
Concept explainers
The flow
where
(a) Given the parameters n
(b) Repeat part (a), but include the cost of excavation. To do this minimize the following cost function,
where
(c) Discuss the implications of your results.
(a)
To calculate: The values of that will minimize the wetted perimeter P if the Manning equation of flow Q
can be written as
Answer to Problem 19P
Solution:
The values of
that will minimize the wetted perimeter P is
respectively.
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The Manning equation of flow Q
can be written as
where n is Manning roughness coefficient,
is cross-sectional are of channel
is given by
where P is wetted perimeter and it is defined by
where H is depth
and the parameters value are given as
Calculation:
Consider the equation,
The constrained can be written as,
This problem can be solved out by Linear programming formulation.
To minimize the wetted perimeter P function with the given constraint, the excel solver can be used.
The excel solver steps are,
Step 1. Initiate quantity
and then write the parameter as shown below,
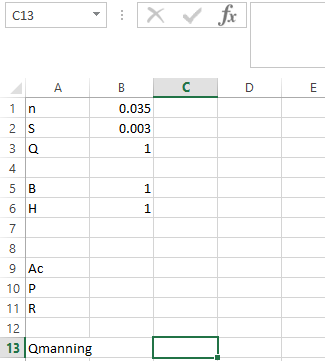
Step 2. Apply the formula in
as shown below,
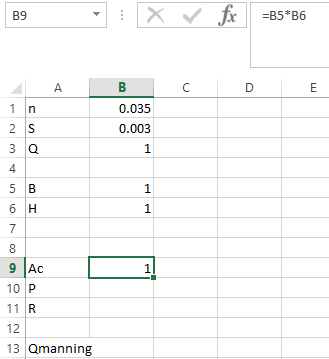
Step 3. Apply the formula in P as shown below,
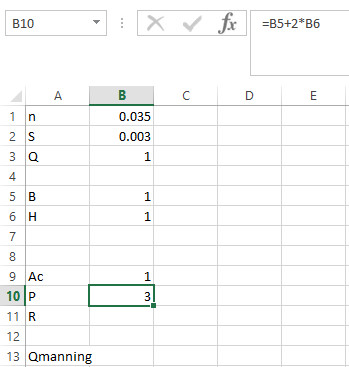
Step 4. Apply the formula in R as shown below,
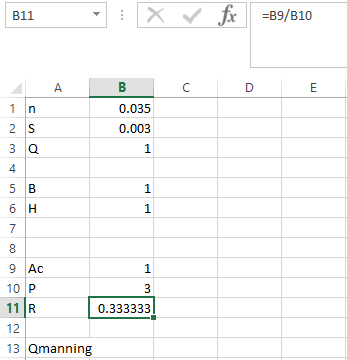
Step 5. Apply the formula in Qmanning as shown below,
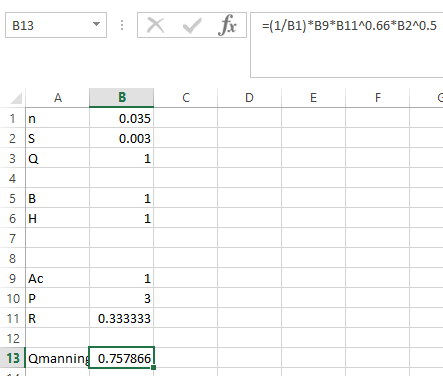
Step 6. Go to DATA and then click on Solver. This dialog box will appear.
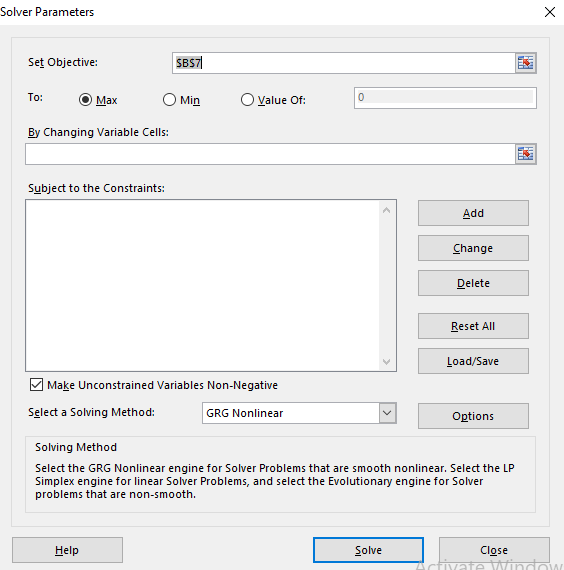
Step 7. Select the set objective, min, changing variable and then add,
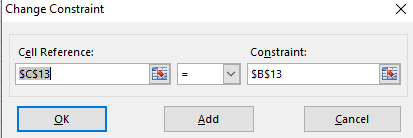
Step 8. Click OK then this dialog box appears.
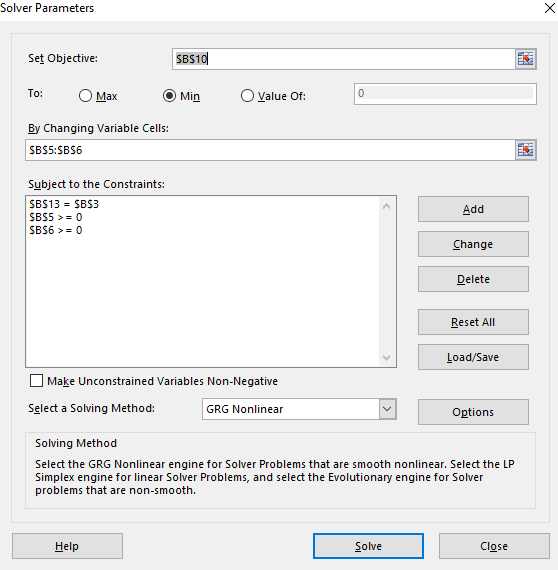
Step 9. Click on Solve and then OK.
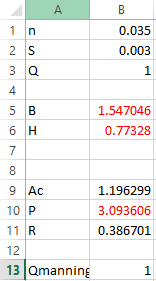
Hence, the values of
that will minimize the wetted perimeter P is
respectively.
(b)
To calculate: The values of
that will minimize the excavation cost function
is
and cost factor for lining
if the Manning equation of flow Q
can be written as
Answer to Problem 19P
Solution:
The values of
that will minimize the cost function P is
respectively.
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The Manning equation of flow Q
can be written as
where n is Manning roughness coefficient,
is cross-sectional are of channel
is given by
where P is wetted perimeter and it is defined by
where H is depth
and the parameters value are given as
Calculation:
Consider the function,
The constrained can be written as,
This problem can be solved out by Linear programming formulation.
To minimize the cost function with the given constraint, the excel solver can be used.
The excel solver steps are,
Step 1. Initiate quantity
and then write the parameter as shown below,

Step 2. Apply the formula in
as shown below,

Step 3. Apply the formula in P as shown below,

Step 4. Apply the formula in R as shown below,

Step 5. Apply the formula in Qmanning as shown below,

Step 6. Apply the formula in Cost as shown below,
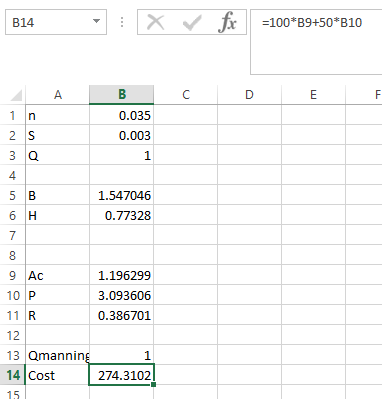
Step 7. Go to DATA and then click on Solver. This dialog box will appear.

Step 8. Select the set objective, min, changing variable and then add,

Step 9. Click OK then this dialog box appears.

Step 10. Click on Solve and then OK.
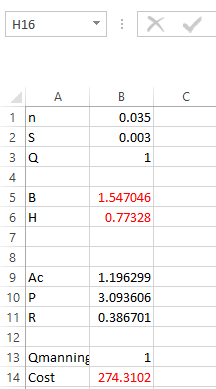
Hence, the values of
that will minimize the cost function is
respectively.
(c)
The implication of the result obtained in part (a) and part (b).
Answer to Problem 19P
Solution:
This can be interpreted that both the excavation and limiting cost can be minimized simultaneously by considering the bottom width B that is twice the length of each vertical side H.
Explanation of Solution
To interpret the result, first consider the constraint equation,
And,
On further simplification,
As
are dependent on B and H, thus both have minimized.
Thus, the excavation cost function
is minimized and as excavation cost C is directly proportional to cross-sectional area.
Hence, both the excavation and limiting cost can be minimized simultaneously by considering the bottom width B that is twice the length of each vertical side H as obtained in part (a) and (b) as
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
EBK NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ENGINEERS
- 26.1. Locate and determine the order of zeros of the following functions: (a). e2z – e*, (b). z2sinhz, (c). z*cos2z, (d). z3 cosz2.arrow_forwardQ/ show that: The function feal = Se²²²+d+ is analyticarrow_forwardComplex Analysis 2 First exam Q1: Evaluate f the Figure. 23+3 z(z-i)² 2024-2025 dz, where C is the figure-eight contour shown in C₂arrow_forward
- Q/ Find the Laurent series of (2-3) cos around z = 1 2-1arrow_forward31.5. Let be the circle |+1| = 2 traversed twice in the clockwise direction. Evaluate dz (22 + 2)²arrow_forwardUsing FDF, BDF, and CDF, find the first derivative; 1. The distance x of a runner from a fixed point is measured (in meters) at an interval of half a second. The data obtained is: t 0 x 0 0.5 3.65 1.0 1.5 2.0 6.80 9.90 12.15 Use CDF to approximate the runner's velocity at times t = 0.5s and t = 1.5s 2. Using FDF, BDF, and CDF, find the first derivative of f(x)=x Inx for an input of 2 assuming a step size of 1. Calculate using Analytical Solution and Absolute Relative Error: = True Value - Approximate Value| x100 True Value 3. Given the data below where f(x) sin (3x), estimate f(1.5) using Langrage Interpolation. x 1 1.3 1.6 1.9 2.2 f(x) 0.14 -0.69 -0.99 -0.55 0.31 4. The vertical distance covered by a rocket from t=8 to t=30 seconds is given by: 30 x = Loo (2000ln 140000 140000 - 2100 9.8t) dt Using the Trapezoidal Rule, n=2, find the distance covered. 5. Use Simpson's 1/3 and 3/8 Rule to approximate for sin x dx. Compare the results for n=4 and n=8arrow_forward
- 1. A Blue Whale's resting heart rate has period that happens to be approximately equal to 2π. A typical ECG of a whale's heartbeat over one period may be approximated by the function, f(x) = 0.005x4 2 0.005x³-0.364x² + 1.27x on the interval [0, 27]. Find an nth-order Fourier approximation to the Blue Whale's heartbeat, where n ≥ 3 is different from that used in any other posts on this topic, to generate a periodic function that can be used to model its heartbeat, and graph your result. Be sure to include your chosen value of n in your Subject Heading.arrow_forward7. The demand for a product, in dollars, is p = D(x) = 1000 -0.5 -0.0002x² 1 Find the consumer surplus when the sales level is 200. [Hints: Let pm be the market price when xm units of product are sold. Then the consumer surplus can be calculated by foam (D(x) — pm) dx]arrow_forward4. Find the general solution and the definite solution for the following differential equations: (a) +10y=15, y(0) = 0; (b) 2 + 4y = 6, y(0) =arrow_forward
- 5. Find the solution to each of the following by using an appropriate formula developed in the lecture slides: (a) + 3y = 2, y(0) = 4; (b) dy - 7y = 7, y(0) = 7; (c) 3d+6y= 5, y(0) = 0arrow_forward1. Evaluate the following improper integrals: (a) fe-rt dt; (b) fert dt; (c) fi da dxarrow_forward8. Given the rate of net investment I(t) = 9t¹/2, find the level of capital formation in (i) 16 years and (ii) between the 4th and the 8th years.arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage

 Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell  College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning



