
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
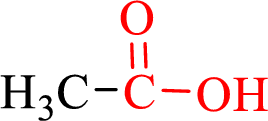
Nomenclature of
- • Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- • Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- • Replace the –e in the
alkane name with –oic acid.
Naming of compounds with two
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
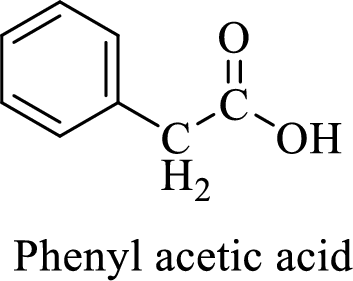
Name of the given compound is phenyl acetic acid.
From the name, we will get the following facts about the structure of the compound.
- ✓ The given compound is a carboxylic acid.
- ✓ A phenyl substituent is attached to the acetic acid; Acetic acid is the common name of ethanoic acid.
Thus,
The structural formula for this compound can be drawn as shown below,
(b)
Interpretation: The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
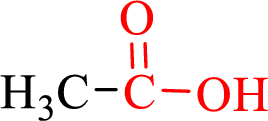
Nomenclature of carboxylic acid:
- • Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- • Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- • Replace the –e in the alkane name with –oic acid. If two or more carboxylic functional groups are present in the same compound then its number should be taken in to consideration and the prefix di, tri, tetra.. must be used.
Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
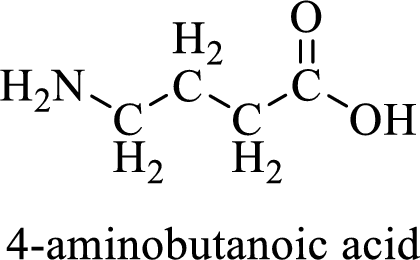
Name of the given compound is 4-Aminobutanoic acid
From the name, we will get the following facts about the structure of the compound.
- ✓ The given compound is a carboxylic acid.
- ✓ Parent chain contains four carbon atoms including the carboxylic acid functional group.
- ✓ An amino substituent is attached to the fourth carbon atom in the parent chain.
Thus,
The structural formula for this compound can be drawn as shown below,
(c)
Interpretation: The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
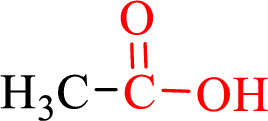
Nomenclature of carboxylic acid:
- • Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- • Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- • Replace the –e in the alkane name with –oic acid.
Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
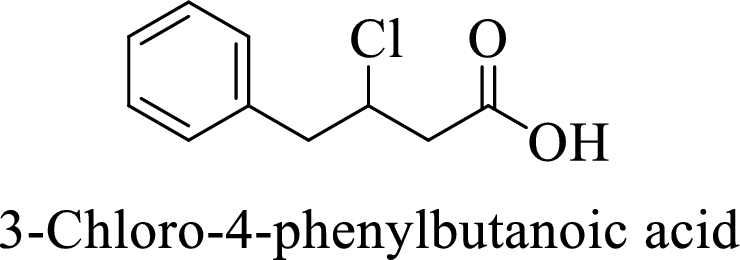
Name of the given compound is 3-Chloro-4-phenylbutanoic acid.
From the name, we will get the following facts about the structure of the compound.
- ✓ The given compound is a carboxylic acid.
- ✓ Parent chain contains four carbon atoms including the carboxylic acid functional group.
- ✓ One chlorine atom and a phenyl ring substituents are attached to the third and fourth carbon atoms in the parent chain respectively.
Thus,
The structural formula for this compound can be drawn as shown below,
(d)
Interpretation: The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
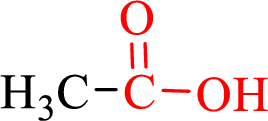
Nomenclature of carboxylic acid:
- • Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- • Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- • Replace the –e in the alkane name with –oic acid.
Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
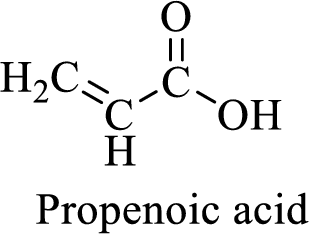
Name of the given compound is Propenoic acid (acrylic acid).
From the name, we will get the following facts about the structure of the compound.
- ✓ The given compound is a carboxylic acid.
- ✓ Parent chain contains three carbon atoms including the carboxylic acid functional group.
- ✓ There is a double bond in the compound.
Thus,
The structural formula for this compound can be drawn as shown below,
(e)
Interpretation: The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
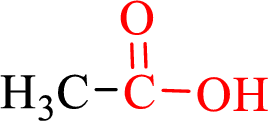
Nomenclature of carboxylic acid:
- • Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- • Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- • Replace the –e in the alkane name with –oic acid.
Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
E-Z designators are used as like cis-trans terminology for non-similar groups attached
In E-Z designations, the groups attached to vinylic positions are checked by their priority on the basis of higher molecular weight. If the higher priority groups are on the same sides, then the configuration is designated as Z. If the higher priority groups are on the opposite sides, then the configuration is designated as E.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Name of the given compound is (Z)-3-Hexenedioic acid.
From the name, we will get the following facts about the structure of the compound.
- ✓ The given compound is a dicarboxylic acid.
- ✓ Parent chain contains six carbon atoms including the carboxylic acid functional group.
- ✓ There is a double bond in the compound. The higher priority substituents are on same side; (Z)
Thus,
The structural formula for this compound can be drawn as shown below,
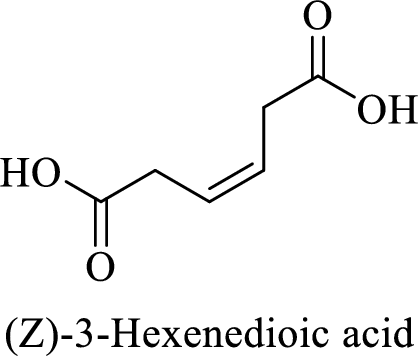
(f)
Interpretation: The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
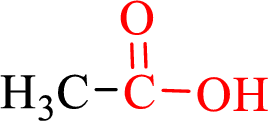
Nomenclature of carboxylic acid:
- • Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- • Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- • Replace the –e in the alkane name with –oic acid. If two or more carboxylic functional groups are present in the same compound then its number should be taken in to consideration and the prefix di, tri, tetra.. must be used.
Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Name of the given compound is 2-Pentynoic acid.
From the name, we will get the following facts about the structure of the compound.
- ✓ The given compound is a monocarboxylic acid.
- ✓ Parent chain contains five carbon atoms including the carboxylic acid functional group.
- ✓ There is a triple bond in between second and third carbon atoms in the compound.
Thus,
The structural formula for this compound can be drawn as shown below,
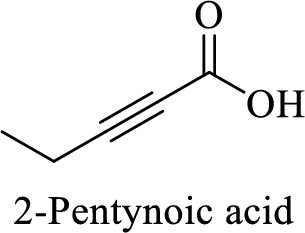
(g)
Interpretation: The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
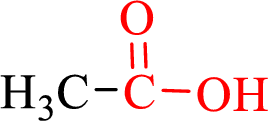
Nomenclature of carboxylic acid:
- • Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- • Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- • Replace the –e in the alkane name with –oic acid. If two or more carboxylic functional groups are present in the same compound then its number should be taken in to consideration and the prefix di, tri, tetra.. must be used.
Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
(g)
Explanation of Solution
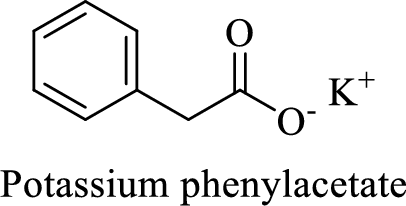
Name of the given compound is Potassium phenylacetate.
From the name, we will get the following facts about the structure of the compound.
- ✓ The given compound is a potassium salt of phenyl acetic acid.
- ✓ A phenyl substituent is attached to the acetic acid; Acetic acid is the common name of ethanoic acid.
Thus,
The structural formula for this compound can be drawn as shown below,
(h)
Interpretation: The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
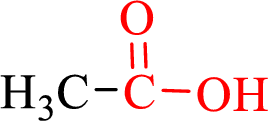
Nomenclature of carboxylic acid:
- • Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- • Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- • Replace the –e in the alkane name with –oic acid. If two or more carboxylic functional groups are present in the same compound then its number should be taken in to consideration and the prefix di, tri, tetra.. must be used.
Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
(h)
Explanation of Solution
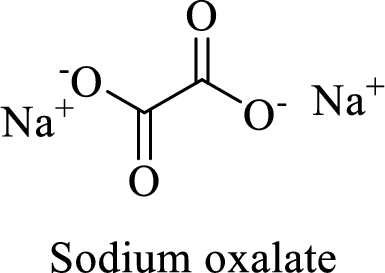
Name of the given compound is sodium oxalate.
From the name, we will get the following facts about the structure of the compound.
- ✓ The given compound is a sodium salt of oxalic acid.
- ✓ Two sodium atoms are attached to the both carboxyl group of oxalic acid.
Thus,
The structural formula for this compound can be drawn as shown below,
(i)
Interpretation: The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
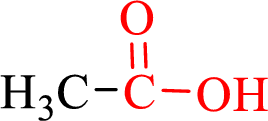
Nomenclature of carboxylic acid:
- • Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- • Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- • Replace the –e in the alkane name with –oic acid. If two or more carboxylic functional groups are present in the same compound then its number should be taken in to consideration and the prefix di, tri, tetra.. must be used.
Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
(i)
Explanation of Solution
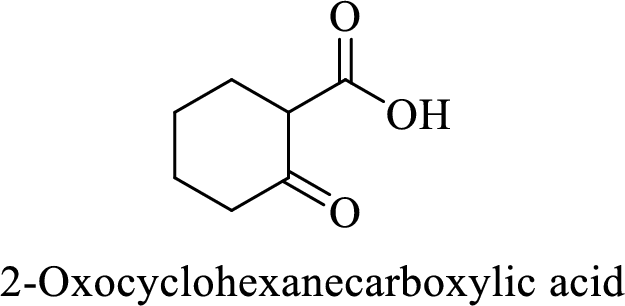
Name of the given compound is 2-Oxocyclohexanecarboxylic acid.
From the name, we will get the following facts about the structure of the compound.
- ✓ The given compound is a monocarboxylic acid.
- ✓ Parent ring contains six carbon atoms including the carboxylic acid functional group.
- ✓ There is a
ketone group on second carbon atom in the parent ring.
Thus,
The structural formula for this compound can be drawn as shown below,
(j)
Interpretation: The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
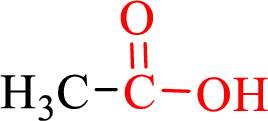
Nomenclature of carboxylic acid:
- • Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- • Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- • Replace the –e in the alkane name with –oic acid. If two or more carboxylic functional groups are present in the same compound then its number should be taken in to consideration and the prefix di, tri, tetra.. must be used.
Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
(j)
Explanation of Solution
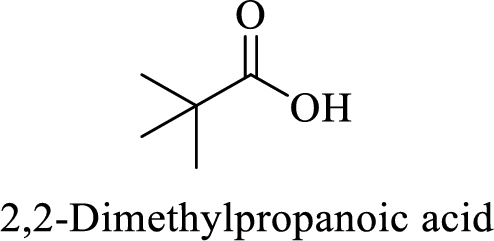
Name of the given compound is 2, 2-Dimethylpropanoic acid.
From the name, we will get the following facts about the structure of the compound.
- ✓ The given compound is a monocarboxylic acid.
- ✓ Parent chain contains three carbon atoms including the carboxylic acid functional group.
- ✓ Two methyl substituents are attached on the second carbon atom in the parent chain.
Thus,
The structural formula for this compound can be drawn as shown below,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Student Study Guide and Solutions Manual for Brown/Iverson/Anslyn/Foote's Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition
- Draw the Fischer projection from the skeletal structure shown below. HO OH OH OH OH H Q Drawing Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges I ☐ T HO H H OH HO I CH2OH H OH Drag H OH -CH2OH CHO -COOH Undo Reset Remove Donearrow_forwardplease provide the structure for this problem, thank youarrow_forwardpresented by Morallen Lig Intermine the hand product for the given mution by adding atoms, bonds, nonhonding diarion panda скуль Step 3: Comp the draw the product Step 2: Agama workup Compithe 429 ملولةarrow_forward
- Reaction A 0,0arrow_forwardpresented by Morillon Leaning Predict the organic product for the min кусур HSC Adithane carved arnown to come than that to the condon slchroruis in acid in in aquishri with ноюarrow_forward6.15PM Sun Mar 30 K Draw the major product of this reaction. Include any relevant stereochemistry. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Problem 1 of O H [PhзPCH2CH3]*C|¯ NaH Drawing > Q Atoms, Bonds and Draw or tap a nearrow_forward
- 8:17 PM Sun Mar 30 Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HSCH2CH2CH2SH, BF3 Probler Drawing Ato Bonds Clarrow_forwardpresented by Mr L How the coprion. (Il Done in no wraction, dew the starting redential) доarrow_forward8:16 PM Sun Mar 30 K Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Proble 1. CH3MgBr 2. H3O+ F Drawingarrow_forward
- о но оarrow_forwardName the major organic product of the following action of 4-chloro-4-methyl-1-pentanol in neutral pollution 10+ Now the product. The product has a molecular formula f b. In a singly hain, the starting, material again converts into a secule with the molecular kormula CIO. but with comply Draw the major organic structure inhalationarrow_forwardMacmillan Learning Alcohols can be oxidized by chromic acid derivatives. One such reagent is pyridinium chlorochromate, (C,H,NH*)(CICTO3), commonly known as PCC. Draw the proposed (neutral) intermediate and the organic product in the oxidation of 1-butanol by PCC when carried out in an anhydrous solvent such as CH₂C₁₂. PCC Intermediate OH CH2Cl2 Draw the intermediate. Select Draw Templates More с H Cr о Product Draw the product. Erase Select Draw Templates More H о Erasearrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole

