
Concept explainers
1. and 2.
Calculate the basic earnings per share and diluted earnings per share.
1. and 2.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the basic earnings per share and diluted earnings per share.
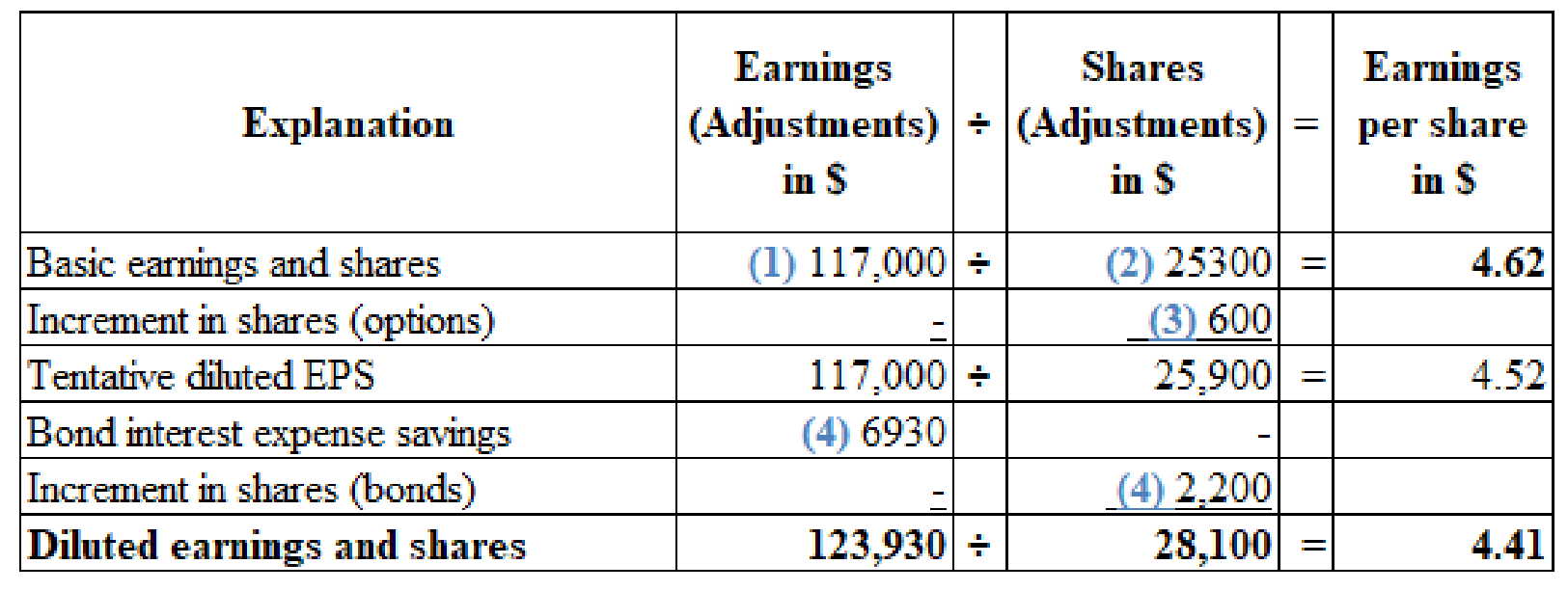
(Figure 1)
Working notes:
(1) Calculate the numerator for the basic earnings per share:
(2) Calculate the number of shares used in computing the basic earnings per share:
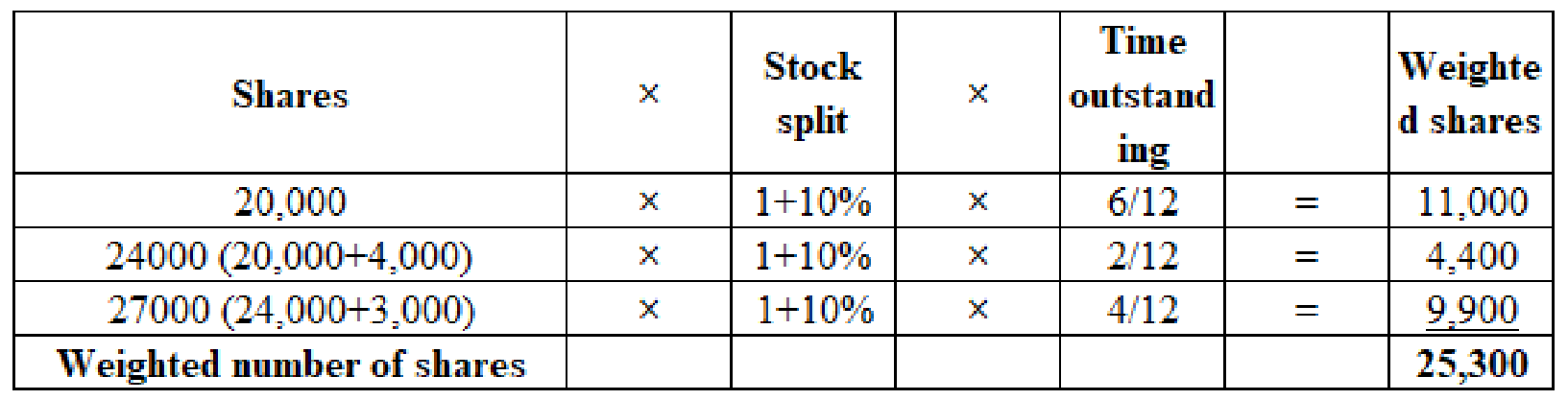
(Figure 2)
(3) Calculate the increase in the share options:
(4) Calculate the impact of 8% preferred on diluted earnings per share and ranking:
(5) Calculate the impact of 9.6% bonds on diluted earnings per share and ranking:
Note:
- The Company has occurred loss form the discontinuing operations, the impact of the convertible security is compared with earnings per share that is related to income from continuing operations.
- The percentage of stock dividend that is required to identify the assumed shared outstanding is ascertained using below formula :
3.
Identify whether basic or diluted earnings per share will be reported by the Company R on its 2016 income statement.
3.
Explanation of Solution
The Company R must report an amount of (6) $4.23 as basic earnings per share and (7) $4.05 as diluted earnings per share in its 2016 income statement.
Working notes:
(6) Calculate the basic earnings per share after deducting loss from discontinuing operations:
(7) Calculate the basic earnings per share after deducting loss from discontinuing operations:
Notes to financial statement:
Note 1: Basic earnings per share of the company are based on average common shares outstanding; 7% and 8% preferred dividends are deducted from net income to ascertain the earnings available to common shareholders. Diluted earnings per share are obtained from 600 shares of stock options and 2,200 shares of bonds that are convertible. Diluted earnings available to common shareholders are assumed to have no interest expense of $6,930 on the converted bonds.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting and Analysis
- What are fixed assets projected to be given this information for this accounting question?arrow_forwardSolve this accounting problemarrow_forwardA machine costing $77,500 with a 5-year life and $4,700 residual value was purchased January 2. Compute depreciation for each of the 5 years, using the double-declining-balance method. Year1 Y2 Y3 Y4 Y5arrow_forward
- Solare Company acquired mineral rights for $536,800,000. The diamond deposit is estimated at 48,800,000 tons. During the current year, 3,390,000 tons were mined and sold. Required: 1.Determine the depletion rate. 2. Determine the amount of depletion expense for the current year. 3.Journalize the adjusting entry to recognize the depletion expense. Refer to the Chart of Accounts for exact wording of account titles. _____________ Debit / Credit _____________ Debit / Crditarrow_forwardExercise 1-24 (Algo) Linking the statement of owner's equity and balance sheet LO P2 Mahomes Company reported the following data at the end of its first year of operations on December 31. Cash Accounts receivable Equipment Land Accounts payable Owner investments Mahomes, Withdrawals Net income $ 15,500 16,500 18,500 62,500 12,500 62,500 31,500 69,500 (a) Prepare its year-end statement of owner's equity. Hint. Mahomes, Capital on January 1 was $0. (b) Prepare its year-end balance sheet, using owner's capital calculated in part a. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required A Required B Prepare its year-end statement of owner's equity. Hint: Mahomes, Capital on January 1 was $0. Cash MAHOMES COMPANY Statement of Owner's Equity For Year Ended December 31arrow_forwardht = ences X On December 1, Jasmin Ernst organized Ernst Consulting. On December 3, the owner contributed $84,920 in assets to launch the business. On December 31, the company's records show the following items and amounts. Cash withdrawals by owner Consulting revenue Salaries expense Cash $ 8,450 Accounts receivable 16,950 Office supplies 4,080 Rent expense Land 46,020 Office equipment 18,860 Telephone expense Accounts payable 9,280 Owner investments 84,920 Miscellaneous expenses $ 2,930 16,950 4,420 7,900 860 680 Exercise 1-18 (Algo) Preparing an income statement LO P2 Using the above information prepare a December income statement for the business. ERNST CONSULTING Income Statement Revenues Rent expense Salaries expense Telephone expense Total revenues $ 4,420 7,900 860 $ SA Assets Cash 8,450 Accounts receivable 16,950 Office supplies 4,080 Land 46,020 Office equipment 18,860 navable 9,280 13,180 5 11 of 14 Next >arrow_forward
- Equipment was acquired at the beginning of the year at a cost of $77,220. The equipment was depreciated using the straight-line method based upon an estimated useful life of 6 years and an estimated residual value of $7,560. P1 What was the depreciation expense for the first year? _______ P2 Assuming the equipment was sold at the end of the second year for $58,320, determine the gain or loss on sale of the equipment. $_______________ P3 Journalize the entry to record the sale. Refer to the Chart of Accounts for exact wording of account titles. 1. ____ Debit / Credit 2.____ Debit / Credit 3.____ Debit / Credit 4.____ Debit / Creditarrow_forwardUse the following information for the Exercises below. (Algo) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] On December 1, Jasmin Ernst organized Ernst Consulting. On December 3, the owner contributed $84,920 in assets to launch the business. On December 31, the company's records show the following items and amounts. Cash Accounts receivable Office supplies Land Office equipment Accounts payable Owner investments $ 8,450 Cash withdrawals by owner 16,950 4,080 Rent expense Consulting revenue Salaries expense 18,860 Telephone expense Miscellaneous expenses 46,020 9,280 84,920 $ 2,930 16,950 4,420 7,900 860 680 Check my work Exercise 1-21 (Algo) Preparing a statement of cash flows LO P2 Also assume the following: a. The owner's initial investment consists of $38,900 cash and $46,020 in land. b. The company's $18,860 equipment purchase is paid in cash. c. Cash paid to employees is $2,700. The accounts payable balance of $9,280 consists of the $4,080 office supplies…arrow_forwardht = ences X On December 1, Jasmin Ernst organized Ernst Consulting. On December 3, the owner contributed $84,920 in assets to launch the business. On December 31, the company's records show the following items and amounts. Cash withdrawals by owner Consulting revenue Salaries expense Cash $ 8,450 Accounts receivable 16,950 Office supplies 4,080 Rent expense Land 46,020 Office equipment 18,860 Telephone expense Accounts payable 9,280 Owner investments 84,920 Miscellaneous expenses $ 2,930 16,950 4,420 7,900 860 680 Exercise 1-18 (Algo) Preparing an income statement LO P2 Using the above information prepare a December income statement for the business. ERNST CONSULTING Income Statement Revenues Rent expense Salaries expense Telephone expense Total revenues $ 4,420 7,900 860 $ SA Assets Cash 8,450 Accounts receivable 16,950 Office supplies 4,080 Land 46,020 Office equipment 18,860 navable 9,280 13,180 5 11 of 14 Next >arrow_forward
- Assets Current Assets Cash Credit card receivables Accounts receivable Marketable securities Food Inventories Prepaid expenses Total Current Assets Golden Bay Balance Sheet as at December 31 Year 2018 Year 2019 $ 18,500 9,807 $ 29,400 11,208 5,983 6,882 15,400 2,000 12,880 14,700 10 800 14 900 73370 79 090 Property Plant & Equipment Land Building Equipment Furnishings $ 60,500 828,400 114,900 75,730 (330,100) 16 600 766 030 839 400 $ 60,500 884,400 157,900 81,110 (422,000) 18 300 7 80 210 859 300 Net: Accumulated depreciation China, glass, silver, & linen Total Assets Liabilities & Stockholders' Equity Current Liabilities Accounts payable Accrued expenses payable Taxes payable Current mortgage payable Total Current assets $ 19,200 4,200 12,400 26 900 62 700 $16,500 5,000 20,900 26 000 68 400 Long-term liabilities Mortgage payable Total Liabilities $ $512 800 $486 400 575 500 $555 200 Stockholders' Equity Common stock ($5 par. 40,000 shares issued & OS) $200,000 Retained earnings…arrow_forwardMat lives in Barbados and is desirous of starting his own business from inheritances that his parents left him. He approached you for advice on the best type of business to register. Mr. Mat said he would love to gain benefits from any tax relief that is available that the government has to offer. Give advice to Mr. Mat whether it would be more beneficial to start a Company or an Individual Trading Business. outline for Mr. Mat why setting up either a company, or a trading as business is more advantageous over the other. cover matters like: Tax rates, Available tax reliefs and or tax credits Ease of operations of a company, as well as ease of operations of an individual trading business.arrow_forwardGeneral accountingarrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning



