
a) Bromobenzene
Interpretation:
The major product(s) formed when bromobenzene is nitrated is to be given. Whether it will react faster or slower than benzene is also to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Monosubstituted benzenes can be nitrated using a mixture of Conc. HNO3 and H2SO4. Electron releasing substituent groups, excep halogens, activate the ring and direct the incoming electrophile to the o- and p-positions. Compounds with these substituent groups are more reactive than benzene. Halogens are o- and p-directors but they deactivate the ring. Hence halobenzenes are less reactive than benzene. Electron withdrawing substituent groups deactivate the ring and direct the incoming electrophile to the m-position. Compounds with these substituent groups are less reactive than benzene.
To give:
The major products formed when bromobenzene is nitrated and to state whether it will react faster or slower than benzene.
Answer to Problem 47AP
The major products formed when bromobenzene is nitrated are o-bromonitrobenzene and p-bromonitrobenzene.
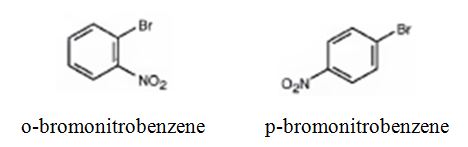
Bromobenzene will react slower than benzene.
Explanation of Solution
Bromine is an o- and p-directing group. It also has considerable electron withdrawing inductive effect which deactivates the ring. Hence bromobenzene is less reactive than benzene.
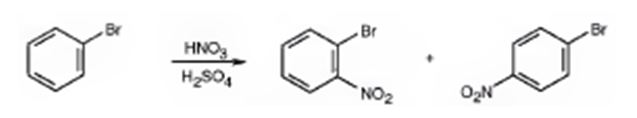
The major products formed when bromobenzene is nitrated are o-bromonitrobenzene and p-bromonitrobenzene.
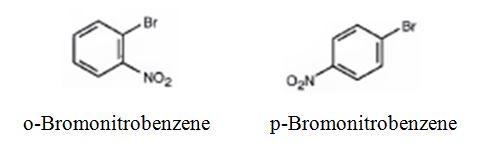
Bromobenzene will react slower than benzene.
b) Benzonitrile
Interpretation:
The major product(s) formed when benzonitrile is nitrated is to be given. Whether it will react faster or slower than benzene is also to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Monosubstituted benzenes can be nitrated using a mixture of Conc. HNO3 and H2SO4. Electron releasing substituent groups, except halogens, activate the ring and direct the incoming electrophile to the o- and p-positions. Compounds with these substituents are more reactive than benzene. Halogens are o- and p-directors but they deactivate the ring. Hence halobenzenes are less reactive than benzene. Electron withdrawing substituent groups deactivate the ring and direct the incoming electrophile to the m-position. Compounds with these substituents are less reactive than benzene.
To give:
The major products formed when benzonitrile is nitrated and to state whether it will react faster or slower than benzene.
Answer to Problem 47AP
The major product formed when benzonitrile is nitrated is m-nitrobenzonitrile.
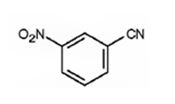
Benzonitrile will react slower than benzene.
Explanation of Solution
The cyanide group is strongly electron withdrawing in nature. Hence it is a meta director. The attraction of electrons away from the ring reduces the electron density in the ring. Thus benzonitrile reacts slower than benzene.
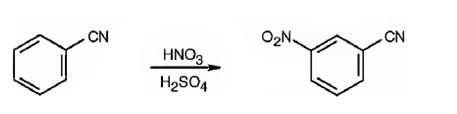
The major product formed when benzonitrile is nitrated is m-nitrobenzonitrile.

Benzonitrile will react slower than benzene.
c) Benzoic acid
Interpretation:
The major product(s) formed when benzoic acid is nitrated is to be given. Whether it will react faster or slower than benzene is also to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Monosubstituted benzenes can be nitrated using a mixture of Conc. HNO3 and H2SO4. Electron releasing substituent groups, except halogens, activate the ring and direct the incoming electrophile to the o- and p-positions. Compounds with these substituents are more reactive than benzene. Halogens are o- and p-directors but they deactivate the ring. Hence halobenzenes are less reactive than benzene. Electron withdrawing substituent groups deactivate the ring and direct the incoming electrophile to the m-position. Compounds with these substituents are less reactive than benzene.
To give:
The major products formed when benzoic acid is nitrated and to state whether it will react faster or slower than benzene.
Answer to Problem 47AP
The major product formed when benzoic acid is nitrated is m-nitrobenzoic acid.
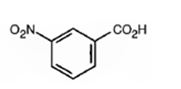
Benzoic acid will react slower than benzene.
Explanation of Solution
The C=O in carboxyl group is strongly electron withdrawing in nature. Hence it is a meta director. The attraction of electrons away from the ring reduces the electron density in the ring. Thus benzoic acid reacts slower than benzene.
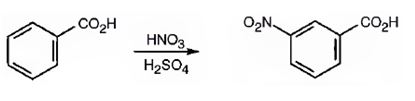
The major product formed when benzoic acid is nitrated is m-nitrobenzoic acid.

Benzoic acid will react slower than benzene.
d) Nitrobenzene
Interpretation:
The major product(s) formed when nitrobenzene is nitrated is to be given. Whether it will react faster or slower than benzene is also to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Monosubstituted benzenes can be nitrated using a mixture of Conc. HNO3 and H2SO4. Electron releasing substituent groups, except halogens, activate the ring and direct the incoming electrophile to the o- and p-positions. Compounds with these substituents are more reactive than benzene. Halogens are o- and p-directors but they deactivate the ring. Hence halobenzenes are less reactive than benzene. Electron withdrawing substituent groups deactivate the ring and direct the incoming electrophile to the m-position. Compounds with these substituents are less reactive than benzene.
To give:
The major products formed when nitrobenzene is nitrated and to state whether it will react faster or slower than benzene.
Answer to Problem 47AP
The major product formed when nitrobenzene is nitrated is m-dinitrobenzene.
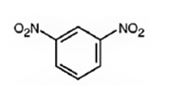
Nitrobenzene will react slower than benzene.
Explanation of Solution
The nitro group is strongly electron withdrawing in nature. Hence it is a meta director. The attraction of electrons away from the ring reduces the electron density in the ring. Thus nitrobenzene reacts slower than benzene.
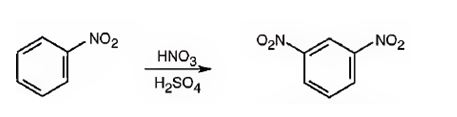
The major product formed when nitrobenzene is nitrated is m-dinitrobenzene.

Nitrobenzene will react slower than benzene.
e) Benzenesulfonic acid
Interpretation:
The major product(s) formed when benzenesulfonic acid is nitrated is to be given. Whether it will react faster or slower than benzene is also to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Monosubstituted benzenes can be nitrated using a mixture of Conc. HNO3 and H2SO4. Electron releasing substituent groups, except halogens, activate the ring and direct the incoming electrophile to the o- and p-positions. Compounds with these substituents are more reactive than benzene. Halogens are o- and p-directors but they deactivate the ring. Hence halobenzenes are less reactive than benzene. Electron withdrawing substituent groups deactivate the ring and direct the incoming electrophile to the m-position. Compounds with these substituents are less reactive than benzene.
To give:
The major products formed when benzenesulfonic acid is nitrated and to state whether it will react faster or slower than benzene.
Answer to Problem 47AP
The major product formed when benzenesulfonic acid is nitrated is m-nitro benzenesulfonic acid.
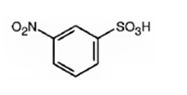
Benzenesulfonic acid will react slower than benzene.
Explanation of Solution
The sulfonic acid group is strongly electron withdrawing in nature. Hence it is a meta director. The attraction of electrons away from the ring reduces the electron density in the ring. Thus benzenesulfonic acid reacts slower than benzene.
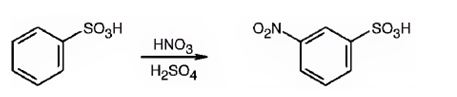
The major product formed when benzenesulfonic acid is nitrated is m-nitro benzenesulfonic acid.

Benzenesulfonic acid will react slower than benzene.
f) Methoxybenzene
Interpretation:
The major product(s) formed when methoxybenzene is nitrated is to be given. Whether it will react faster or slower than benzene is also to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Monosubstituted benzenes can be nitrated using a mixture of Conc. HNO3 and H2SO4. Electron releasing substituent groups, except halogens, activate the ring and direct the incoming electrophile to the o- and p-positions. Compounds with these substituents are more reactive than benzene. Halogens are o- and p-directors but they deactivate the ring. Hence halobenzenes are less reactive than benzene. Electron withdrawing substituent groups deactivate the ring and direct the incoming electrophile to the m-position. Compounds with these substituents are less reactive than benzene.
To give:
The major products formed when methoxybenzene is nitrated and to state whether it will react faster or slower than benzene.
Answer to Problem 47AP
The major products formed when methoxybenzene is nitrated are o-nitromethoxybenene and p-nitromethoxybenene.
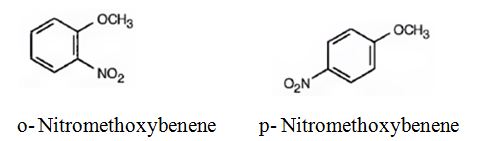
Methoxybenzene will react faster than benzene.
Explanation of Solution
The methoxy group is electron releasing in nature. Hence it is an o- and p-director. The attraction of electrons towards the ring increases the electron density in the ring. Thus methoxybenzene reacts faster than benzene.
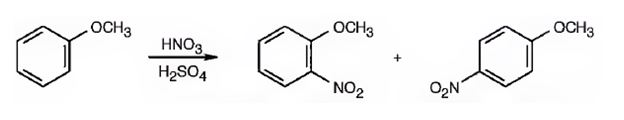
The major products formed when methoxybenzene is nitrated are o-nitromethoxybenene and p-nitromethoxybenene.
Methoxybenzene will react faster than benzene.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Bundle: Organic Chemistry, 9th, Loose-Leaf + OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- In a reaction between two reactants A and B, the half-life is the same for both only if(A) the stoichiometry A:B is 1:1.(B) the stoichiometry A:B is 1:2 or 2:1.arrow_forwardIn a reaction between two reactants A and B, the half-life is the same for both.(1) Only if the stoichiometry A:B is 1:1.(2) If the initial quantities of A and B are in their stoichiometric ratios.arrow_forwardThere are 48 pairs of students in the following table. Each pair has quantitatively determined the mass of taurine in a 250 mL can of the popular energy drink marketed as “Munster” using High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). The class results are presented below: QUESTION: Calculate the measurement of uncertainty and provide the data in a spreadsheet table. Mass of Taurine (mg) Mass of Taurine (mg) (Table continued) 152.01 152.23 151.87 151.45 154.11 152.64 152.98 153.24 152.88 151.45 153.49 152.48 150.68 152.33 151.52 153.63 152.48 151.68 153.17 153.40 153.77 153.67 152.34 153.16 152.57 153.02 152.86 151.50 151.23 152.57 152.72 151.54 146.47 152.38 152.44 152.54 152.53 152.54 151.32 152.87 151.24 153.26 152.02 152.90 152.87 151.49 152.46 152.58arrow_forward
- 1. Predict the organic product(s) of the following reactions. Assume excess of reagents unless otherwise noted. a) &l BH3 •THF b) 1) NaOH 2) H3O+ solve d) ala 1) EtMgBr 2) H3O+ e) H2N سكر CuLi NH2 1) SOCI2 2) EtMgBr 3) H3O+ NC H3O+ Δarrow_forwardThere are 48 pairs of students in the following table. Each pair has quantitatively determined the mass of taurine in a 250 mL can of the popular energy drink marketed as “Munster” using High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). The class results are presented below: QUESTION: Summarise and report these results including an indication of measurement uncertainty. In both calculation samples calculate if an outlier is present, max value, number of samples, mean, standard deviation, g (suspect), g (critical) and t (critical). Mass of Taurine (mg) Mass of Taurine (mg) (Table continued) 152.01 152.23 151.87 151.45 154.11 152.64 152.98 153.24 152.88 151.45 153.49 152.48 150.68 152.33 151.52 153.63 152.48 151.68 153.17 153.40 153.77 153.67 152.34 153.16 152.57 153.02 152.86 151.50 151.23 152.57 152.72 151.54 146.47 152.38 152.44 152.54 152.53 152.54 151.32…arrow_forwardIndicate the rate expressions for reactions that have order 0, 1, and 2.arrow_forward
- PROBLEMS Q1) Label the following salts as either acidic, basic, or neutral a) Fe(NOx) c) AlBr b) NH.CH COO d) HCOON (1/2 mark each) e) Fes f) NaBr Q2) What is the pH of a 0.0750 M solution of sulphuric acid?arrow_forward8. Draw all the resonance forms for each of the fling molecules or ions, and indicate the major contributor in each case, or if they are equivalent (45) (2) -PH2 سمة مدarrow_forwardA J то گای ه +0 Also calculate the amount of starting materials chlorobenzaldehyde and p-chloroacetophenone required to prepare 400 mg of the given chalcone product 1, 3-bis(4-chlorophenyl)prop-2-en-1-one molar mass ok 1,3-bis(4-Chlorophenyl) prop-2-en-1-one = 277.1591m01 number of moles= 0.400/277.15 = 0.00144 moles 2 x 0.00 144=0.00288 moves arams of acetophenone = 0.00144 X 120.16 = 0.1739 0.1739x2=0.3469 grams of benzaldehyde = 0.00144X106.12=0.1539 0.1539x2 = 0.3069 Starting materials: 0.3469 Ox acetophenone, 0.3069 of benzaldehyde 3arrow_forward
- 1. Answer the questions about the following reaction: (a) Draw in the arrows that can be used make this reaction occur and draw in the product of substitution in this reaction. Be sure to include any relevant stereochemistry in the product structure. + SK F Br + (b) In which solvent would this reaction proceed the fastest (Circle one) Methanol Acetone (c) Imagine that you are working for a chemical company and it was your job to perform a similar reaction to the one above, with the exception of the S atom in this reaction being replaced by an O atom. During the reaction, you observe the formation of three separate molecules instead of the single molecule obtained above. What is the likeliest other products that are formed? Draw them in the box provided.arrow_forward3. For the reactions below, draw the arrows corresponding to the transformations and draw in the boxes the reactants or products as indicated. Note: Part A should have arrows drawn going from the reactants to the middle structure and the arrows on the middle structure that would yield the final structure. For part B, you will need to draw in the reactant before being able to draw the arrows corresponding to product formation. A. B. Rearrangement ΘΗarrow_forward2. Draw the arrows required to make the following reactions occur. Please ensure your arrows point from exactly where you want to exactly where you want. If it is unclear from where arrows start or where they end, only partial credit will be given. Note: You may need to draw in lone pairs before drawing the arrows. A. B. H-Br 人 C Θ CI H Cl Θ + Br Oarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





