
Statics and Mechanics of Materials Plus Mastering Engineering with Pearson eText - Access Card Package (5th Edition)
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780134301006
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 15.2, Problem 24P
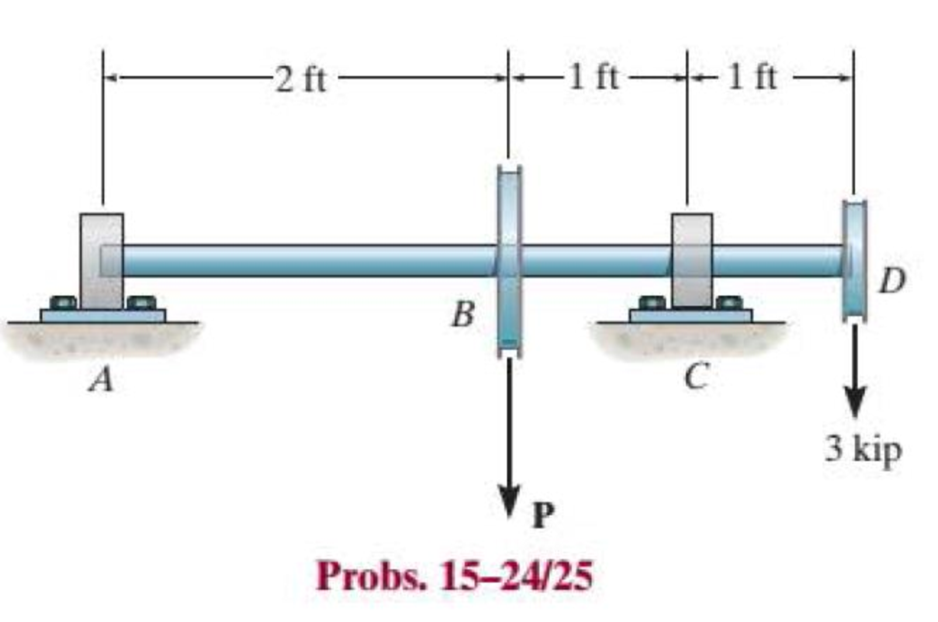
Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the shaft, and determine its required diameter to the nearest
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
I need drawing solution,draw each one by one no Ai
Qu. 17 Compute linear density values for [100] for silver (Ag). Express your answer in nm''.
. Round off the
answer to three significant figures.
Qu. 18 Compute linear density value for [111] direction for silver (Ag). Express your answer in nm'. Round off the answer to three significant figures.
Qu. 19 Compute planar density value for (100) plane for chromium (Cr). Express your answer in nm?.
Round off the answer to two significant figures.
Qu. 20 Compute planar density value for (110) plane for chromium (Cr). Express your answer in nm ≥ to four significant figures.
show all work please in material engineering
3-142
Chapter 15 Solutions
Statics and Mechanics of Materials Plus Mastering Engineering with Pearson eText - Access Card Package (5th Edition)
Ch. 15.2 - Determine the minimum dimension a to the nearest...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 2FPCh. 15.2 - Prob. 3FPCh. 15.2 - Determine the minimum dimension h to the nearest...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 5FPCh. 15.2 - Select the lightest W410-shaped section that can...Ch. 15.2 - The beam is made of timber that has an allowable...Ch. 15.2 - Determine the minimum width of the beam to the...Ch. 15.2 - Determine the minimum width of the beam to the...Ch. 15.2 - The brick wall exerts a uniform distributed load...
Ch. 15.2 - Select the lightest-weight wide-flange beam from...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 6PCh. 15.2 - Select the lightest-weight wide-flange beam with...Ch. 15.2 - Select the lightest-weight wide-flange beam from...Ch. 15.2 - Select the lightest W360 wide-flange beam from...Ch. 15.2 - Investigate if the W250 58 beam can safely...Ch. 15.2 - The beam is constructed from two boards. If each...Ch. 15.2 - The joists of a floor in a warehouse are to be...Ch. 15.2 - The timber beam has a width of 6 in. Determine its...Ch. 15.2 - The beam is constructed from four boards. If each...Ch. 15.2 - The beam is constructed from two boards. If each...Ch. 15.2 - If the cable is subjected to a maximum force of P...Ch. 15.2 - If the W360 45 wide-flange beam has an allowable...Ch. 15.2 - If P = 800 lb, determine the minimum dimension a...Ch. 15.2 - If a = 3 in. and the wood has an allowable normal...Ch. 15.2 - The beam is constructed from three plastic strips....Ch. 15.2 - If the allowable bending stress is allow = 6 MPa,...Ch. 15.2 - The beam is made of Douglas fir having an...Ch. 15.2 - Select the lightest-weight wide-flange beam from...Ch. 15.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the shaft,...Ch. 15.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the shaft,...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I need solutionsarrow_forward3-137arrow_forwardLarge wind turbines with a power capacity of 8 MW and blade span diameters of over 160 m areavailable for electric power generation. Consider a wind turbine with a blade span diameter of 120m installed at a site subjected to steady winds at 8.25 m/s. Taking the overall efficiency of thewind turbine to be 33 percent and the air density to be 1.25 kg/m3, determine the electric powergenerated by this wind turbine. Also, assuming steady winds of 8.25 m/s during a 24-h period,determine the amount of electric energy and the revenue generated per day for a unit price of$0.08/kWh for electricity.arrow_forward
- The basic barometer can be used to measure the height of a building. If the barometric readingsat the top and at the bottom of a building are 672 and 696 mmHg, respectively, determine theheight of the building. Take the densities of air and mercury to be 1.18 kg/m3 and 13,600 kg/m3,respectivelyarrow_forwardA 7.25-hp (shaft) pump is used to raise water to an elevation of 17 m. If the mechanical efficiencyof the pump is 84 percent, determine the maximum volume flow rate of water.arrow_forwardConsider a double-fluid manometer attached to an air pipe shown below. If the specific gravity ofone fluid is 13.8, determine the specific gravity of the other fluid for the indicated absolutepressure of air. Take the atmospheric pressure to be 95 kPaarrow_forward
- A race car enters the circular portion of a track that has a radius of 65 m. Disregard the 70 m in the picture. When the car enters the curve at point P, it is traveling with a speed of 120 km/h that is increasing at 5 m/s^2 . Three seconds later, determine the x and y components of velocity and acceleration of the car. I'm having trouble getting the correct y component of acceleration. all the other answers are correct. thank you!arrow_forwardFigure: 06_P041 Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, publishing a Prentice Hall 2. Determine the force that the jaws J of the metal cutters exert on the smooth cable C if 100-N forces are applied to the handles. The jaws are pinned at E and A, and D and B. There is also a pin at F. 400 mm 15° 20 mm A 15° 15 D B 30 mm² 80 mm 20 mm 400 mm Figure: 06_P090 Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, publishing as Prentice Hall 15° 100 N 100 N 15°arrow_forwardA telemetry system is used to quantify kinematic values of a ski jumper immediately before the jumper leaves the ramp. According to the system r=560 ft , r˙=−105 ft/s , r¨=−10 ft/s2 , θ=25° , θ˙=0.07 rad/s , θ¨=0.06 rad/s2 Determine the velocity of the skier immediately before leaving the jump. The velocity of the skier immediately before leaving the jump along with its direction is ? I have 112.08 ft/s but can't seem to get the direction correct. Determine the acceleration of the skier at this instant. At this instant, the acceleration of the skier along with its direction is ? acceleration is 22.8 ft/s^2 but need help with direction. Need help with velocity direction and acceleration direction please.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
BEARINGS BASICS and Bearing Life for Mechanical Design in 10 Minutes!; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aU4CVZo3wgk;License: Standard Youtube License