
Illumination on the screen for each case.
To sketch: The graph of a obtained data.
To find: The shape of the graph. Also, the relationship between the illuminance and distance.
Answer to Problem 74A
Illumination on the screen for each case is shown in Table 1.
The graph of the obtained data is shown in Figure 1.
The shape of the graph is hyperbola.
The relationship between illuminance and distance in the graph is inverse square.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The distance of
Formula used:
The expression for the point source illuminance is,
Here,
Calculation:
The luminous flux of the light source is,
The point source illuminance at
Similarly, calculate the point source illuminance for every meter of increasing distance up to
Table 1
| Distance of light source from screen | Point of illuminance |
| 1 | 111 |
| 2 | 28 |
| 3 | 12 |
| 4 | 7 |
| 5 | 4 |
| 6 | 3 |
| 7 | 2 |
Sketch the graph as shown in Figure below.
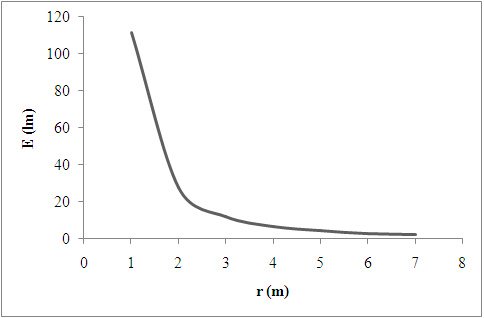
Figure 1
The shape of the graph is hyperbola.
The luminous flux
The illuminance of the point source (lamp) is inversely proportional to the square of the distance
The illuminance decreases with the increase in distance of the light source from screen.Hence, the relationship between illuminance and distance in the graph is Inverse Square.
Chapter 16 Solutions
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
- A particle with a charge of − 5.20 nC is moving in a uniform magnetic field of (B→=−( 1.22 T )k^. The magnetic force on the particle is measured to be(F→=−( 3.50×10−7 N )i^+( 7.60×10−7 N )j^. Calculate the scalar product v→F→. Work the problem out symbolically first, then plug in numbers after you've simplified the symbolic expression.arrow_forwardNeed help wity equilibrium qestionarrow_forwardneed answer asap please thanks youarrow_forward
- A man slides two boxes up a slope. The two boxes A and B have a mass of 75 kg and 50 kg, respectively. (a) Draw the free body diagram (FBD) of the two crates. (b) Determine the tension in the cable that the man must exert to cause imminent movement from rest of the two boxes. Static friction coefficient USA = 0.25 HSB = 0.35 Kinetic friction coefficient HkA = 0.20 HkB = 0.25 M₁ = 75 kg MB = 50 kg P 35° Figure 3 B 200arrow_forwardA golf ball is struck with a velocity of 20 m/s at point A as shown below (Figure 4). (a) Determine the distance "d" and the time of flight from A to B; (b) Determine the magnitude and the direction of the speed at which the ball strikes the ground at B. 10° V₁ = 20m/s 35º Figure 4 d Barrow_forwardThe rectangular loop of wire shown in the figure (Figure 1) has a mass of 0.18 g per centimeter of length and is pivoted about side ab on a frictionless axis. The current in the wire is 8.5 A in the direction shown. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field parallel to the y-axis that will cause the loop to swing up until its plane makes an angle of 30.0 ∘ with the yz-plane. Find the direction of the magnetic field parallel to the y-axis that will cause the loop to swing up until its plane makes an angle of 30.0 ∘ with the yz-plane.arrow_forward
- A particle with a charge of − 5.20 nC is moving in a uniform magnetic field of (B→=−( 1.22 T )k^. The magnetic force on the particle is measured to be (F→=−( 3.50×10−7 N )i^+( 7.60×10−7 N )j^. Calculate the y and z component of the velocity of the particle.arrow_forwardneed answer asap please thank youarrow_forward3. a. Determine the potential difference between points A and B. b. Why does point A have a higher potential energy? Q = +1.0 C 3.2 cm 4.8 cm Aarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





