Tutorials In Introductory Physics: Homework
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780130662453
Author: Lillian C. McDermott, Peter S. Shaffer
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 15.1, Problem 2bTH
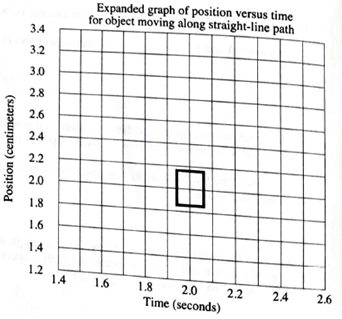
In the small box on the graph above is a portion of the graph that corresponds to the motion from
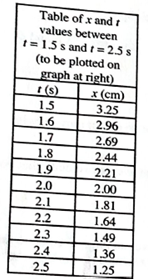
The position and time coordinates from points in this small interval are given in the following table. Plot these points on the graph below to obtain an expanded view of this small interval.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Need help on the following questions on biomechanics. (Please refer to images below)A gymnast weighing 68 kg attempts a handstand using only one arm. He plants his handat an angle resulting in the reaction force shown.A) Find the resultant force (acting on the Center of Mass)B) Find the resultant moment (acting on the Center of Mass)C) Draw the resultant force and moment about the center of mass on the figure below. Will the gymnast rotate, translate, or both? And in which direction?
Please help me on the following question (Please refer to image below)An Olympic lifter (m = 103kg) is holding a lift with a mass of 350 kg. The barexerts a purely vertical force that is equally distributed between both hands. Each arm has amass of 9 kg, are 0.8m long and form a 40° angle with the horizontal. The CoM for each armis 0.5 m from hand. Assuming the lifter is facing us in the diagram below, his right deltoidinserts 14cm from the shoulder at an angle of 13° counter-clockwise from the humerus.A) You are interested in calculating the force in the right deltoid. Draw a free body diagramof the right arm including the external forces, joint reaction forces, a coordinate system andstate your assumptions.B) Find the force exerted by the right deltoidC) Find the shoulder joint contact force. Report your answer using the magnitude and directionof the shoulder force vector.
I need help with part B. I cant seem to get the correct answer. Please walk me through what youre doing to get to the answer and what that could be
Chapter 15 Solutions
Tutorials In Introductory Physics: Homework
Ch. 15.1 - Describe the motion. During which periods of time,...Ch. 15.1 - Find the object’s instantaneous velocity at each...Ch. 15.1 - For each of the following intervals, find the...Ch. 15.1 - In which of the cased from part c, if any, is the...Ch. 15.1 - In the interval from t=0s to t=6s , does the...Ch. 15.1 - In the small box on the graph above is a portion...Ch. 15.1 - Next, we expand the section of the previous graph...Ch. 15.1 - All three graphs are representations of the same...Ch. 15.1 - Suppose that the object is speeding up. Which of...Ch. 15.1 - Suppose that the object is slowing down. Which of...
Ch. 15.1 - Describe how you could use these devices to...Ch. 15.1 - Describe how you could use these devices to...Ch. 15.2 - In each of the following exercises, a motion will...Ch. 15.2 - In each of the following exercises, a motion will...Ch. 15.2 - In each of the following exercises, a motion will...Ch. 15.2 - In each of the following exercises, a motion will...Ch. 15.2 - In each of the following exercises, a motion will...Ch. 15.2 - In each of the following exercises, a motion will...Ch. 15.2 - In each of the following exercises, a motion will...Ch. 15.2 - In each of the following exercises, a motion will...Ch. 15.2 - There are several answers for most of the...Ch. 15.2 - There are several answers for most of the...Ch. 15.2 - There are several answers for most of the...Ch. 15.3 - A ball rolls up, then down an incline. Sketch an...Ch. 15.3 - Sketch x versus t, v versus t, and a versus t...Ch. 15.3 - Sketch x versus t, v versus t, and a versus t...Ch. 15.3 - Sketch x versus t, v versus t, and a versus t...Ch. 15.3 - Describe the motion of an object: For which the...Ch. 15.3 - Describe the motion of an object: b. For which the...Ch. 15.3 - Describe the motion of an object: c. For which the...Ch. 15.3 - Describe the motion of an object: d. For which the...Ch. 15.3 - Two carts roll toward each other on a level table....Ch. 15.3 - Two carts roll toward each other on a level table....Ch. 15.3 - Two carts roll toward each other on a level table....Ch. 15.3 - In this problem, a Cart moves in various ways on a...Ch. 15.3 - In this problem, a Cart moves in various ways on a...Ch. 15.3 - In this problem, a Cart moves in various ways on a...Ch. 15.3 - Carts A and B move along a horizontal track. The...Ch. 15.3 - Carts A and B move along a horizontal track. The...Ch. 15.3 - Carts A and B move along a horizontal track. The...Ch. 15.3 - Carts A and B move along a horizontal track. The...Ch. 15.3 - Two cars, C and D, travel in the same direction on...Ch. 15.3 - Two cars, P and Q, travel in the same direction on...Ch. 15.3 - Two cars, P and Q, travel in the same direction on...Ch. 15.4 - Prob. 1aTHCh. 15.4 - Prob. 1bTHCh. 15.4 - Describe how you would determine the acceleration...Ch. 15.4 - Copy vG and vH (placed “tailtotail”) in the space...Ch. 15.4 - Generalize your results above and from tutorial to...Ch. 15.4 - For each instant, state whether the object is...Ch. 15.4 - The diagram at right illustrates how the...Ch. 15.4 - For each of the instants 14, compare your...Ch. 15.4 - Choose a point about 1/8th of the way around the...Ch. 15.4 - Prob. 3bTHCh. 15.4 - How would you characterize the direction of v as...Ch. 15.4 - Each of the following statements in incorrect....Ch. 15.4 - On the diagram at right, draw vectors that...Ch. 15.4 - On the diagram at right, draw vectors that...Ch. 15.4 - Draw arrows on the diagram at points AG to...Ch. 15.4 - Next to each of the labeled points, state whether...Ch. 15.4 - Draw arrows on the diagram below to show the...Ch. 15.4 - On the diagram at right, draw velocity vectors for...Ch. 15.4 - On the diagram at right, draw the acceleration...Ch. 15.4 - How does the magnitude of the acceleration at E...Ch. 15.5 - Reference frame of boat B: Complete the upper...Ch. 15.5 - Reference frame of boat A: Complete the diagram at...Ch. 15.5 - Is the speed of the kayak in the frame of boat A...Ch. 15.5 - Rank the following quantities in order of...Ch. 15.5 - A third riverboat, boat C, moves downstream so as...Ch. 15.5 - Prob. 2aTHCh. 15.5 - A car, a truck, and a traffic cone are on a...Ch. 15.5 - The relationship vcar,cone=vcar,truck+vtruck,cone...Ch. 15.5 - Car P moves to the west with constant speed v0...Ch. 15.5 - Car P moves to the west with constant speed v0...Ch. 15.5 - Car P moves to the west with constant speed v0...Ch. 15.5 - Car P moves to the west with constant speed v0...Ch. 15.5 - Car P moves to the west with constant speed v0...Ch. 15.5 - A bicycle coasts up a hill while a car drives up...Ch. 15.5 - A bicycle coasts up a hill while a car drives up...Ch. 15.5 - A bicycle coasts up a hill while a car drives up...Ch. 15.5 - A bicycle coasts up a hill while a car drives up...Ch. 15.5 - A bicycle coasts up a hill while a car drives up...Ch. 15.5 - A bicycle coasts up a hill while a car drives up...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Approximately how many feet is the Missouri River above sea level? Height above sea level: _________ feet
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Calculate the lattice energy of CaCl2 using a Born-Haber cycle and data from Appendices F and L and Table 7.5. ...
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Your bore cells, muscle cells, and skin cells look different because a. different kinds of genes are present in...
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
2. Define equilibrium population. Outline the conditions that must be met for a population to stay in genetic e...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
12. A 2.0 cm × 2.0 cm parallel-plate capacitor has a 2.0 mm spacing. The electric field strength inside the cap...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
53. This reaction was monitored as a function of time:
A plot of In[A] versus time yields a straight ...
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 6: Chlorine is widely used to purify municipal water supplies and to treat swimming pool waters. Suppose that the volume of a particular sample of Cl₂ gas is 8.70 L at 895 torr and 24°C. (a) How many grams of Cl₂ are in the sample? ⚫ Atomic mass of CI = 35.453 g/mol • Molar mass of Cl₂ = 2 x 35.453 = 70.906 g/mol Solution: Use the Ideal Gas Law: Step 1: Convert Given Values • Pressure: P = 895 torr → atm PV= = nRT 1 P = 895 × = 1.1789 atm 760 • Temperature: Convert to Kelvin: T24273.15 = 297.15 K • Gas constant: R = 0.0821 L atm/mol. K Volume: V = 8.70 L Step 2: Solve for n . PV n = RT n = (1.1789)(8.70) (0.0821)(297.15) 10.25 n = = 0.420 mol 24.405 Step 3: Calculate Mass of Cl₂ Final Answer: 29.78 g of Cl₂. mass nx M mass= (0.420)(70.906) mass= 29.78 garrow_forwardE1 R₁ w 0.50 20 Ω 12 R₁₂ ww ΒΩ R₂ 60 E3 C RA w 15 Ω E2 0.25 E4 0.75 Ω 0.5 Ωarrow_forwardSolve plzarrow_forward
- how would i express force in vector form I keep getting a single numberarrow_forwardplease help me solve this questions. show all calculations and a good graph too :)arrow_forwardWhat is the force (in N) on the 2.0 μC charge placed at the center of the square shown below? (Express your answer in vector form.) 5.0 με 4.0 με 2.0 με + 1.0 m 1.0 m -40 με 2.0 μCarrow_forward
- What is the force (in N) on the 5.4 µC charge shown below? (Express your answer in vector form.) −3.1 µC5.4 µC9.2 µC6.4 µCarrow_forwardAn ideal gas in a sealed container starts out at a pressure of 8900 N/m2 and a volume of 5.7 m3. If the gas expands to a volume of 6.3 m3 while the pressure is held constant (still at 8900 N/m2), how much work is done by the gas? Give your answer as the number of Joules.arrow_forwardThe outside temperature is 25 °C. A heat engine operates in the environment (Tc = 25 °C) at 50% efficiency. How hot does it need to get the high temperature up to in Celsius?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Speed Distance Time | Forces & Motion | Physics | FuseSchool; Author: FuseSchool - Global Education;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EGqpLug-sDk;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY