
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780137605385
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 1.5, Problem 31P
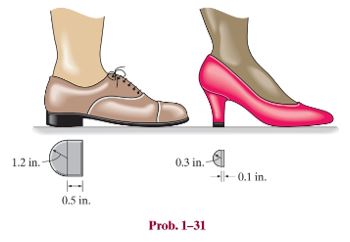
A 175-lb woman stands on a vinyl floor wearing stiletto high-heel shoes. If the heel has the dimensions shown. determine the average normal stress she exerts on the floor and compare it with the average normal stress developed when a man having the same weight is wearing flat-heeled shoes. Assume the entire weight is supported only by the heel of one shoe.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The gears shown in the figure have a diametral pitch of 2 teeth per inch and a 20° pressure angle.
The pinion rotates at 1800 rev/min clockwise and transmits 200 hp through the idler pair to gear
5 on shaft c. What forces do gears 3 and 4 transmit to the idler shaft?
TS
I
y
18T
32T
This
a
12
x
18T
C
48T
5
Question 1. Draw 3 teeth for the following pinion and gear respectively. The teeth
should be drawn near the pressure line so that the teeth from the pinion should
mesh those of the gear. Drawing scale (1:1). Either a precise hand drawing or
CAD drawing is acceptable. Draw all the trajectories of the involute lines and the
circles.
Specification: 18tooth pinion and 30tooth gear. Diameter pitch=P=6 teeth /inch.
Pressure angle:20°, 1/P for addendum (a) and 1.25/P for dedendum (b). For fillet,
c=b-a.
5. The figure shows a gear train. There is no friction at the bearings except for the gear tooth forces.
The material of the milled gears is steel having a Brinell hardness of 170. The input shaft speed (n2)
is 800 rpm. The face width and the contact angle for all gears are 1 in and 20° respectively. In this
gear set, the endurance limit (Se) is 15 kpsi and nd (design factor) is 2.
(a) Find the revolution speed of gear 5.
(b) Determine whether each gear satisfies the design factor of 2.0 for bending fatigue.
(c) Determine whether each gear satisfies the design factor of 2.0 for surface fatigue (contact stress).
(d) According to the computation results of the questions (b) and (c), explain the possible failure
mechanisms for each gear.
N4=28
800rpm
N₁=43
N5=34
N₂=14
P(diameteral pitch)=8 for all gears
Coupled to 2.5hp motor
Chapter 1 Solutions
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - The shaft is supported by a smooth thrust bearing...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal and shear...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal torque acting on...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings in the...
Ch. 1.2 - The shaft is supported by a smooth thrust bearing...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loading on the...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loading on the...Ch. 1.2 - The 800-lb load is being hoisted at a constant...Ch. 1.2 - Determine resultant internal loadings acting on...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings on the...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings on the...Ch. 1.2 - The blade of the hacksaw is subjected to a...Ch. 1.2 - The blade of the hacksaw is subjected to a...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings on the...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings on the...Ch. 1.2 - The sky hook is used to support the cable of a...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal torque acting on...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings on the...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings on the...Ch. 1.2 - The metal stud punch is subjected to a force of...Ch. 1.2 - The metal stud punch is subjected to a force of...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - A force of 80 N is supported by the bracket....Ch. 1.2 - The curved rod has a radius r and is fixed to the...Ch. 1.2 - The pipe assembly is subjected to a force of 600 N...Ch. 1.2 - If the drill bit jams when the handle of the hand...Ch. 1.2 - The curved rod AD of radius r has a weight per...Ch. 1.2 - A differential element taken from a curved bar is...Ch. 1.5 - The uniform beam is supported by two rods AB and...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress on the cross...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress on the cross...Ch. 1.5 - If the 600-kN force acts through the centroid of...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress at points A,...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress in rod AB if...Ch. 1.5 - A 175-lb woman stands on a vinyl floor wearing...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the largest intensity w of the uniform...Ch. 1.5 - The specimen failed in a tension test at an angle...Ch. 1.5 - The built-up shaft consists of a pipe AB and solid...Ch. 1.5 - If the material fails when the average normal...Ch. 1.5 - If the block is subjected to a centrally applied...Ch. 1.5 - The plate has a width of 0.5 m. If the stress...Ch. 1.5 - The member is subjected to a tensile force of 200...Ch. 1.5 - The boom has a uniform weight of 600 lb and is...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress in each of the...Ch. 1.5 - If the average normal stress in each of the...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the maximum average shear stress in pin...Ch. 1.5 - The 150-kg bucket is suspended from end E of the...Ch. 1.5 - The 150-kg bucket is suspended from end E of the...Ch. 1.5 - If the pedestal is subjected to a compressive...Ch. 1.5 - The beam is supported by two rods AB and CD that...Ch. 1.5 - The beam is supported by two rods AB and CD that...Ch. 1.5 - The beam is supported by a pin at B and a short...Ch. 1.5 - The railcar docklight is supported by the...Ch. 1.5 - The plastic block is subjected to an axial...Ch. 1.5 - During a tension test, the wooden specimen is...Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area of 400(106) m2....Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area of 400(106) m2....Ch. 1.5 - Prob. 54PCh. 1.5 - The 2-Mg concrete pipe has a center of mass at...Ch. 1.5 - The 2-Mg concrete pipe has a center of mass at...Ch. 1.5 - The pier is made of material having a specific...Ch. 1.5 - Prob. 58PCh. 1.5 - The uniform bar, having a cross-sectional area of...Ch. 1.5 - Prob. 60PCh. 1.5 - Prob. 61PCh. 1.5 - The triangular blocks are glued along each side of...Ch. 1.5 - The triangular blocks are glued along each side of...Ch. 1.5 - Prob. 64PCh. 1.5 - Determine the maximum magnitude P of the load the...Ch. 1.5 - Prob. 66PCh. 1.5 - Prob. 67PCh. 1.7 - Rods AC and BC are used to suspend the 200-kg...Ch. 1.7 - If it is subjected to double shear, determine the...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum average shear stress...Ch. 1.7 - If each of the three nails has a diameter of 4 mm...Ch. 1.7 - The strut is glued to the horizontal member at...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum average shear stress...Ch. 1.7 - If the eyebolt is made of a material having a...Ch. 1.7 - If the bar assembly is made of a material having a...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum force P that can be applied...Ch. 1.7 - The pin is made of a material having a failure...Ch. 1.7 - If the bolt head and the supporting bracket are...Ch. 1.7 - Six nails are used to hold the hanger at A against...Ch. 1.7 - If A and B are both made of wood and are 38 in....Ch. 1.7 - Prob. 70PCh. 1.7 - The connection is made using a bolt and nut and...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the required cross-sectional area of...Ch. 1.7 - Prob. 73PCh. 1.7 - The spring mechanism is used as a shock absorber...Ch. 1.7 - Prob. 75PCh. 1.7 - The hangers support the joist in such a way that...Ch. 1.7 - Prob. 77PCh. 1.7 - Prob. 78PCh. 1.7 - The two aluminum rods AB and BC have diameters of...Ch. 1.7 - The cotter is used to hold the two rods together....Ch. 1.7 - Prob. 81PCh. 1.7 - The 60mm60mm oak post is supported on the pine...Ch. 1.7 - Prob. 83PCh. 1.7 - Prob. 84PCh. 1.7 - The assembly consists of three disks A, B, and C...Ch. 1.7 - Prob. 86PCh. 1.7 - Prob. 87PCh. 1.7 - Prob. 88PCh. 1.7 - Prob. 89PCh. 1.7 - Prob. 90PCh. 1.7 - Prob. 91PCh. 1.7 - Prob. 92PCh. 1.7 - Prob. 93PCh. 1.7 - The aluminum bracket A is used to support the...Ch. 1.7 - If the allowable tensile stress for the bar is...Ch. 1.7 - The bar is connected to the support using a pin...Ch. 1 - The beam AB is pin supported at A and supported by...Ch. 1 - The long bolt passes through the 30-mm-thick...Ch. 1 - Determine the required thickness of member BC to...Ch. 1 - The circular punch B exerts a force of 2 kN on the...Ch. 1 - Determine the average punching shear stress the...Ch. 1 - The 150 mm by 150 mm block of aluminum supports a...Ch. 1 - The yoke-and-rod connection is subjected to a...Ch. 1 - The cable has a specific weight (weight/volume)...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. The rotating steel shaft is simply supported by bearings at points of B and C, and is driven by a spur gear at D, which has a 6-in pitch diameter. The force F from the drive gear acts at a pressure angle of 20°. The shaft transmits a torque to point A of TA =3000 lbĘ in. The shaft is machined from steel with Sy=60kpsi and Sut=80 kpsi. (1) Draw a shear force diagram and a bending moment diagram by F. According to your analysis, where is the point of interest to evaluate the safety factor among A, B, C, and D? Describe the reason. (Hint: To find F, the torque Tд is generated by the tangential force of F (i.e. Ftangential-Fcos20°) When n=2.5, K=1.8, and K₁ =1.3, determine the diameter of the shaft based on (2) static analysis using DE theory (note that fatigue stress concentration factors need to be used for this question because the loading condition is fatigue) and (3) a fatigue analysis using modified Goodman. Note) A standard diameter is not required for the questions. 10 in Darrow_forward3 N2=28 P(diametral pitch)=8 for all gears Coupled to 25 hp motor N3=34 Full depth spur gears with pressure angle=20° N₂=2000 rpm (1) Compute the circular pitch, the center-to-center distance, and base circle radii. (2) Draw the free body diagram of gear 3 and show all the forces and the torque. (3) In mounting gears, the center-to-center distance was reduced by 0.1 inch. Calculate the new values of center-to-center distance, pressure angle, base circle radii, and pitch circle diameters. (4)What is the new tangential and radial forces for gear 3? (5) Under the new center to center distance, is the contact ratio (mc) increasing or decreasing?arrow_forward2. A flat belt drive consists of two 4-ft diameter cast-iron pulleys spaced 16 ft apart. A power of 60 hp is transmitted by a pulley whose speed is 380 rev/min. Use a service factor (Ks) pf 1.1 and a design factor 1.0. The width of the polyamide A-3 belt is 6 in. Use CD=1. Answer the following questions. (1) What is the total length of the belt according to the given geometry? (2) Find the centrifugal force (Fc) applied to the belt. (3) What is the transmitted torque through the pulley system given 60hp? (4) Using the allowable tension, find the force (F₁) on the tight side. What is the tension at the loose side (F2) and the initial tension (F.)? (5) Using the forces, estimate the developed friction coefficient (f) (6) Based on the forces and the given rotational speed, rate the pulley set. In other words, what is the horse power that can be transmitted by the pulley system? (7) To reduce the applied tension on the tight side, the friction coefficient is increased to 0.75. Find out the…arrow_forward
- The tooth numbers for the gear train illustrated are N₂ = 24, N3 = 18, №4 = 30, №6 = 36, and N₁ = 54. Gear 7 is fixed. If shaft b is turned through 5 revolutions, how many turns will shaft a make? a 5 [6] barrow_forwardCE-112 please solve this problem step by step and give me the correct answerarrow_forwardCE-112 please solve this problem step by step and give me the correct answerarrow_forward
- CE-112 solve this problem step by step and give me the correct answer pleasearrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
General Industrial Safety; Author: Jim Pytel;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RXtF_vQRebM;License: Standard youtube license