
(a)
Interpretation: The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
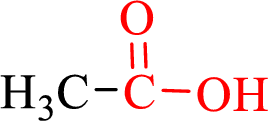
Nomenclature of
- • Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- • Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- • Replace the –e in the
alkane name with –oic acid.
Naming of compounds with two
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
Carboxylic salts are the water-soluble ammonium or alkali metal salts of carboxylic acids.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
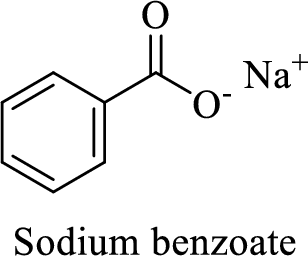
Name of the given salt is sodium benzoate.
From the name, we will get the following fact about the structure of the compound.
- ✓ The given compound is a sodium salt of benzoic acid.
Thus,
The structural formula for this salt can be drawn as shown below,
(b)
Interpretation: The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
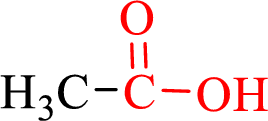
Nomenclature of carboxylic acid:
- • Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- • Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- • Replace the –e in the alkane name with –oic acid. If two or more carboxylic functional groups are present in the same compound then its number should be taken in to consideration and the prefix di, tri, tetra.. must be used.
Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
Carboxylic salts are the water-soluble ammonium or alkali metal salts of carboxylic acids.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
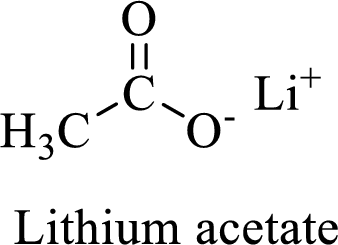
Name of the given salt is Lithium acetate.
From the name, we will get the following fact about the structure of the compound.
- ✓ The given compound is a Lithium salt of acetic acid
Thus,
The structural formula for this compound can be drawn as shown below,
(c)
Interpretation: The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
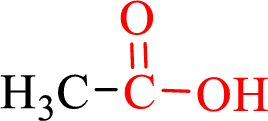
Nomenclature of carboxylic acid:
- • Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- • Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- • Replace the –e in the alkane name with –oic acid.
Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
Carboxylic salts are the water-soluble ammonium or alkali metal salts of carboxylic acids.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Name of the given salt is Ammonium acetate.
From the name, we will get the following fact about the structure of the compound.
- ✓ The given compound is an ammonium salt of acetic acid.
Thus,
The structural formula for this compound can be drawn as shown below,
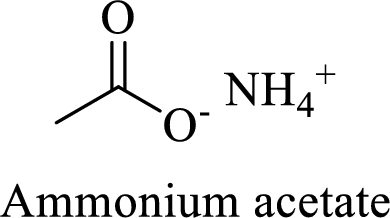
(d)
Interpretation: The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
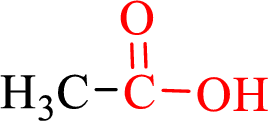
Nomenclature of carboxylic acid:
- • Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- • Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- • Replace the –e in the alkane name with –oic acid.
Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
Carboxylic salts are the water-soluble ammonium or alkali metal salts of carboxylic acids.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
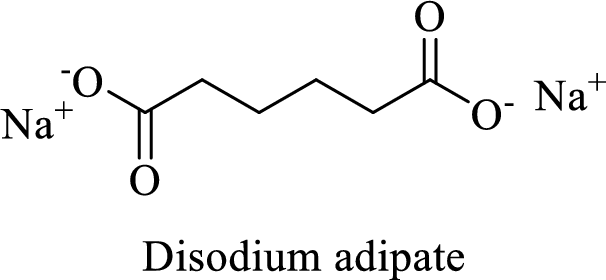
Name of the given salt is Disodium adipate.
From the name, we will get the following facts about the structure of the compound.
- ✓ The given compound is a sodium salt of adipic acid.
- ✓ Two sodium atoms are attached to the both carboxyl group of adipic acid.
The structure of adipic acid is shown below,
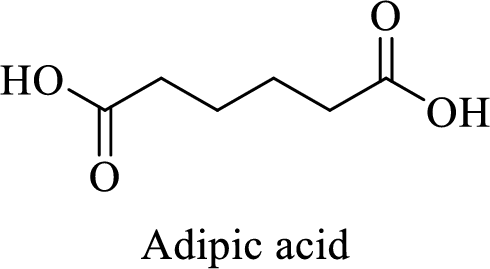
Thus,
The structural formula for this compound can be drawn as shown below,
(e)
Interpretation: The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
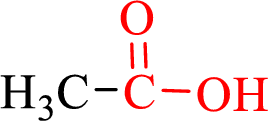
Nomenclature of carboxylic acid:
- • Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- • Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- • Replace the –e in the alkane name with –oic acid.
Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
Carboxylic salts are the water-soluble ammonium or alkali metal salts of carboxylic acids.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
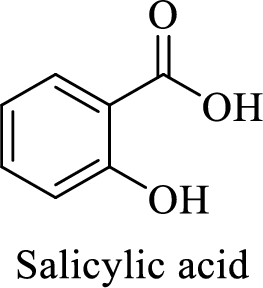
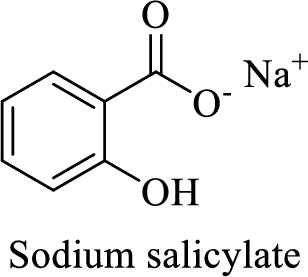
Name of the given salt is sodium salicylate.
From the name, we will get the following fact about the structure of the compound.
- ✓ The compound is a sodium salt of salicylic acid.
Structure of salicylic acid is shown below,
Thus,
The structural formula for this compound can be drawn as shown below,
(f)
Interpretation: The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
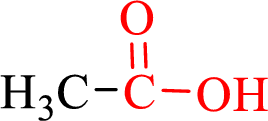
Nomenclature of carboxylic acid:
- • Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- • Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- • Replace the –e in the alkane name with –oic acid. If two or more carboxylic functional groups are present in the same compound then its number should be taken in to consideration and the prefix di, tri, tetra.. must be used.
Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
Carboxylic salts are the water-soluble ammonium or alkali metal salts of carboxylic acids.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
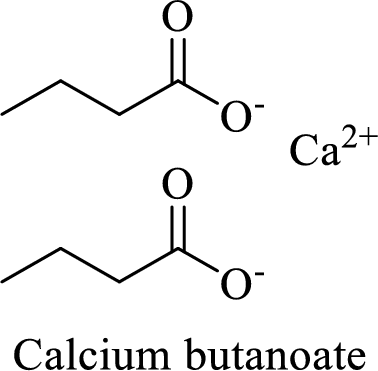
Name of the given salt is calcium butanoate.
From the name, we will get the following fact about the structure of the compound.
- ✓ The given compound is a calcium salt of butanoic acid.
Thus,
The structural formula for this compound can be drawn as shown below,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- What are the angles a and b in the actual molecule of which this is a Lewis structure? H- :0: C=N: b Note for advanced students: give the ideal angles, and don't worry about small differences from the ideal that might be caused by the fact that different electron groups may have slightly different sizes. a = 0° b=0 Xarrow_forwardA student proposes the transformation below in one step of an organic synthesis. There may be one or more products missing from the right-hand side, but there are no reagents missing from the left-hand side. There may also be catalysts, small inorganic reagents, and other important reaction conditions missing from the arrow. • Is the student's transformation possible? If not, check the box under the drawing area. • If the student's transformation is possible, then complete the reaction by adding any missing products to the right-hand side, and adding required catalysts, inorganic reagents, or other important reaction conditions above and below the arrow. • You do not need to balance the reaction, but be sure every important organic reactant or product is shown. + This transformation can't be done in one step. T iarrow_forwardDetermine the structures of the missing organic molecules in the following reaction: H+ O OH H+ + H₂O ☑ ☑ Note: Molecules that share the same letter have the exact same structure. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the missing organic molecule X. Molecule X shows up in multiple steps, but you only have to draw its structure once. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X § ©arrow_forward
- Table 1.1 Stock Standard Solutions Preparation. The amounts shown should be dissolved in 100 mL. Millipore water. Calculate the corresponding anion concentrations based on the actual weights of the reagents. Anion Amount of reagent (g) Anion Concentration (mg/L) 0.1649 Reagent Chloride NaCl Fluoride NaF 0.2210 Bromide NaBr 0.1288 Nitrate NaNO3 0.1371 Nitrite NaNO2 0.1500 Phosphate KH2PO4 0.1433 Sulfate K2SO4 0.1814arrow_forwardDraw the structure of the pound in the provided CO as a 300-1200 37(2), 11 ( 110, and 2.5 (20arrow_forwardPlease help me with # 4 and 5. Thanks in advance!arrow_forward
- A small artisanal cheesemaker is testing the acidity of their milk before it coagulates. During fermentation, bacteria produce lactic acid (K₁ = 1.4 x 104), a weak acid that helps to curdle the milk and develop flavor. The cheesemaker has measured that the developing mixture contains lactic acid at an initial concentration of 0.025 M. Your task is to calculate the pH of this mixture and determine whether it meets the required acidity for proper cheese development. To achieve the best flavor, texture and reduce/control microbial growth, the pH range needs to be between pH 4.6 and 5.0. Assumptions: Lactic acid is a monoprotic acid H H :0:0: H-C-C H :0: O-H Figure 1: Lewis Structure for Lactic Acid For simplicity, you can use the generic formula HA to represent the acid You can assume lactic acid dissociation is in water as milk is mostly water. Temperature is 25°C 1. Write the K, expression for the dissociation of lactic acid in the space provided. Do not forget to include state symbols.…arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. :0: :0 H. 0:0 :0: :6: S: :0: Select to Edit Arrows ::0 Select to Edit Arrows H :0: H :CI: Rotation Select to Edit Arrows H. < :0: :0: :0: S:arrow_forward3:48 PM Fri Apr 4 K Problem 4 of 10 Submit Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Mg. :0: Select to Add Arrows :0: :Br: Mg :0: :0: Select to Add Arrows Mg. Br: :0: 0:0- Br -190 H 0:0 Select to Add Arrows Select to Add Arrows neutralizing workup H CH3arrow_forward
- Iarrow_forwardDraw the Markovnikov product of the hydrobromination of this alkene. Note for advanced students: draw only one product, and don't worry about showing any stereochemistry. Drawing dash and wedge bonds has been disabled for this problem. + Explanation Check 1 X E 4 1 1 1 1 1 HBr Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 80 LE #3 @ 2 $4 0 I அ2 % 85 F * K M ? BH 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center & 6 27 FG F10 8 9 R T Y U D F G H P J K L Z X C V B N M Q W A S H option command H command optiarrow_forwardBe sure to use wedge and dash bonds to show the stereochemistry of the products when it's important, for example to distinguish between two different major products. Predict the major products of the following reaction. Explanation Q F1 A Check F2 @ 2 # 3 + X 80 F3 W E S D $ 4 I O H. H₂ 2 R Pt % 05 LL ee F6 F5 T <6 G Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 27 & A 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Acce Y U H DII 8 9 F10 4 J K L Z X C V B N M T H option command F11 P H commandarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning




