
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The plausible mechanism for the formation of the product B has to be proposed.
Concept introduction:
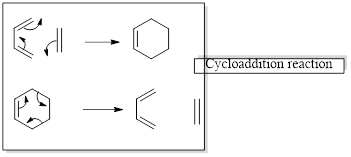
There are mainly three types of pericyclic reactions,
- 1) Electrocyclic reactions
- 2) Cycloaddition reactions
- 3) Sigmatropic reactions
In a cycloaddition reaction “ two new sigma-bonds are formed or brocken”
Click reaction:
Azide reaction with
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of compound C has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
There are mainly three types of pericyclic reactions,
- 1) Electrocyclic reactions
- 2) Cycloaddition reactions
- 3) Sigmatropic reactions
In a cycloaddition reaction “ two new sigma-bonds are formed or brocken”

Click reaction:
Azide reaction with alkyne in the presence of CuSO4 and provides trazole as a product.
(c)
Interpretation:
The reason for decrease in rate if the alkyne A is replaced by alkynes from D-F has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Angle strain: The strain experienced because of existence of the non-bonded interactions of the atoms which are placed spatially close to each other is called the angle strain.
The angle strain will be very much low for sp-hybridised carbon in linear alkyne but is more in cyclic alkyne.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRYPKGDRL+MLCRL MDL
- Problem 6-29 Identify the functional groups in the following molecules, and show the polarity of each: (a) CH3CH2C=N CH, CH, COCH (c) CH3CCH2COCH3 NH2 (e) OCH3 (b) (d) O Problem 6-30 Identify the following reactions as additions, eliminations, substitutions, or rearrangements: (a) CH3CH2Br + NaCN CH3CH2CN ( + NaBr) Acid -OH (+ H2O) catalyst (b) + (c) Heat NO2 Light + 02N-NO2 (+ HNO2) (d)arrow_forwardPredict the organic product of Y that is formed in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic product. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardPlease choose the best reagents to complete the following reactionarrow_forward
- Problem 6-17 Look at the following energy diagram: Energy Reaction progress (a) Is AG for the reaction positive or negative? Label it on the diagram. (b) How many steps are involved in the reaction? (c) How many transition states are there? Label them on the diagram. Problem 6-19 What is the difference between a transition state and an intermediate? Problem 6-21 Draw an energy diagram for a two-step reaction with Keq > 1. Label the overall AG°, transition states, and intermediate. Is AG° positive or negative? Problem 6-23 Draw an energy diagram for a reaction with Keq = 1. What is the value of AG° in this reaction?arrow_forwardProblem 6-37 Draw the different monochlorinated constitutional isomers you would obtain by the radical chlorination of the following compounds. (b) (c) Problem 6-39 Show the structure of the carbocation that would result when each of the following alkenes reacts with an acid, H+. (a) (b) (c)arrow_forwardPlease draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts and the carboxylic side productarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





