
Find Missing Data for Profit
Required
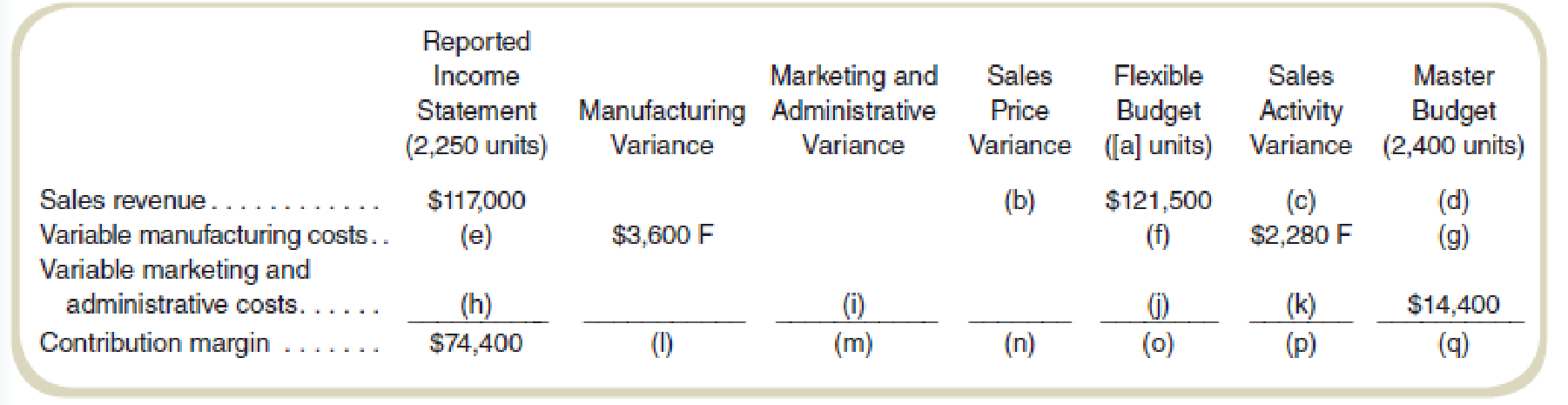
Find the values of the missing items (a) through (q). Assume that the actual sales volume equals actual production volume. (There are no inventory level changes.)
Find the missing data for profit variance analysis.
Explanation of Solution
Profit variance analysis:
The analysis that studies the difference between the actual operating profit and the standard operating profit is called the profit variance analysis.
Prepare profit variance analysis:
| Actual Revenue & Costs | Manufacturing variance | Marketing and administrative variance | Sales price variance | Flexible budget | Sales Activity Variance | Master budget | |
| Units Produced | 2,250 | 2,250 | 150U(1) | 2,400 | |||
| Sales revenue | $117,000 | $4,500U(2) | $121,500 | $8,100(13) | $129,600(3) | ||
| Less: Variable costs | |||||||
| Manufacturing | $30,600(7) | $3,600F | $34,200(5) | $2,280F | $36,480(6) | ||
| Marketing &administrative costs | $12,000(8) | $1,500F(11) | $13,500(10) | $900F | $14,400 | ||
| Contribution margin | $74,400 | $3,600F | $1,500F | $4,500U | $73,800 | $4,920U | $78,720 |
Table: (1)
Working Note 1:
Sales activity variance units and sales revenue:
Working Note 2:
Working Note 3:
Working Note 4:
Working Note 5:
Working Note 6:
Working Note 7:
Working Note 8:
Working Note 9:
Working Note 10:
Working Note 11:
Working Note 12:
Working Note 13:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Fundamentals Of Cost Accounting (6th Edition)
- Determine the following requirements of this financial accounting questionarrow_forwardProvide correct answer this financial accounting questionarrow_forwardChapter 15 Homework 13 Saved Help Save & Exit Submit Part 1 of 2 0.83 points eBook Ask Required information Use the following information to answer questions. (Algo) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Information on Kwon Manufacturing's activities for its first month of operations follows: a. Purchased $100,800 of raw materials on credit. b. Materials requisitions show the following materials used for the month. Job 201 Job 202 Total direct materials Indirect materials Total materials used $ 49,000 24,400 73,400 9,420 $ 82,820 c. Time tickets show the following labor used for the month. Print References Job 201 $ 40,000 Job 202 13,400 Total direct labor 53,400 25,000 $ 78,400 Indirect labor Total labor used d. Applied overhead to Job 201 and to Job 202 using a predetermined overhead rate of 80% of direct materials cost. e. Transferred Job 201 to Finished Goods Inventory. f. Sold Job 201 for $166,160 on credit. g. Incurred the following actual other…arrow_forward
- quesrion 2arrow_forwardAnti-Pandemic Pharma Co. Ltd. reports the following information in its income statement: Sales = $5,250,000; Costs = $2, 173,000; Other expenses = $187,400; Depreciation expense = $79,000; Interest expense= $53,555; Taxes $76,000; Dividends $69,000. $136,700 worth of new shares were also issued during the year and long-term debt worth $65,300 was redeemed. a) Compute the cash flow from assets b) Compute the net change in working capital (325 marks)arrow_forwardQS 15-18 (Algo) Computing and recording over- or underapplied overhead LO P4 A company applies overhead at a rate of 170% of direct labor cost. Actual overhead cost for the current period is $1,081,900, and direct labor cost is $627,000. 1. Compute the under- or overapplied overhead. 2. Prepare the journal entry to close over- or underapplied overhead to Cost of Goods Sold. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Compute the under- or overapplied overhead.arrow_forward
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning





