
To sketch:
A titration curve for the titration of
a.
b.
c.
d.
Answer to Problem 16.46QA
Solution:
a)
b)
c)
d)
Explanation of Solution
1) Concept:
Oxalic acid is a weak diprotic acid, i.e., there are two protons that can dissociate from one molecule of oxalic acid in aqueous solution. The dissociation of protons occurs stepwise.
The first equivalence point occurs where the first dissociated proton is completely neutralized when titrated with a strong base
The second equivalence point occurs where both dissociated protons fully neutralized, and the equation is
Equation for complete titration is
At equivalence point, the equal moles of weak acid and strong base react and undergo neutralization. The second
2) Formula:
i)
ii)
iii)
iv)
v)
3) Given:
i) Molarity of oxalic acid,
ii) Volume of oxalic acid,
iii) Molarity of
iv)
v)
vi) pKa1 = 1.23 (Appendix 5 Table A5.1)
vii) pKa2 = 4.19 (Appendix 5 Table A5.1)
4) Calculation:
Converting volume in
Calculating moles of oxalic acid
These are the initial moles of oxalic acid present before any
Now, calculating the
a)
Converting volume in ml to L,
Calculating the moles of
Set up the RICE table that is used to calculate the moles of acid reacted and moles of conjugate base formed.
| Reaction | + | + | |||||
| Initial | 0 | ||||||
| Change | |||||||
| Final | 0 | ||||||
Calculating the concentration of
b)
Converting volume in ml to L,
Calculating the moles of
Setting up the RICE table to calculate the moles of acid reacted and moles of conjugate base formed,
| Reaction | + | + | |||||
| Initial | 0 | ||||||
| Change | |||||||
| Final | 0 | ||||||
Moles of the weak acid and conjugate base are equal.Thisis the half equivalence point to the first equivalence point, and the pH at half equivalence point is
c)
Converting volume in ml to L,
Calculating the moles of
Setting up the RICE that is used to calculate the moles of acid reacted and moles of conjugate base formed,
| Reaction | + | + | |||||
| Initial | 0 | ||||||
| Change | |||||||
| Final | 0 | ||||||
Calculating the concentration of
d)
Converting volume in ml to L,
Calculating the moles of
Set up the RICE table to calculate the moles of acid reacted and moles of conjugate base formed.
| Reaction | + | + | |||||
| Initial | 0 | ||||||
| Change | |||||||
| Final | 0 | ||||||
This is the first equivalence point since no moles of weak acid or strong base are left.
There is not much difference in the
At the equivalence point, the major species present is
Total volume of solution
Molarity of
| Initial (M) | |||
| Change (M) | |||
| Equilibrium (M) | |||
Writing the
A titration curve for the titration of
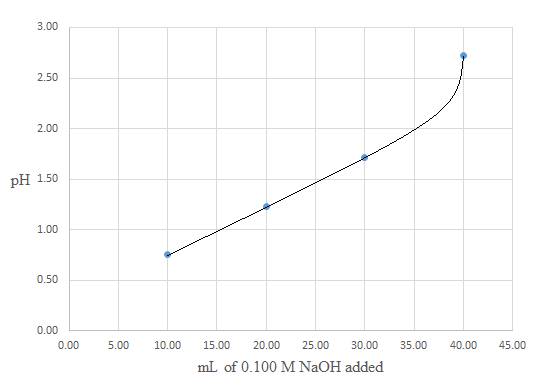
Conclusion:
Using the RICE table, we can determinethe
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Chemistry: An Atoms-Focused Approach (Second Edition)
- 2-(3-Aminopropyl)cyclohexan-1-one is reacted with H₂SO₄. Draw the structures of the products.arrow_forwardPlease help me solve number 2arrow_forwardChoose the best reagents to complete the following reaction. 오 Na2Cr2O7 H2SO4, H2O Problem 22 of 35 A Na2Cr2O7 H2SO4, H2O H2/Pt B pressure OH 1. NaBH4 C 2. H3O+ D DMP (Dess-Martin Periodinane) CH2Cl2 CrO3 Done Dramabana_Minor Submitarrow_forward
- Indicate the products of the reaction of Cycloheptanone with pyrrolidine (cat. H+). Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products of the reaction of 2-(3-aminopropyl)cyclohexan-1-one with H2SO4. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products of the reaction of 2-cyclopentyl-2-methyl-1,3-dioxolane with H3O+. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Question 4 For the molecule shown below, (7 marks): A) Sketch the Newman projection for the view looking along the bond from the perspective of the arrow. B) Then, draw the Newman projection for each 60° rotation along the bond until it returns to the starting point. C) Clearly indicate which Newman projection is the one we see in the structure shown below, and clearly indicate which Newman projection is the highest in energy and which is the lowest in energy. H H Me 'H Me Mearrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts and the amine side product. 'N' 1. NaOH, heat 2. Neutralizing work-up Select to Drawarrow_forwardSubmit Problem 3 of 10 Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts and the amine side product. O 'N' NH 1. NaOH, heat 2. Neutralizing work-up Select to Drawarrow_forward
- b) Certain cyclic compounds are known to be conformationally similar to carbohydrates, although they are not themselves carbohydrates. One example is Compound C shown below, which could be imagined as adopting four possible conformations. In reality, however, only one of these is particularly stable. Circle the conformation you expect to be the most stable, and provide an explanation to justify your choice. For your explanation to be both convincing and correct, it must contain not only words, but also "cartoon" orbital drawings contrasting the four structures. Compound C Possible conformations (circle one): Детarrow_forwardLab Data The distance entered is out of the expected range. Check your calculations and conversion factors. Verify your distance. Will the gas cloud be closer to the cotton ball with HCI or NH3? Did you report your data to the correct number of significant figures? - X Experimental Set-up HCI-NH3 NH3-HCI Longer Tube Time elapsed (min) 5 (exact) 5 (exact) Distance between cotton balls (cm) 24.30 24.40 Distance to cloud (cm) 9.70 14.16 Distance traveled by HCI (cm) 9.70 9.80 Distance traveled by NH3 (cm) 14.60 14.50 Diffusion rate of HCI (cm/hr) 116 118 Diffusion rate of NH3 (cm/hr) 175.2 175.2 How to measure distance and calculate ratearrow_forwardFor the titration of a divalent metal ion (M2+) with EDTA, the stoichiometry of the reaction is typically: 1:1 (one mole of EDTA per mole of metal ion) 2:1 (two moles of EDTA per mole of metal ion) 1:2 (one mole of EDTA per two moles of metal ion) None of the abovearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





