
Concept explainers
(a)
An expression for the electric field in the region x>0.
Answer to Problem 90QAP
An expression for the electric field in the region x>0 is,
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Charge,
Charge,
Distance, r
Formula used:
The electric force is given by,
Where,
r=Distance
Calculation:
The electric force is given by,
As charge 1 is placed at origin and charge 2 is placed at a distance a from origin. So, charge 1 is at distance x from reference point and charge 2 is at distance x+a from reference point.
(b)
An expression for the electric field in the region 0
Answer to Problem 90QAP
An expression for the electric field in the region 0
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Charge,
Charge,
Distance, r
Formula used:
The electric force is given by,
Where,
r=DistanceCalculation:
The electric force is given by,
Thus,
(c)
An expression for the electric field in the region x>a.
Answer to Problem 90QAP
An expression for the electric field in the region x>a is,
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Charge,
Charge,
Distance, r
Formula used:
The electric force is given by,
Where,
r=Distance
Calculation:
The electric force is given by,
Thus,
(d)
The point at which the electric field is zero.
Answer to Problem 90QAP
At
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Charge,
Charge,
Distance, r
Formula used:
The electric force is given by,
Where,
r=Distance
Calculation:
The electric force is given by,
Thus,
(e)
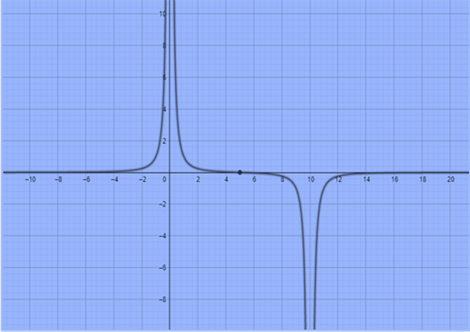
To plot:
The graph of Exverses x.
Explanation of Solution
Formula used:
The electric force is given by,
Where,
r=Distance
The electric force is given by,
(f)
An expression for the electric field in the region -8
Answer to Problem 90QAP
An expression for the electric field in the region -8
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Charge,
Charge,
Distance, r
Formula used:
The electric force is given by,
Where,
r=Distance
Calculation:
The electric force is given by,
Thus,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS
- Problem Eleven. A hollow sphere with rotational inertia 1 = (2/3)MR2 is moving with speed v down an incline of angle 0 toward a spring with spring constant k. After traveling a distance d down the incline with no slipping, the sphere makes contact with the spring and compresses it a distance x before it comes momentarily to rest. Find the distance d in terms of the other quantities given. (21) 19.) (A) d=- 2Mg sin kx²-Mv² +x (B) d= 2Mg sin kx²+Mv² +x kx²-Mv² (C) d=- -x (D) d= 2Mg sin 2Mg cos kx²-Mv² 2Mg sin -x (E) d= kx²-Mv²arrow_forward1. A light bulb operates at a temperature of 4,300 K and has an emissivity of 0.600 and a surface area of 5.50 mm². How long would the light bulb have to shine on a 2.00 g piece of ice that is at -30.0°C in order to turn the ice into steam at 120°C? Assume all the energy radiated by the light bulb is absorbed by the ice while it becomes liquid and eventually steam. Give an answer in seconds. The following are specific heats for ice, water, and steam. Cice = 2,090 ***C kg kg."C Cwater = 4,186 C Csteam = 2,010 C kg"C The following are latent heats for water. L 3.33 x 10' J/kg Lv = 2.26 x 10° J/kg (A) 31.6 (B) 56.9 (C) 63.5 (D) 21.6 (E) 97.4 Suppose q; consists of three protons and 92 consists of two protons. Let q; be at the origin and q2 be located at d along the x-axis. See the diagram below. 91 92 Χ d 2. Where would the net electric potential due to these two charges be zero? (A) to the left of gi (B) to the right of 92 (D) to the right of 92, as well as to the left of gi (E) Between…arrow_forwardProblem Six: A homogeneous solid object floats in water with 60.0% of its volume below the surface. When placed in a second liquid, the same object floats with 90.0% of its volume below the surface. (The density of water is 1,000 kg/m³.) Determine the density of the object in kg/m³. 19.) (A) 430 (B) 280 Determine the specific gravity of the liquid. 20.) (A) 0.331 (B) 0.760 (C) 560 (D) 600 (E) 720 (C) 0.880 (D) 0.280 (E) 0.667arrow_forward
- A 1000-kg car traveling east at 30.0 m/s collides with a 950-kg car traveling north at 25.0 m/s. The cars stick together. Assume that any other unbalanced forces are negligible. What is the speed of the wreckage just after the collision? Please do on paper and show all equations and work done to get to the final answer. Along with any helpful diagrams if needed. These are a part of my review questions in the book but i keep getting different answers from what the book says, it is not a graded assignment***arrow_forwardWas not explained in my physics 2 lecture, and I'm confused!arrow_forwardA 75.0-kg person drops from rest a distance of 1.20 m to a platform of negligible mass supported by an ideal stiff spring of negligible mass. The platform drops 6.00 cm before the person comes to rest. What is the spring constant of the spring? Please do on paper and show all equations and work done to get to the final answer. Along with any helpful diagrams if needed. These are a part of my review questions in the book but i keep getting different answers from what the book says, it is not a graded assignment***arrow_forward
- Problem Ten. A uniform rod is suspended in mechanical equilibrium by two strings. If T₁ = 500 N, what is the weight of the rod (in N)? 18.) (A) 120 N (D) 600 N (B) 900 N (C) 500 N (E) 220 N T T Mg STAY Carrow_forwardIn the figure, two boxes, each of mass 35 kg, are at rest and connected as shown. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the inclined surface and the box is 0.38. Find the speed of the boxes just after they have moved 5.5 m. Please do on paper and show all formulas and work done to get final answer This is a review problem , I just keep getting the wrong thing from what the textbook says , so i would like to see the work donearrow_forwardA 64.0-kg skier starting from rest travels 200.0 m down a hill that has a 30.0° slope and a uniform surface. When the skier reaches the bottom of the hill, her speed is 30.0 m/s. How much work is done by friction as the skier comes down the hill? Please do on paper and show all the equations and work done to get to the final answer.arrow_forward
- A 550-kg car moving at 18.5 m/s hits from behind a 560-kg car moving at 11.8 m/s in the same direction. If the new speed of the heavier car is 16.0 m/s, what is the speed of the lighter car after the collision, assuming that any unbalanced forces on the system are negligibly small? Please do on paper and show all equations and work done to get to the final answer. Along with any helpful diagrams if needed. These are a part of my review questions in the book but i keep getting different answers from what the book says, it is not a graded assignment***arrow_forwardA 150kg piano rolls down a 30° incline. A man tries to keep it from accelerating, and manages to keep its acceleration to 1.4 m/s^2 . If the piano rolls 8 m, what is the net work, in joules, done on it by all the forces acting on it? Please do it on paper and show all formulas and work used to get the answerarrow_forwardThe rectangular loop of wire shown in the figure (Figure 1) has a mass of 0.18 g per centimeter of length and is pivoted about side ab on a frictionless axis. The current in the wire is 8.5 A in the direction shown. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field parallel to the y-axis that will cause the loop to swing up until its plane makes an angle of 30.0 ∘ with the yz-plane. The answer is .028 T, I just need help understanding how to do it. Please show all steps.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





