
Concept explainers
The right leg of an athlete on a rowing machine can be modeled as a linkage as shown, where A represents the ankle (which is stationary), K the knee, and H the hip. At the instant when θ = 75°, the shank AK has an angular velocity of 1 rad/s and an angular acceleration of 1.5 rad/s2, both counterclockwise. Determine the velocity and acceleration of the hip H at this instant in time.
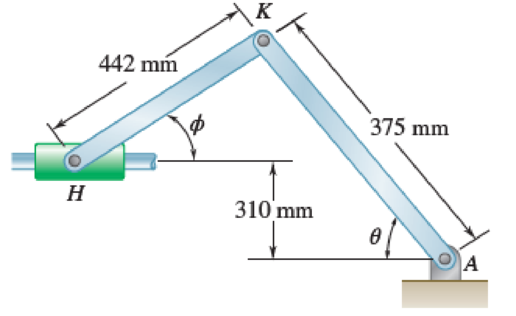
Fig. P15.123
Find the velocity and acceleration of the hip H at the instant.
Answer to Problem 15.123P
The velocity and acceleration of the hip H are
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The ankle, knee and the hip are denoted by A, K, and H.
The ankle A is stationary.
The value of the angle is
The angular velocity of the shank AK is
The angular acceleration of the shank AK is
Calculation:
Show the modelled linkage as shown in Figure 1.
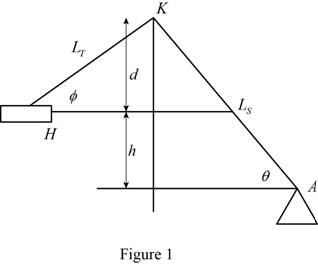
Refer to Figure 1.
Consider the distance KH and KA are denoted by
Show the relation between the distances KH and KA as follows:
Modify Equation (1) using Equation (2).
Substitute
Show the relative velocity for AK as follows:
Show the relative velocity for KH as follows:
Consider the position of the point K with respect to A is denoted by
Consider the position of the point H with respect to K is denoted by
Substitute
Equate the j component of the Equation (4).
Substitute
Equate i component of the Equation (4).
Substitute
Thus, the velocity at H is
Consider AK.
Show the relation between the acceleration of A and K as follows:
Substitute
Consider HK.
Show the relation between the acceleration of H and K as follows:
Substitute
Equate j component of the Equation (7).
Substitute
Equate i component of the Equation (7).
Substitute
Thus, the acceleration at H is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYN.(LL)-W/ACCESS
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
- A tensile specimen made of hot-rolled AISI 1020 steel is loaded to point corresponding to a strain of 40%. 60 Su = 66 ksi Stress σ (ksi) S₁ = 39 ksi 40 Se = 36 ksi Hot-rolled 1020 steel 20 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 Strain € (%) 0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 Area ratio R 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 Area reduction A, What value of area ratio is applicable to this location? 0.6arrow_forwardA tensile specimen made of hot-rolled AISI 1020 steel is loaded to point corresponding to a strain of 43%. 60 Su = 66 ksi Stress σ (ksi) 20 Sy = 39 ksi Se = 36 ksi Hot-rolled 1020 steel F 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 Strain € (%) 0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 Area ratio R 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 Area reduction A, What value of area reduction is applicable to this location? 0.6arrow_forwardTable of Measurements and Results: Reading m/s Ji- a (wh Nu h Re Nu Error% (C) (°C) 2 1 Discussion: 1-Estimate the heat transfer and experimental value of the heat transfer coefficient hex with its unit and Nusselt number Nu expl 2- Find the percentage error for the value of the experimental Nusselt number. 3-Draw the graph showing a relationship between the temperatures difference (T-T) and theoretical and experimental value of Nusselt number. 4-The forced convection heat transfer coefficient of a plate depends on which of the following: a-gravity. b-velocity of fluid. e-conductivity of fluid. d-conductivity of plate material. Experiment: Internal Forced convenction Heat trovate on now through t objectives. Study the convection heat transfer of air flow through stage Calculations. Q & (T-T) Vary Re Q. heup A (TT) (T. Te-T ASPL Nep Re 117 RITT 14 ' 14arrow_forward
- If AE = 1.6 m, ED = CD = 1.9 m and F = 3.1 kN, then find the magnitude of the force acting in EB. B 30° 30° C E D ED m DC m ♥F KNarrow_forwardAssume multiple single degree of freedom systems with natural periods T ∈ [0.05, 2.00] seconds with in- crement of period dT = 0.05 seconds. Assume three cases of damping ratio: Case (A) ξ = 0%; Case (B) ξ = 2%; Case (C) ξ = 5%. The systems are initially at rest. Thus, the initial conditions are u(t = 0) = 0 and ̇u(t = 0) = 0. The systems are subjected to the base acceleration that was provided in the ElCentro.txt file (i.e., first column). For the systems in Case (A), Case (B), and Case (C) and for each natural period compute the peak acceleration, peak velocity, and peak displacement responses to the given base excitation. Please, use the Newmark method for β = 1/4 (average acceleration) to compute the responses. Create three plots with three lines in each plot. The first plot will have the peak accelerations in y-axis and the natural period of the system in x-axis. The second plot will have the peak velocities in y-axis and the natural period of the system in x-axis. The third plot…arrow_forwardDetermine the resultant stress at points P and Q.arrow_forward
- For the notched specimen with h = 0.13 m and r =11 mm, calculate the nominal stress for F=5 kN. F h F 25 mm Please submit your answer in the units of MPa.arrow_forwardA tensile specimen made of hot-rolled AISI 1020 steel is loaded to point corresponding to a strain of 49%. 60 Su = 66 ksi Stress σ (ksi) Sy = 39 ksi 400B Se = 36 ksi Hot-rolled 1020 steel 20 F 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 Strain € (%) 0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 Area ratio R 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 Area reduction A, What value of Su is applicable to this location? 0.6arrow_forwardA tensile specimen made of hot-rolled AISI 1020 steel is loaded to point corresponding to a strain of 40%. 60 Su = 66 ksi Stress σ (ksi) 40 20 Sy= = 39 ksi Se = 36 ksi Hot-rolled 1020 steel F | G | H 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 0 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 Strain € (%) ☐ T 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 Area ratio R 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 Area reduction A, What value of Sy is applicable to this location? 0.6arrow_forward
- A vertical .2m by .2m square plate is exposed to saturated water vapor at atmospheric pressure. If the surface temperature is 80 degrees C and the flow is laminar, estimate the loal heat transfer coefficents at the middles and at the bottom of the plate.arrow_forwardA transformer that is 10 cm long, 6.2 cm wide, and 5 cm high is to be cooled by attaching a 10 cm by 6.2 cm wide polished aluminum heat sink(emissivity=.03) to its top surface. The heat sink has seven fins, which are 5 mm high, 2mm thick, and 10 cm long. A fan blows air at 25 degrees C parallel to the passages between the fins. The heat sink is to dissipate 12W of heat, and the base temp of the ehat sink is not to exceed 60 degrees C. Assuming the fins and the base plate to be nearly isothermal and the radiation heat transfer to be negligible, determine the minimum free-stream velocity the fan needs to supply to avoid overheating. Assume the flow is laminar over the entire finned surface of the transformer.arrow_forwardI need a mechanical engineering expert to solve this question,no Ai pleasearrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





