
Concept explainers
The figure depicts the sequence of events in each cylinder of a four-cylinder internal combustion engine. Each piston moves up and down and is connected by a pivoted arm to a rotating crankshaft. Let P(t) and V(t) be the pressure and volume within a cylinder at time t, where a ≤ t ≤ b gives the time required for a complete cycle. The graph shows how P and V vary through one cycle of a four-stroke engine.
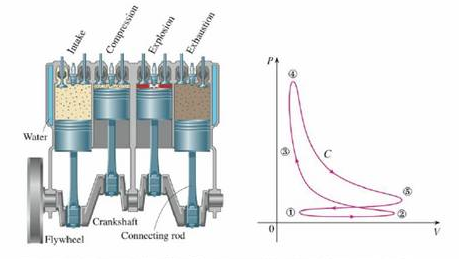
During the intake stroke (from ① to ②) a mixture of air and gasoline at atmospheric pressure is drawn into a cylinder through the intake valve as the piston moves downward. Then the piston rapidly compresses the mix with the valves closed in the compression stroke (from ② to ③) during which the pressure rises and the volume decreases. At ③ the sparkplug ignites the fuel, raising the temperature and pressure at almost constant volume to ④. Then, with valves closed, the rapid expansion forces the piston downward during the power stroke (from ④ to ⑤). The exhaust valve opens, temperature and pressure drop, and mechanical energy stored in a rotating flywheel pushes the piston upward, forcing the waste products out of the exhaust valve in the exhaust stroke. The exhaust valve closes and the intake valve opens. We’re now back at ① and the cycle starts again.
(a) Show that the work done on the piston during one cycle of a four-stroke engine is W = ∫C P dV, where C is the curve in the PV-plane shown in the figure. [Hint: Let x(t) be the distance from the piston to the top of the cylinder and note that the force on the piston is F = AP(t) i, where A is the area of the top of the piston. Then W = ∫
(b) Use Formula 16.4.5 to show that the work is the difference of the areas enclosed by the two loops of C.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 16 Solutions
Multivariable Calculus
- Solve by DrWz WI P L B dy Sind Ⓡ de max ⑦Ymax dx Solve by Dr ③Yat 0.75m from A w=6KN/M L=2 W2=9 kN/m P= 10 KN Solve By Drarrow_forwardHow to find the radius of convergence for the series in the image below? I'm stuck on how to isolate the x in the interval of convergence.arrow_forwardDetermine the exact signed area between the curve g(x): x-axis on the interval [0,1]. = tan2/5 secx dx andarrow_forward
- A factorization A = PDP 1 is not unique. For A= 7 2 -4 1 1 1 5 0 2 1 one factorization is P = D= and P-1 30 = Use this information with D₁ = to find a matrix P₁ such that - -1 -2 0 3 1 - - 1 05 A-P,D,P P1 (Type an integer or simplified fraction for each matrix element.)arrow_forwardMatrix A is factored in the form PDP 1. Use the Diagonalization Theorem to find the eigenvalues of A and a basis for each eigenspace. 30 -1 - 1 0 -1 400 0 0 1 A= 3 4 3 0 1 3 040 3 1 3 0 0 4 1 0 0 003 -1 0 -1 Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer boxes to complete your choice. (Use a comma to separate vectors as needed.) A basis for the corresponding eigenspace is { A. There is one distinct eigenvalue, λ = B. In ascending order, the two distinct eigenvalues are λ₁ ... = and 2 = Bases for the corresponding eigenspaces are { and ( ), respectively. C. In ascending order, the three distinct eigenvalues are λ₁ = = 12/2 = and 3 = Bases for the corresponding eigenspaces are {}, }, and { respectively.arrow_forwardN Page 0.6. 0.4. 0.2- -0.2- -0.4- -6.6 -5 W 10arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning


