
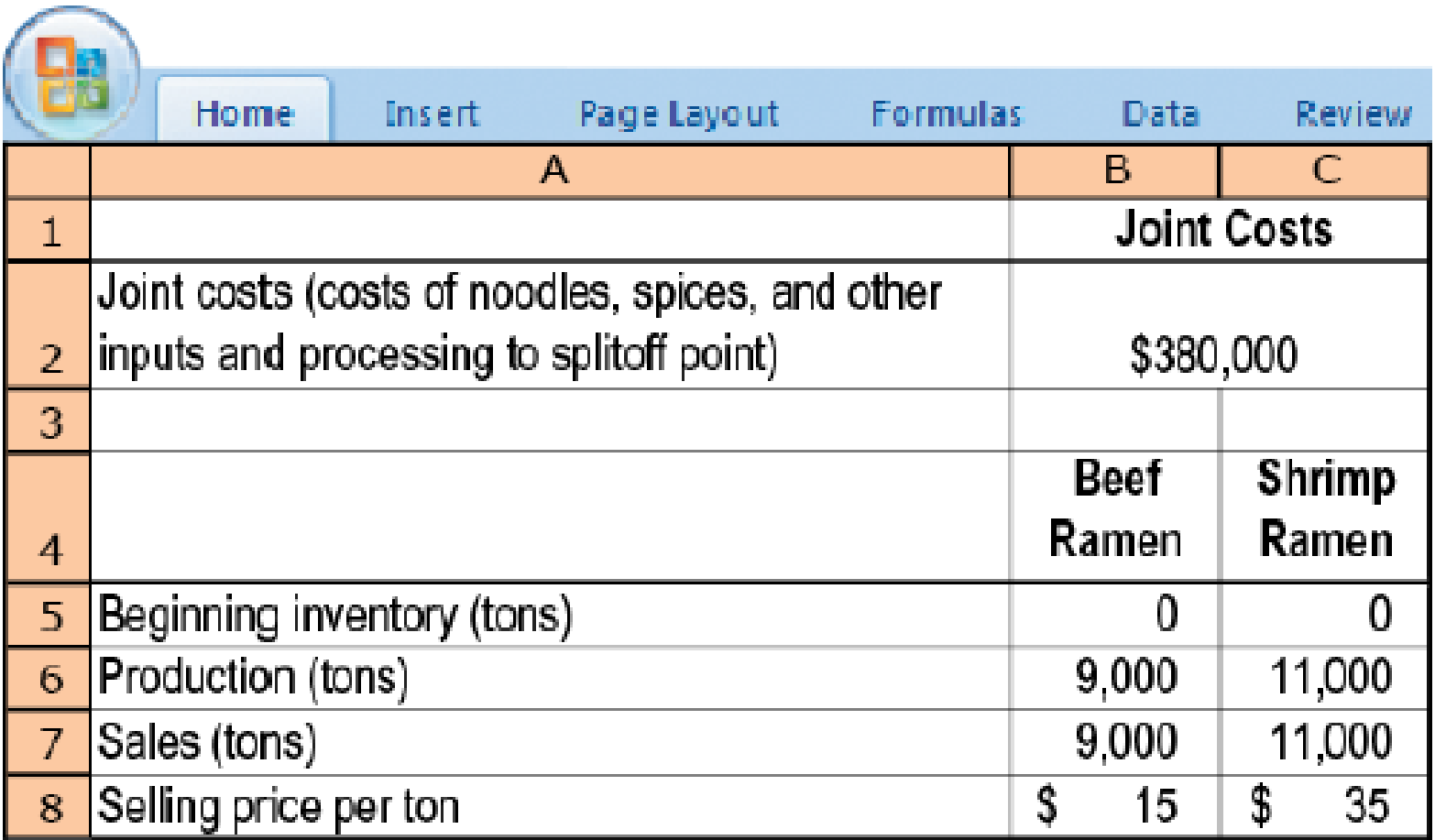
Joint-cost allocation, sales value, physical measure, NRV methods. Tasty Foods produces two types of microwavable products: beef-flavored ramen and shrimp-flavored ramen. The two products share common inputs such as noodle and spices. The production of ramen results in a waste product referred to as stock, which Tasty dumps at negligible costs in a local drainage area. In June 2017, the following data were reported for the production and sales of beef-flavored and shrimp-flavored ramen:
Due to the popularity of its microwavable products, Tasty decides to add a new line of products that targets dieters. These new products are produced by adding a special ingredient to dilute the original ramen and are to be sold under the names Special B and Special S, respectively. Following are the monthly data for all the products:
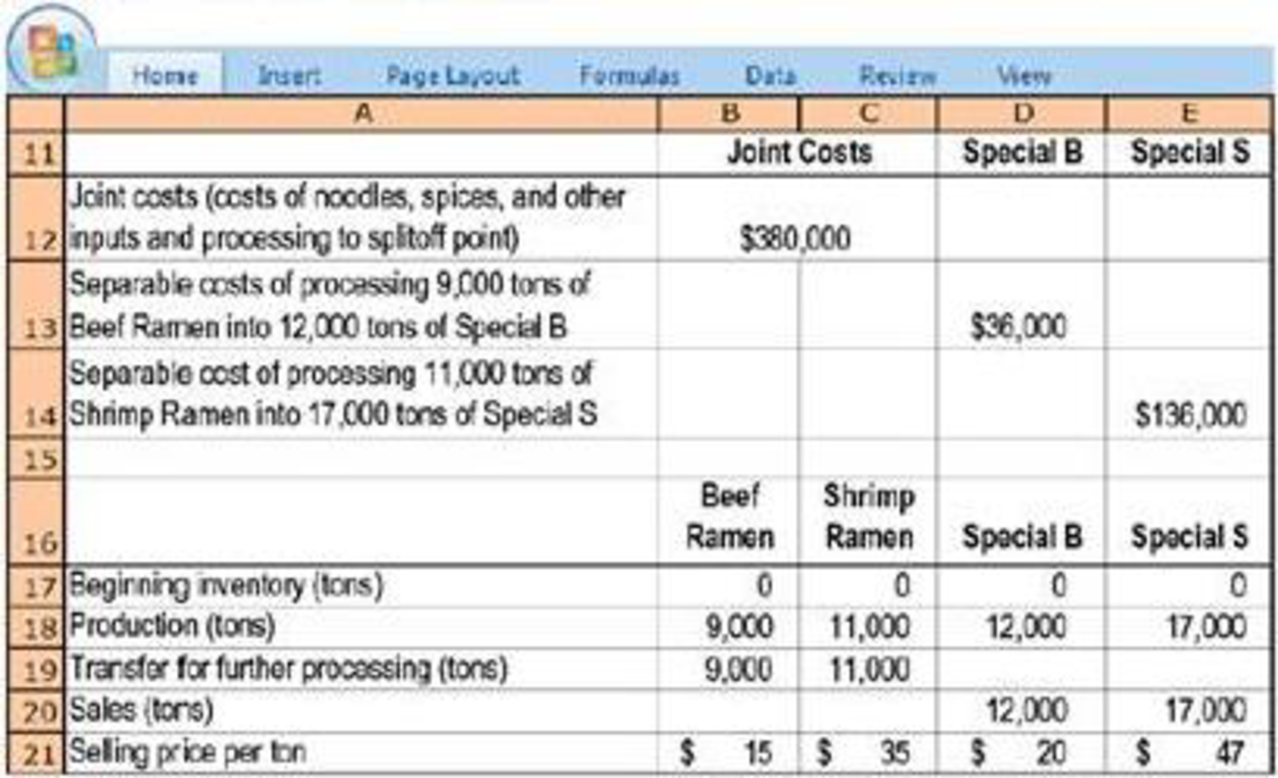
- 1. Calculate Tasty’s gross-margin percentage for Special B and Special S when joint costs are allocated using the following:
Required
- a. Sales value at splitoff method
- b. Physical-measure method
- c. Net realizable value method
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 16 Solutions
EBK HORNGREN'S COST ACCOUNTING
- Need answerarrow_forwardDelta Corporation has revenues of $400,000 and deductible expenses of $390,000. It received a $50,000 dividend from Luna Enterprises, in which it holds a 15% stake. What is Delta Corporation's taxable income?arrow_forwardPlease provide correct answer this financial accounting questionarrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub  Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,



