
Concept explainers
Sub part (a):
The monopsony market.
Sub part (a):
Explanation of Solution
The total labor cost can be calculated by using the following formula.
Substitute the respective value in the equation (1) to calculate the total labor cost at one unit of labor.
The total labor cost is $3.
The marginal resource cost can be calculated by using the following formula.
Substitute the respective values in the equation (2) to calculate the marginal resource cost at one unit of labor.
The marginal resource cost is $3.
Table -1 shows the value of the total labor cost and the marginal resources cost that are obtained by using the equation (1) and (2).
Table -1
| Units of labor | Wage rate | Total labor cost | Marginal resources cost |
| 0 | - | 0 | |
| 1 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 2 | 9 | 18 | 12 |
| 3 | 12 | 36 | 18 |
| 4 | 15 | 60 | 24 |
| 5 | 18 | 90 | 30 |
| 6 | 21 | 120 | 36 |
The total revenue can be calculated by using the following formula.
The
Substitute the respective value in the equation (3) to calculate the total revenue at one unit of labor.
The total revenue is $34.
The marginal product can be calculated by using the following formula.
Substitute the respective values in the equation (4) to calculate the marginal resource cost at one unit of labor.
The marginal product is $17.
The marginal revenue product can be calculated by using the following formula.
The
Substitute the respective values in the equation (5) to calculate the marginal revenue product.
The marginal revenue product is $34.
Table -2 shows the value of the total revenue, the marginal revenue product and the marginal product that is obtained by using the equation (3), (4) and (5).
Table -2
| Units of labor | Total product | Marginal product | Product price | Total revenue | Marginal revenue product |
| 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | ||
| 1 | 17 | 17 | 2 | 34 | 34 |
| 2 | 31 | 14 | 2 | 62 | 28 |
| 3 | 43 | 12 | 2 | 86 | 24 |
| 4 | 53 | 10 | 2 | 106 | 20 |
| 5 | 60 | 7 | 2 | 120 | 14 |
| 6 | 65 | 5 | 2 | 130 | 10 |
Graph -1 shows the firms labor supply and the marginal resources cost.7
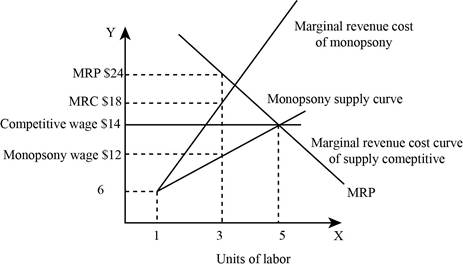
In graph -1, the horizontal axis measures the units of labor and the vertical axis represents the wage rate. The discrete nature of problem requires that the (MRP) marginal revenue product should be equal or greater than the marginal resources cost. This marginal revenue cost curve lies above the labor supply because the employing of the next worker needs a higher wage in the market and will have to pay a higher wage for all the workers.
Concept introduction:
Monopsony: The monopsony market refers to a market which consists of a single buyer who hires a particular type of labor. The workers provide labor to this type of market that has a limited employment opportunity as they need to acquire new skills to be hired. The firm is the wage marker.
Subpart (b):
How many workers should the firm employ.
Subpart (b):
Answer to Problem 3P
The firm should employ 3 workers.
Explanation of Solution
When the marginal revenue product for this worker is greater than the marginal cost, then the firm should employ the workers. From the table, the firm should employ three workers. For the first worker, the marginal revenue product is $34 and the marginal revenue cost is $6. Thus, the firm should employ the first worker. For the second worker, the marginal revenue product is $28 and the marginal revenue cost is $12. So, the firm should employ the second worker. For the third worker, the marginal revenue product is $24 and the marginal revenue cost is $18. So the firm should employ the third worker. But for the fourth worker, the marginal revenue product is $20 and the marginal revenue cost is $24. So, the firm should not employ the forth worker.
Subpart (c):
What happens to the monopolist employment and equilibrium wage rate.
Subpart (c):
Explanation of Solution
In this, the monopolist employment decreases by 2 units and the equilibrium wage rate is $2 which is less than the competitive wage.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Microeconomics: Principles, Problems, & Policies (McGraw-Hill Series in Economics)
- not use ai pleasearrow_forward• Prismatic Cards: A prismatic card will be a card that counts as having every suit. We will denote, e.g., a prismatic Queen card by Q*. With this notation, 2.3045 Q would be a double flush since every card is a diamond and a heart. • Wild Cards: A wild card counts as having every suit and every denomination. Denote wild cards with a W; if there are multiple, we will denote them W₁, W2, etc. With this notation, W2 20.30054 would be both a three-of-a-kind (three 2's) and a flush (5 diamonds). If we add multiple wild cards to the deck, they count as distinct cards, so that (e.g.) the following two hands count as "different hands" when counting: W15 5Q and W255◊♡♡♣♣ In addition, 1. Let's start with the unmodified double-suited deck. (a) Call a hand a flush house if it is a flush and a full house, i.e. if all cards share a suit and there are 3 cards of one denomination and two of another. For example, 550. house. How many different flush house hands are there? 2. Suppose we add one wild…arrow_forwardnot use ai pleasearrow_forward
- In a classic oil-drilling example, you are trying to decide whether to drill for oil on a field that might or might not contain any oil. Before making this decision, you have the option of hiring a geologist to perform some seismic tests and then predict whether there is any oil or not. You assess that if there is actually oil, the geologist will predict there is oil with probability 0.85 . You also assess that if there is no oil, the geologist will predict there is no oil with probability 0.90. Please answer the two questions below, as I am trying to ensure that I am correct. 1. Why will these two probabilities not appear on the decision tree? 2. Which probabilities will be on the decision tree?arrow_forwardAsap pleasearrow_forwardnot use ai pleasearrow_forward
- not use ai pleasearrow_forwardIn this question, you will test relative purchasing parity (PPP) using the data. Use yearly data from FRED website from 1971 to 2020: (i) The Canadian Dollars to U.S. Dollar Spot Exchange Rate (ER) (ii) Consumer price index for Canada (CAN_CPI), and (iii) Consumer price index for the US (US_CPI). Inflation is measured by the consumer price index (CPI). The relative PPP equation is: AE CAN$/US$ ECAN$/US$ = π CAN - πUS Submit the Excel sheet that you worked on. 1. First, compute the percentage change in the exchange rate (left-hand side of the equation). Caculate the variable for each year from 1972 to 2020 in Column E (named Change_ER) of the Excel sheet. For example, for 1972, compute E3: (B3-B2)/B2). ER1972 ER1971 ER 1971 (in Excel, the formula in cellarrow_forwardnot use ai pleasearrow_forward
- 8. The current price of 3M stock is $87 per share. The previous dividend paid was $5.96, and the next dividend is $6.25, assuming a growth rate of 4.86% per year. What is the forward (next 12 months) dividend yield? Show at least two decimal places, as in x.xx% %arrow_forwardJoy's Frozen Yogurt shops have enjoyed rapid growth in northeastern states in recent years. From the analysis of Joy's various outlets, it was found that the demand curve follows this pattern: Q=200-300P+1201 +657-250A +400A; where Q = number of cups served per week P = average price paid for each cup I = per capita income in the given market (thousands) Taverage outdoor temperature A competition's monthly advertising expenditures (thousands) = A; = Joy's own monthly advertising expenditures (thousands) One of the outlets has the following conditions: P = 1.50, I = 10, T = 60, A₁ = 15, A; = 10 1. Estimate the number of cups served per week by this outlet. Also determine the outlet's demand curve. 2. What would be the effect of a $5,000 increase in the competitor's advertising expenditure? Illustrate the effect on the outlet's demand curve. 3. What would Joy's advertising expenditure have to be to counteract this effect?arrow_forwardThe Compute Company store has been selling its special word processing software, Aceword, during the last 10 months. Monthly sales and the price for Aceword are shown in the following table. Also shown are the prices for a competitive software, Goodwrite, and estimates of monthly family income. Calculate the appropriate elasticities, keeping in mind that you can calculate an elasticity measure only when all other factors do not change (using Excel). For example, price elasticities, months 1-2. Month Price Aceword Quantity Aceword Family Income Price Goodwrite 1 $120 200 $4,000 $130 21 120 210 4,000 145 3 120 220 4,200 145 4 110 240 4,200 145 90 5 115 230 4,200 145 6 115 215 4,200 125 10 7899 115 220 4,400 125 105 230 4,400 125 105 235 4,600 125 105 220 4,600 115arrow_forward
 Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax
Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning





