
Concept explainers
15.113 and 15.114 A 3-in.-radius drum is rigidly attached to a 5-in.- radius drum as shown. One of the drums rolls without sliding on the surface shown, and a cord is wound around the other drum. Knowing that at the instant shown end D of the cord has a velocity of 6 in./s and an acceleration of 20 in./s2, both directed to the right, determine the accelerations of points A, B, and C of the drums.
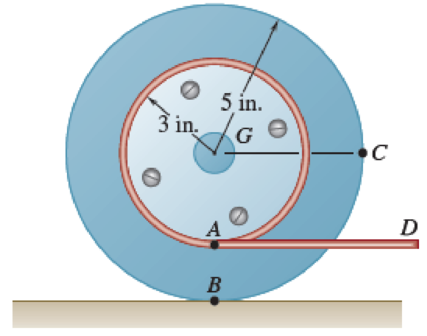
Fig. P15.113
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics, 11th Edition
Manufacturing Engineering & Technology
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, and Service (5th Edition)
Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (3rd Edition)
- A 3-in.-radius drum is rigidly attached to a 5-in.-radius drum as shown. One of the drums rolls without sliding on the surface shown, and a cord is wound around the other drum. Knowing that at the instant shown. point A has a velocity of 5.75 in./s and an acceleration of 19 in./s2, both directed to the right, determine the accelerations of points A, B, and C of the drums. a) The accelerations of point B is _ upward? b) The accelerations of point A is _ and _? (magnitude and direction) c) The accelerations of point C is _ and _? (magnitude and direction)arrow_forward15.115 and 15.116 A 60-mm-radius drum is rigidly attached to a 100-mm-radius drum as shown. One of the drums rolls without sliding on the surface shown, and a cord is wound around the other drum. Knowing that at the instant shown end D of the cord has a velocity of 160 mm/s and an acceleration of 600 mm/s², both directed to the left, determine the accel- erations of points A, B, and C of the drums. a D 100 mm G 60 mm 40 B Carrow_forwardonly HANDWRITTEN answer needed ( NOT TYPED)arrow_forward
- B10arrow_forwardProblem (8) The belt shown moves over two pulleys without slipping. At the instant shown the pulleys are rotating clockwise and the speed of point B on the belt is 4 m/s, increasing at the rate of 32 m/s?. Determine, at this instant, (a) the angular velocity and angular acceleration of each pulley, (b) the acceleration of point P on pulley C. B 160 mm fi00 mmarrow_forward15.113 The 360-mm-radius flywheel is rigidly attached to a 30-mm- radius shaft that can roll along parallel rails. Knowing that at the instant shown the center of the shaft has a velocity of 24 mm/s and an acceleration of 10 mm/s, both directed down to the left, determine the acceleration (a) of point A, (b) of point B. A 2₂x 360 mm- 20° Barrow_forward
- A carriage c is supported by a caster A and a cylinder B each of 60 mm diameter. Knowing that at an instant the carriage has an acceleration of 3 m/s^2 and a velocity of 2 m/s , both directed to the left , calculate the angular accelerations of the caster and of the cylinder then calculate the accelerations of the centers of the caster and of the cylinder?arrow_forward6) Bar BDE is attached to two links AB and CD. Knowing that at the instant shown link AB rotates with a constant angular velocity of 3 rad/s clockwise, determine the acceleration (a) of point D, (b) of point E. 19.1 cm 19.1 cm C -30.5 cm -22.9 cm- B ODarrow_forwardRequired information NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. For a 5-m steel beam AE, the acceleration of point A is 2.5 m/s² downward and the angular acceleration of the beam is 1.5 rad/s2 counterclockwise. Knowing that at the instant considered the angular velocity of the beam is zero, determine the acceleration of cable B and cable D. A -1.5 m- B Determine the acceleration of cable B The acceleration of cable Bis 2 m 1.375 5 m/s2. D -1.5 m- Earrow_forward
- 5.- Knowing that at the instant shown bar AB has an angular velocity of 4 rad/s and an angular acceleration of 2 rad/s?, both clockwise, determine the angular acceleration (a) of bar BD, (b) of bar DE by using the vector approach. 100 mm 175 mm - B A 200 mm 75 mm D Earrow_forwardProblem (1) A belt-driven pulley and attached disk are rotating with increasing angular velocity. If at a given instant, the speed of the belt is v = 1.5 m/s, and the total acceleration of point A is 100 m/s?, determine: (a) The angular acceleration a of the pulley and disk (b) The total acceleration of point B (c) The acceleration of point C on the belt. A 150 mm 200 mmarrow_forwardplease show presentation, drawing diagram, vector’s forces & position, etc.. and showing work steps. thank youarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





