
Concept explainers
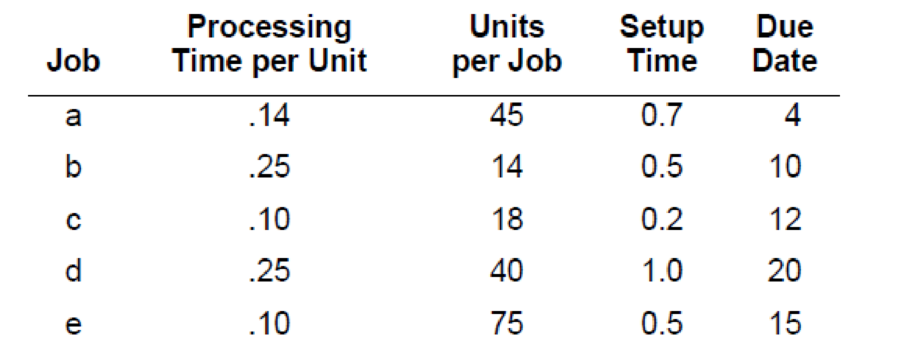
Using the information presented in the following table, identify the processing sequence that would result using (1) FCFS, (2) SPT, (3) EDD, and (4) CR. For each method, determine (1) average job flow time, (2) average job tardiness, and (3) average number of jobs in the system. Jobs are listed in order of arrival. (Hint: First determine the total job time for each job by computing the total processing time for the job and then adding in the setup time. All times and due dates are in hours.)
1)
To determine: Sequence of jobs based on decision rule First Come First Served (FCFS).
Introduction: First Come First Served is the scheduling rule, which helps to arrange the sequence in the order. Here, the first come would be served first.
Answer to Problem 7P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time per unit | Units per job | Setup time | Due date |
| a | 0.14 | 45 | 0.7 | 4 |
| b | 0.25 | 14 | 0.5 | 10 |
| c | 0.1 | 18 | 0.2 | 12 |
| d | 0.25 | 40 | 1 | 20 |
| e | 0.1 | 75 | 0.5 | 15 |
Due date is given. Job time should be determined using the given processing time per unit, units per job, and setup time.
Example:
The procedure should be repeated for all the jobs. The resultant table is as follows:
| Job | Job time (hours) | Due date (hours) |
| a | 7 | 4 |
| b | 4 | 10 |
| c | 2 | 12 |
| d | 11 | 20 |
| e | 8 | 15 |
Determine the sequence using FCFS:
According to FCFS, the first come would be served first. Hence, the jobs should be sequenced in the order as per its arrival.
Hence, the sequence of jobs using FCFS is a-b-c-d-e.
Determine average flow time, average tardiness, and average number of jobs for FCFS:
| Job | Processing time (hours) | Due date (hours) | Flow time | Tardiness |
| a | 7 | 4 | 7 | 3 |
| b | 4 | 10 | 11 | 1 |
| c | 2 | 12 | 13 | 1 |
| d | 11 | 20 | 24 | 4 |
| e | 8 | 15 | 32 | 17 |
| Total | 32 | 61 | 87 | 26 |
| Average | 6.4 | 12.2 | 17.4 | 5.2 |
Supporting calculation:
Processing time and due date are given for each job. Flow time is the cumulative of the processing time.
Tardiness of Job a:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job b is 3.
Tardiness of Job b:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job b is 1.
Tardiness of Job c:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job c is 1.
Tardiness of Job d:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job d is 4.
Tardiness of Job e:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job e is 17.
Average flow time:
It is calculated by dividing the total flow time and number of jobs.
Hence, average flow time is 17.40 hours.
Average tardiness:
It is calculated by dividing the total tardiness and number of jobs.
Hence, average tardiness is 5.20 hours.
Average number of jobs:
It can be determined by dividing the total flow time and total processing time.
Hence, average number of jobs is 2.72 jobs.
2)
To determine: Sequence of jobs based on decision rule Shortest Processing Time (SPT).
Introduction: Shortest Processing Tine is the scheduling rule, which helps to arrange the sequence in the order. Here, job with the shortest duration would be served first. Then, the process would be going on from shortest to largest duration.
Answer to Problem 7P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time per unit | Units per job | Setup time | Due date |
| a | 0.14 | 45 | 0.7 | 4 |
| b | 0.25 | 14 | 0.5 | 10 |
| c | 0.1 | 18 | 0.2 | 12 |
| d | 0.25 | 40 | 1 | 20 |
| e | 0.1 | 75 | 0.5 | 15 |
Due date is given. Job time should be determined using the given processing time per unit, units per job, and setup time.
Example:
The procedure should be repeated for all the jobs. The resultant table is as follows:
| Job | Job time (hours) | Due date (hours) |
| a | 7 | 4 |
| b | 4 | 10 |
| c | 2 | 12 |
| d | 11 | 20 |
| e | 8 | 15 |
Determine the sequence using SPT:
According to SPT, the job that has the shortest processing would be served first and it goes on as the processing time increase. Duration should be assembled in the ascending order
Hence, the sequence of jobs using SPT is c-b-a-e-d.
Determine average flow time, average tardiness, and average number of jobs for SPT:
| Job | Job time (hours) | Due date (hours) | Flow time | Tardiness |
| c | 2 | 12 | 2 | 0 |
| b | 4 | 10 | 6 | 0 |
| a | 7 | 4 | 13 | 9 |
| e | 8 | 15 | 21 | 6 |
| d | 11 | 20 | 32 | 12 |
| Total | 32 | 61 | 74 | 27 |
| Average | 6.4 | 12.2 | 14.8 | 5.4 |
Supporting calculation:
Processing time and due date are given for each job. Flow time is the cumulative of the processing time.
Tardiness of Job c, and Job b:
Flow time of Job c and Job b is less than its respective due date. Hence, there would be no tardiness.
Tardiness of Job a:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job a is 9.
Tardiness of Job e:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job e is 6.
Tardiness of Job d:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job d is 12.
Average flow time:
It is calculated by dividing the total flow time and number of jobs.
Hence, average flow time is 14.80 hours.
Average tardiness:
It is calculated by dividing the total tardiness and number of jobs.
Hence, average tardiness is 5.40 hours.
Average number of jobs:
It can be determined by dividing the total flow time and total processing time.
Hence, average number of jobs is 2.31 jobs.
3)
To determine: Sequence of jobs based on decision rule Earliest Due Date (EDD).
Introduction: Earliest Due Date is the scheduling rule, which helps to arrange the sequence in the order. Here, job with the earliest due date would be served first. Then, the process would be going on from earliest due date to latest due date.
Answer to Problem 7P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time per unit | Units per job | Setup time | Due date |
| a | 0.14 | 45 | 0.7 | 4 |
| b | 0.25 | 14 | 0.5 | 10 |
| c | 0.1 | 18 | 0.2 | 12 |
| d | 0.25 | 40 | 1 | 20 |
| e | 0.1 | 75 | 0.5 | 15 |
Due date is given. Job time should be determined using the given processing time per unit, units per job, and setup time.
Example:
The procedure should be repeated for all the jobs. The resultant table is as follows:
| Job | Job time (hours) | Due date (hours) |
| a | 7 | 4 |
| b | 4 | 10 |
| c | 2 | 12 |
| d | 11 | 20 |
| e | 8 | 15 |
Determine the sequence using EDD:
According to EDD, the job that has the earliest due date would be served first and it goes on as the due date increases. The job should be arranged based on due date. Due date should be assembled in the ascending order
Hence, the sequence of jobs using EDD is a-b-c-e-d.
Determine average flow time, average tardiness, and average number of jobs for EDD:
| Job | Job time (hours) | Due date (hours) | Flow time | Tardiness |
| a | 7 | 4 | 7 | 3 |
| b | 4 | 10 | 11 | 1 |
| c | 2 | 12 | 13 | 1 |
| e | 8 | 15 | 21 | 6 |
| d | 11 | 20 | 32 | 12 |
| Total | 32 | 61 | 84 | 23 |
| Average | 6.4 | 12.2 | 16.8 | 4.6 |
Supporting calculation:
Processing time and due date are given for each job. Flow time is the cumulative of the processing time.
Tardiness of Job a:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job b is 3.
Tardiness of Job b:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job b is 1.
Tardiness of Job c:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job c is 1.
Tardiness of Job e:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job e is 6.
Tardiness of Job d:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job d is 12.
Average flow time:
It is calculated by dividing the total flow time and number of jobs.
Hence, average flow time is 16.80 hours.
Average tardiness:
It is calculated by dividing the total tardiness and number of jobs.
Hence, average tardiness is 4.60 hours.
Average number of jobs:
It can be determined by dividing the total flow time and total processing time.
Hence, average number of jobs is 2.63 jobs.
4)
To determine: Sequence of jobs based on decision rule critical ratio.
Introduction: Critical ratio is kind of scheduling rule that helps to identify that, the task or job is on the correct track. It would help to identify if the task is behind or ahead of the schedule.
Answer to Problem 7P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time per unit | Units per job | Setup time | Due date |
| a | 0.14 | 45 | 0.7 | 4 |
| b | 0.25 | 14 | 0.5 | 10 |
| c | 0.1 | 18 | 0.2 | 12 |
| d | 0.25 | 40 | 1 | 20 |
| e | 0.1 | 75 | 0.5 | 15 |
Due date is given. Job time should be determined using the given processing time per unit, units per job, and setup time.
Example:
The procedure should be repeated for all the jobs. The resultant table is as follows:
| Job | Job time (hours) | Due date (hours) |
| a | 7 | 4 |
| b | 4 | 10 |
| c | 2 | 12 |
| d | 11 | 20 |
| e | 8 | 15 |
Determine the sequence using critical ratio:
Initial critical ratio should be determined at day 0:
| Job | Processing time (hours) | Due date | Critical ratio |
| a | 7 | 4 | 0.57 |
| b | 4 | 10 | 2.5 |
| c | 2 | 12 | 6 |
| d | 11 | 20 | 1.82 |
| e | 8 | 15 | 1.88 |
Critical ratio for Job a:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of previous job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Note: Process continues for all the jobs.
Job a has the lowest critical ratio. Thus, it will be completed first. Hence, Job a would be completed first in the sequence of jobs.
Determine the critical ratio after the completion of Job a:
As the processing time of job a is 7 hours, completion day of completed day would be 7.
| Job | Processing time (hours) | Due date | Critical ratio |
| a | - | - | - |
| b | 4 | 10 | 0.75 |
| c | 2 | 12 | 2.5 |
| d | 11 | 20 | 1.18 |
| e | 8 | 15 | 1 |
Critical ratio for Job b:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of completed job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Note: Process continues for all the jobs.
Job b has the lowest critical ratio. Hence, Job b would be completed next in the sequence of jobs.
Determine the critical ratio after the completion of Job a and Job b:
As the processing time of job a is 7 hours and Job b is 4, completion day of completed day would be 11 (7+4).
| Job | Processing time (hours) | Due date | Critical ratio |
| a | - | - | - |
| b | - | - | - |
| c | 2 | 12 | 0.5 |
| d | 11 | 20 | 0.82 |
| e | 8 | 15 | 0.5 |
Critical ratio for Job c:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of completed job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Job c has the lowest critical ratio (break the tie arbitrarily). Hence, Job c would be completed next in the sequence of jobs after Job a and Job b.
Determine the critical ratio after the completion of Job a, Job b and Job c:
As the processing time of job a is 7 hours, Job b is 4, and Job c is 2 hours. completion day of completed day would be 13 (7+4+2).
| Job | Processing time (hours) | Due date | Critical ratio |
| a | - | - | - |
| b | - | - | - |
| c | - | - | - |
| d | 11 | 20 | 0.82 |
| e | 8 | 15 | 0.5 |
Critical ratio for Job d:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of completed job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Job e has the lowest critical ratio. Hence, Job e would be completed next in the sequence of jobs after Job a, Job b, and Job c.
As Job d is the remaining job, it will be completed next.
Hence, the sequence of jobs using critical ratio is a-b-c-e-d.
Average flow time:
It is calculated by dividing the total flow time and number of jobs.
Hence, average flow time is 16.80 hours.
Average tardiness:
It is calculated by dividing the total tardiness and number of jobs.
Hence, average tardiness is 4.60 hours.
Average number of jobs:
It can be determined by dividing the total flow time and total processing time.
Hence, average number of jobs is 2.63 jobs.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Operations Management (The Mcgraw-hill Series in Operations and Decision Sciences)
- Employee In-Service Training ASSIGNMENT: In-Service Training. The intern is required to plan and implement two in-service training sessions for employees. Each in-service should last at least 10 but not more than 30 minutes and should be given to all employees affected. The preceptor or supervisor/unit manager must approve all in-service topics. 1) One presentation should be related to a policy or procedure of any kind (e.g. proper use of equipment); 2) The second presentation must be related to sanitation or safety. For each in-service presentation, the intern must develop a written class plan and a visual aid (may be a handout, poster, PowerPoint slide presentation, etc.) appropriate to the life experiences, cultural diversity and educational background of the target audience. The intern must also measure behavior change. Note, this cannot be measured by a written pre- and post- test. That would be measuring knowledge. The intern mustactually observe and document that the learners…arrow_forwardFor a dietary manager in a nursing home to train a dietary aidearrow_forwardDietary Management in a Nursing Home. As detailed as possible.arrow_forward
- For dietary management in a nursing home. As detailed as possible.arrow_forwardA small furniture manufacturer produces tables and chairs. Each product must go through three stages of the manufacturing process – assembly, finishing, and inspection. Each table requires 3 hours of assembly, 2 hours of finishing, and 1 hour of inspection. The profit per table is $120 while the profit per chair is $80. Currently, each week there are 200 hours of assembly time available, 180 hours of finishing time, and 40 hours of inspection time. Linear programming is to be used to develop a production schedule. Define the variables as follows: T = number of tables produced each week C= number of chairs produced each week According to the above information, what would the objective function be? (a) Maximize T+C (b) Maximize 120T + 80C (c) Maximize 200T+200C (d) Minimize 6T+5C (e) none of the above According to the information provided in Question 17, which of the following would be a necessary constraint in the problem? (a) T+C ≤ 40 (b) T+C ≤ 200 (c) T+C ≤ 180 (d) 120T+80C ≥ 1000…arrow_forwardAs much detail as possible. Dietary Management- Nursing Home Don't add any fill-in-the-blanksarrow_forward
- Menu Planning Instructions Use the following questions and points as a guide to completing this assignment. The report should be typed. Give a copy to the facility preceptor. Submit a copy in your Foodservice System Management weekly submission. 1. Are there any federal regulations and state statutes or rules with which they must comply? Ask preceptor about regulations that could prescribe a certain amount of food that must be kept on hand for emergencies, etc. Is the facility accredited by any agency such as Joint Commission? 2. Describe the kind of menu the facility uses (may include standard select menu, menu specific to station, non-select, select, room service, etc.) 3. What type of foodservice does the facility have? This could be various stations to choose from, self-serve, 4. conventional, cook-chill, assembly-serve, etc. Are there things about the facility or system that place a constraint on the menu to be served? Consider how patients/guests are served (e.g. do they serve…arrow_forwardWork with the chef and/or production manager to identify a menu item (or potential menu item) for which a standardized recipe is needed. Record the recipe with which you started and expand it to meet the number of servings required by the facility. Develop an evaluation rubric. Conduct an evaluation of the product. There should be three or more people evaluating the product for quality. Write a brief report of this activity • Product chosen and the reason why it was selected When and where the facility could use the product The standardized recipe sheet or card 。 o Use the facility's format or Design one of your own using a form of your choice; be sure to include the required elements • • Recipe title Yield and portion size Cooking time and temperature Ingredients and quantities Specify AP or EP Procedures (direction)arrow_forwardASSIGNMENT: Inventory, Answer the following questions 1. How does the facility survey inventory? 2. Is there a perpetual system in place? 3. How often do they do a physical inventory? 4. Participate in taking inventory. 5. Which type of stock system does the facility use? A. Minimum stock- includes a safety factor for replenishing stock B. Maximum stock- equal to a safety stock plus estimated usage (past usage and forecasts) C. Mini-max-stock allowed to deplete to a safety level before a new order is submitted to bring up inventory up to max again D. Par stock-stock brought up to the par level each time an order is placed regardless of the amount on hand at the time of order E. Other-(describe) Choose an appropriate product and determine how much of an item should be ordered. Remember the formula is: Demand during lead time + safety stock = amount to order Cost out an inventory according to data supplied. Remember that to do this, you will need to take an inventory, and will need to…arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Understanding Management (MindTap Course List)ManagementISBN:9781305502215Author:Richard L. Daft, Dorothy MarcicPublisher:Cengage Learning
Understanding Management (MindTap Course List)ManagementISBN:9781305502215Author:Richard L. Daft, Dorothy MarcicPublisher:Cengage Learning


