company when there is any change in sales.
A
Answer to Problem 17PS
The expected profit is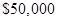
Explanation of Solution
The following formula will be used for the calculation of the expected profit −
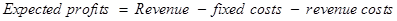 Equ (1)
Equ (1)
Given that −
Revenue = $120,000
Fixed costs = $30,000
Revenue costs 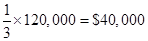
Put the given values in Equ (1) −
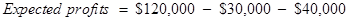
Expected profit 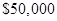
B
To calculate: the degree of operating leverage based on the estimate of the fixed cost and expected profits.
Introduction:
The expected profit can be defined as the probability to get the certain profit times the profit on business.
Degree of leverage is used to measure the change that will occur in operating income of the company when there is any change in sales.
B
Answer to Problem 17PS
The degree of operating leverage is 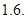
Explanation of Solution
The following formula will be used for the calculation of the degree of the operating leverage −
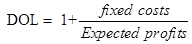 Equ (2)
Equ (2)
Given that −
Fixed costs = $30,000
Expected profits = $50,000
Put the given values is Equ (2)
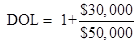
DOL = 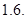 Or
Or
The degree of operating leverage = 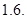
C
To calculate: the decrease in profits when sales are below 10% expectation.
Introduction:
The expected profit can be defined as the probability to get the certain profit times the profit on business.
Degree of leverage is used to measure the change that will occur in operating income of the company when there is any change in sales.
C
Answer to Problem 17PS
The decrease in profits is 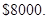
Explanation of Solution
The following formula will be used for the calculation of the expected profit −
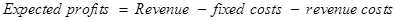 Equ (3)
Equ (3)
Given that −
DOL = 1.6
Given that −
Revenue = $120,000
Fixed costs = $30,000
Revenue costs 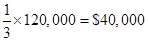
Decrement in sales = 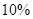
Put the given values in Equ (3)
The calculation of the profit after the decrement in sale can be given as −
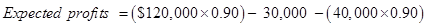
Expected profit after the decrement in sale = 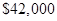
From the part (a), expected profit before decrement in sale 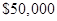
Then the decrease in profit = 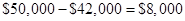
D
To calculate: It is to be proved that the percentage decrease in profits equal to the DOL times 10% drop in sales.
Introduction:
The expected profit can be defined as the probability to get the certain profit times the profit on business.
Degree of leverage is used to measure the change that will occur in operating income of the company when there is any change in sales.
D
Answer to Problem 17PS
The percentage decrease in profit is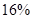
Explanation of Solution
The following formula will be used for the calculation of the percentage decrease −
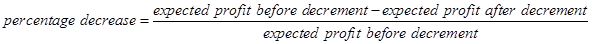 Equ (4)
Equ (4)
Put the calculated values in Equ (4)
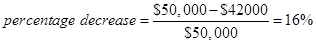
The percentage decrease = 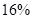 which prove that the decrease in profits equal to the DOL times
which prove that the decrease in profits equal to the DOL times  drop in sales.
drop in sales.
E
To calculate: The largest percentage shortfall in sales relative to the original expectation.
Introduction:
The expected profit can be defined as the probability to get the certain profit times the profit on business.
Degree of leverage is used to measure the change that will occur in operating income of the company when there is any change in sales.
E
Answer to Problem 17PS
The decrease in sales is 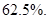
Explanation of Solution
The following formula will be used for the calculation of the decrease in sales −
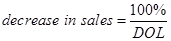 Equ (5)
Equ (5)
Given that −
DOL = 1.6
Put the given value in Equ (5)
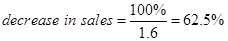
The decrease in sales = 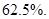
F
To calculate: The break-even sales at this point are to be determined.
Introduction:
The expected profit can be defined as the probability to get the certain profit times the profit on business.
Degree of leverage is used to measure the change that will occur in operating income of the company when there is any change in sales.
The break-even point can be defined as the point at which total cost and total revenue are equal to each other or even to each other.
F
Answer to Problem 17PS
The break-even sale is
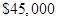
Explanation of Solution
From the above the revenue which decreases by 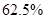 and which is
and which is 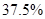 of the original revenue.
of the original revenue.
The following formula will be used for the calculation of the break-even sales −
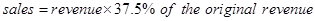 Equ (6)
Equ (6)
Put the given value in above Equ
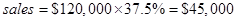
Then the break-even sales = $45,000
G
To calculate: The profit at break-even level of sales to prove that the part (f) is correct.
Introduction:
The expected profit can be defined as the probability to get the certain profit times the profit on business.
Degree of leverage is used to measure the change that will occur in operating income of the company when there is any change in sales.
The break-even point can be defined as the point at which total cost and total revenue are equal to each other or even to each other.
G
Answer to Problem 17PS
The expected profit at break-even level is $0.
Explanation of Solution
The following formula will be used for the calculation of the expected profit at the break-even level −
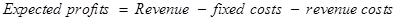 Equ (7)
Equ (7)
Given that −
Revenue = $45,000
Fixed costs = $30,000
Revenue costs 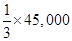
Put the given values is above Equ (7) −
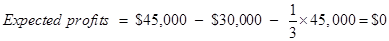
The expected profit = $0, this shows that the answer of the part (f) is correct.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Investments
- critically discuss the hockey stick model of a start-up financing. In your response, explain the model and discibe its three main stages, highlighting the key characteristics of each stage in terms of growth, risk, and funding expectations.arrow_forwardSolve this problem please .arrow_forwardSolve this finance question.arrow_forward
- solve this question.Pat and Chris have identical interest-bearing bank accounts that pay them $15 interest per year. Pat leaves the $15 in the account each year, while Chris takes the $15 home to a jar and never spends any of it. After five years, who has more money?arrow_forwardWhat is corporate finance? explain all thingsarrow_forwardSolve this finance problem.arrow_forward
