
(a)
Interpretation:
The strongest acid should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Titration is a process that determines the concentration of solution by known volume to react with a standard solution of another substance.
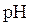 titration curve is a plot of pH of solution versus volume of titrant. The shape of
titration curve is a plot of pH of solution versus volume of titrant. The shape of 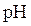 titration curve identifies the equivalence point in titration.
titration curve identifies the equivalence point in titration.
The point at which equivalent quantity of acid and base have been mixed together is called equivalent point. 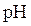 at equivalence point depends upon the relative strength of acids or bases.
at equivalence point depends upon the relative strength of acids or bases.
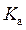 is defined as the acid dissociation constant in conjugate acid-base pairs.
is defined as the acid dissociation constant in conjugate acid-base pairs. 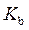 is defined as the base ionization constant in acid-base pairs.
is defined as the base ionization constant in acid-base pairs. 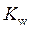 is the equilibrium constant for water. At
is the equilibrium constant for water. At 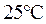
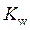 is equal to
is equal to 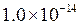
The expression for relation between 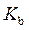 and
and 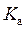 is as follows:
is as follows:
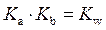
Rearrange above equation for 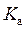
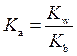
Rearrange above equation for 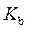
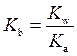
At 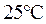
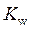 is equal to
is equal to 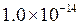 the equation will be modified as follows:
the equation will be modified as follows:
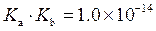
(b)
Interpretation:
The weakest acid should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Titration is a process that determines the concentration of solution by known volume to react with a standard solution of another substance.
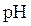 titration curve is a plot of pH of solution versus volume of titrant. The shape of
titration curve is a plot of pH of solution versus volume of titrant. The shape of 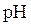 titration curve identifies the equivalence point in titration.
titration curve identifies the equivalence point in titration.
The point at which equivalent quantity of acid and base have been mixed together is called equivalent point. 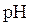 at equivalence point depends upon the relative strength of acids or bases.
at equivalence point depends upon the relative strength of acids or bases.
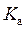 is defined as the acid dissociation constant in conjugate acid-base pairs.
is defined as the acid dissociation constant in conjugate acid-base pairs. 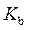 is defined as the base ionization constant in acid-base pairs.
is defined as the base ionization constant in acid-base pairs. 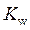 is the equilibrium constant for water. At
is the equilibrium constant for water. At 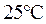
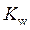 is equal to
is equal to 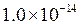
The expression for relation between 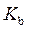 and
and 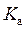 is as follows:
is as follows:
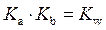
Rearrange above equation for 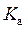
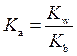
Rearrange above equation for 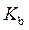
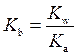
At 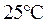
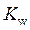 is equal to
is equal to 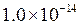 the equation will be modified as follows:
the equation will be modified as follows:
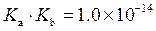
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 17 Solutions
CHEMISTRY-MASTERINGCHEMISTRY W/ETEXT
- What would happen if you added the HCI to the Grignard reagent before adding benzophenone? Draw a reaction mechanism to support your answer.arrow_forwardAt 300 K, in the decomposition reaction of a reactant R into products, several measurements of the concentration of R over time have been made (see table). Calculate the order of the reaction. t/s [R]/ (mol L-1) 0 0,5 171 0,16 720 0,05 1400 0,027arrow_forwardWrite the correct IUPAC names of the molecules in the picturearrow_forward
- How many grams of solid NaCN have to be added to 1.5L of water to dissolve 0.18 mol of Fe(OH)3 in the form Fe(CN)63 - ? ( For simplicity, ignore the reaction of CN - ion with water) Ksp for Fe(OH)3 is 2.8E -39, and Kform for Fe(CN)63 - is 1.0E31arrow_forwardDraw the most stable chair conformation of 1-ethyl-1-methylcyclohexane, clearly showing the axial and equatorial substituents. [4] Draw structures corresponding to the following IUPAC name for each of the following compounds; [5] i) 4-Isopropyl-2,4,5-trimethylheptane ii) trans-1-tert-butyl-4-ethylcyclohexane iii) Cyclobutylcycloheptane iv) cis-1,4-di-isopropylcyclohexane (chair conformation) v) 3-Ethyl-5-isobutylnonanearrow_forwardDraw and name molecules that meet the following descriptions; [4] a) An organic molecule containing 2 sp2 hybridised carbon and 1 sp-hybridised carbon atom. b) A cycloalkene, C7H12, with a tetrasubstituted double bond. Also answer question 2 from the imagearrow_forward
- H 14. Draw the line angle form of the following molecule make sure you use the proper notation to indicate spatial positioning of atoms. F F H 15. Convert the following condensed form to line angle form: (CH3)3CCH2COCH2CON(CH2CH3)2arrow_forwardIn a reaction between two reactants A and B, the half-life is the same for both only if(A) the stoichiometry A:B is 1:1.(B) the stoichiometry A:B is 1:2 or 2:1.arrow_forwardIn a reaction between two reactants A and B, the half-life is the same for both.(1) Only if the stoichiometry A:B is 1:1.(2) If the initial quantities of A and B are in their stoichiometric ratios.arrow_forward
- There are 48 pairs of students in the following table. Each pair has quantitatively determined the mass of taurine in a 250 mL can of the popular energy drink marketed as “Munster” using High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). The class results are presented below: QUESTION: Calculate the measurement of uncertainty and provide the data in a spreadsheet table. Mass of Taurine (mg) Mass of Taurine (mg) (Table continued) 152.01 152.23 151.87 151.45 154.11 152.64 152.98 153.24 152.88 151.45 153.49 152.48 150.68 152.33 151.52 153.63 152.48 151.68 153.17 153.40 153.77 153.67 152.34 153.16 152.57 153.02 152.86 151.50 151.23 152.57 152.72 151.54 146.47 152.38 152.44 152.54 152.53 152.54 151.32 152.87 151.24 153.26 152.02 152.90 152.87 151.49 152.46 152.58arrow_forward1. Predict the organic product(s) of the following reactions. Assume excess of reagents unless otherwise noted. a) &l BH3 •THF b) 1) NaOH 2) H3O+ solve d) ala 1) EtMgBr 2) H3O+ e) H2N سكر CuLi NH2 1) SOCI2 2) EtMgBr 3) H3O+ NC H3O+ Δarrow_forwardThere are 48 pairs of students in the following table. Each pair has quantitatively determined the mass of taurine in a 250 mL can of the popular energy drink marketed as “Munster” using High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). The class results are presented below: QUESTION: Summarise and report these results including an indication of measurement uncertainty. In both calculation samples calculate if an outlier is present, max value, number of samples, mean, standard deviation, g (suspect), g (critical) and t (critical). Mass of Taurine (mg) Mass of Taurine (mg) (Table continued) 152.01 152.23 151.87 151.45 154.11 152.64 152.98 153.24 152.88 151.45 153.49 152.48 150.68 152.33 151.52 153.63 152.48 151.68 153.17 153.40 153.77 153.67 152.34 153.16 152.57 153.02 152.86 151.50 151.23 152.57 152.72 151.54 146.47 152.38 152.44 152.54 152.53 152.54 151.32…arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning




