
Concept explainers
Develop the observation equations for the given baseline
Given that
Baseline vector are given as
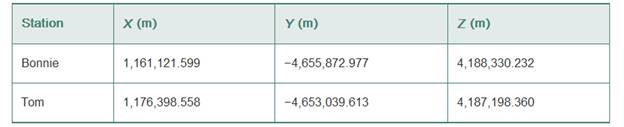
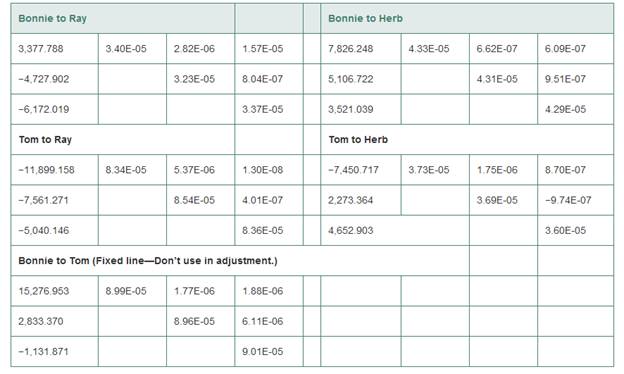
Explanation:
Writing observation equation for X coordinate for jim to troy:
WHERE
XB= X coordinate of the station bonnie =
∆XB-R= X component in baseline vector =
∆1= residual
Writing observation equation for Y coordinate for Bonnie to Ray:
WHERE
YB= Y coordinate of the station BONNIE =
∆2= residual
Writing observation equation for Y coordinate for Bonnie to Ray:
WHERE
ZB= Z coordinate of the station bonnie =
∆ZB-R= Z component in baseline vector =
∆3= residual
Writing observation equation for X coordinate for tom to herb:
WHERE
XT= X coordinate of the station Tom =
∆XT-H= X component in baseline vector =
∆4= residual
Writing observation equation for y coordinate for tom to herb:
WHERE
YT= Y coordinate of the station tom = -4,653,039.613m
∆YT-H= Y component in baseline vector = 2,273.364m
∆5= residual
Writing observation equation for Z coordinate for tom to herb
WHERE
ZT= Z coordinate of the station tom = 4,187,198.360m
∆ZT-H= Z component in baseline vector = 4652.903m
∆6= residual
Conclusion:
Hence, the observation equations for baseline components are:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
Elementary Surveying, Global Edition
- (40 pts Q: By using the PERT technique to calculate the duration of activities, as shown in the table below, Draw an activity network for the following project by using AOA method and find: 1. The project's total duration and date of completion and CP (assume the project start date 1st of May 2024). 2. The overall variance of the project? 3. The probability of completing the project in 50 days? 4. The probability of completing the project in 5th of June 2024? 5. With a probability of 90%, what is the expected duration and date for completing the project? Activity Preceding activity Optimistic duration (day) A Most likely duration (day) Pessimistic duration (day) 6 12 18 B 5 7 C 15 8 10 D 12 A 7 10 19 E C 12 15 F 18 A 7 8 G 15 A 5 9 25 H B.D.E 15 17 25 I C 14 19 30 J F 6 8 10arrow_forward1. For the system shown below, calculate the power supplied to the pump if its efficiency is 82%. Methyl alcohol at 25°C is flowing at the rate of 50m³/hour. The suction line is a standard DN100 schedule 40 steel pipe, 15m long. The total length of DN50 schedule 40 steel pipe in the discharge line is 180m. Assume that the entrance from reservoir 1 is through a square-edged inlet and that the elbows are standard. The valve is a fully open globe valve. 12m Discharge line DN 50 schedule 40 steel Pump Suction line Fully open globe valve DN 100 schedule 40 steel Flow Standard elbows (2)arrow_forwardDetermine rotations at all the nodes of the beam and reactions at the supports using stiffness method. Assume support 1 and 3 are roller and support 2 is pinned, L1=1.25m, L2=3.75m and w=60kN/m. Please show all working and FBD's where relevant.arrow_forward
- Draw the BMD of the beam on the compression side showing the salient values. What are the maximum bending moments of the beam? Draw the deflected shape of the beam. Assume support 1 and 3 are roller and support 2 is pinned, L1=1.25m, L2=3.75m and w=60kN/m.arrow_forwardSize a flash and floc tank: Provide a sketch with dimensions and calculations Provide for vertical mixers Size the mixer and motor Flow Rate 33 MGD Peaking Factor 1.5 Use VDH Regs (Online) Low Temp 40 degrees High Temp = 70 degrees Redundant Tanksarrow_forwardI do not know how to solve this questionarrow_forward
- I don't know how to solve this questionarrow_forwardA national pricing service says the National price is $12.35 per unit. The adjusted price adjustment for Los Angeles is 1.15. The price adjustment for Tulsa is 0.94. What is the expected price difference between Tulsa and Los Angeles? c.$2.98 b.$2.59 d.$0.00 a.$0.21arrow_forwardPROBLEM: Design the transversely reinforced concrete deck slab shown in the cross-sectional detail below. 8" REINFORCED CONCRETE SLAB 1/4" PER FT. T 3-3% 8'-0" 8'-0" 4'-0" GIVEN: Bridge to carry two traffic lanes. Concrete strength =4.5 ksi. Grade 60 reinforcement f, = 60 ksi. Account for 25 psf future wearing surface. Assume stringers are W36 x 150. Deck has a 0.5 in integrated wearing surface.arrow_forward

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning





