
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether table sugar is a monosaccharide, disaccharide, or polysaccharide is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
On the basis of the structural differences carbohydrates are classified into three parts.
Monosaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy
Disaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Sucrose, lactose.
Polysaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing more than two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Cellulose, starch.
Answer to Problem 17.4E
Table sugar is a disaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
Table sugar is also known as sucrose. Sucrose on hydrolysis gives two monosaccharides, glucose and fructose which are linked through a glycosidic linkage. This shows that sucrose or table sugar is a disaccharide.
Table sugar is a disaccharide.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether the given carbohydrate is a monosaccharide, disaccharide, or polysaccharide is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
On the basis of the structural differences carbohydrates are classified into three parts.
Monosaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing only one aldehyde or ketone unit. For example: glucose and fructose.
Disaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Sucrose, lactose.
Polysaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing more than two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Cellulose, starch.
Answer to Problem 17.4E
The given carbohydrate is an example of monosaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula of the given carbohydrate is shown below.
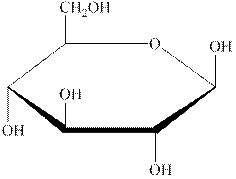
Figure 1
The above structure of carbohydrate shows that there is no glycosidic linkage through which another carbohydrate is linked. Therefore, the above carbohydrate is a monosaccharide.
The carbohydrate shown in Figure 1 is an example of monosaccharide.
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether starch is a monosaccharide, disaccharide, or polysaccharide is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
On the basis of the structural differences carbohydrates are classified into three parts.
Monosaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing only one aldehyde or ketone unit. For example: glucose and fructose.
Disaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Sucrose, lactose.
Polysaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing more than two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Cellulose, starch.
Answer to Problem 17.4E
Starch is a polysaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
Starch is the
Starch is an example of polysaccharide.
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether fructose is a monosaccharide, disaccharide, or polysaccharide is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
On the basis of the structural differences carbohydrates are classified into three parts.
Monosaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing only one aldehyde or ketone unit. For example: glucose and fructose.
Disaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Sucrose, lactose.
Polysaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing more than two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Cellulose, starch.
Answer to Problem 17.4E
Fructose is a monosaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
Hydrolysis of sucrose produces glucose and fructose which do not undergo further hydrolysis. Therefore, fructose comes under the category of monosaccharide.
Fructose is an example of monosaccharide.
(e)
Interpretation:
Whether cellulose is a monosaccharide, disaccharide, or polysaccharide is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
On the basis of the structural differences carbohydrates are classified into three parts.
Monosaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing only one aldehyde or ketone unit. For example: glucose and fructose.
Disaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Sucrose, lactose.
Polysaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing more than two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Cellulose, starch.
Answer to Problem 17.4E
Cellulose is a polysaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
Cellulose is a polymeric form of D-glucose because cellulose on hydrolysis gives a large number of glucose as monosaccharide. Each glucose is linked with
Cellulose on hydrolysis gives a large number of molecules of glucose. As a result, cellulose is a polysaccharide.
(f)
Interpretation:
Whether the given carbohydrate is a monosaccharide, disaccharide, or polysaccharide is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
On the basis of the structural differences carbohydrates are classified into three parts.
Monosaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing only one aldehyde or ketone unit. For example: glucose and fructose.
Disaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Sucrose, lactose.
Polysaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing more than two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Cellulose, starch.
Answer to Problem 17.4E
The given carbohydrate is a disaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula of the given carbohydrate is shown below.
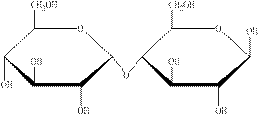
Figure 2
The above structure of carbohydrate shows that two monosaccharides are linked to each other through glycosidic linkage and results in the formation of a disaccharide. Therefore, the above carbohydrate is a disaccharide.
The carbohydrate shown in Figure 2 is an example of disaccharide.
(g)
Interpretation:
Whether glycogen is a monosaccharide, disaccharide, or polysaccharide is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
On the basis of the structural differences carbohydrates are classified into three parts.
Monosaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing only one aldehyde or ketone unit. For example: glucose and fructose.
Disaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Sucrose, lactose.
Polysaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing more than two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Cellulose, starch.
Answer to Problem 17.4E
Glycogen is a polysaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
Glycogen is a polymeric form of D-glucose which on hydrolysis gives glucose units. Each glucose unit is linked by
Glycogen on hydrolysis gives a large number of molecules of glucose. As a result, glycogen is a polysaccharide.
(h)
Interpretation:
Whether amulose is a monosaccharide, disaccharide, or polysaccharide is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
On the basis of the structural differences carbohydrates are classified into three parts.
Monosaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing only one aldehyde or ketone unit. For example: glucose and fructose.
Disaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Sucrose, lactose.
Polysaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing more than two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Cellulose, starch.
Answer to Problem 17.4E
Amylose is a polysaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
Amylose is a polymeric form of
Amylose on hydrolysis gives a large number of glucose units. As a result, amylose is a polysaccharide.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Bundle: Chemistry For Today: General, Organic, And Biochemistry, 9th + Owlv2 With Mindtap Reader, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
- What is the final product when hexanedioic acid reacts with 1º PCl5 and 2º NH3.arrow_forwardWhat is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forward
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





