
(1)
Journalize the stock investment transactions in the books of Company Z.
(1)
Explanation of Solution
Trading securities: These are short-term investments in debt and equity securities with an intention of trading and earning profits due to changes in market prices.
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in
stockholders’ equity accounts. - Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
Prepare journal entry for the purchase of 4,800 shares of Company AP, at $26 per share, and a brokerage commission of $192.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Year 1 | |||||
| February | 14 | Investments–Company AP Stock | 124,992 | ||
| Cash | 124,992 | ||||
| (To record purchase of shares for cash) | |||||
Table (1)
- Investments–Company AP Stock is an asset account. Since stock investments are purchased, asset value increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of cash paid to purchase Company AP’s stock.
Prepare journal entry for the purchase of 2,300 shares of Company
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Year 1 | |||||
| April | 1 | Investments–Company AR Stock | 43,792 | ||
| Cash | 43,792 | ||||
| (To record purchase of shares for cash) | |||||
Table (2)
- Investments–Company AR Stock is an asset account. Since stock investments are purchased, asset value increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of cash paid to purchase Company AR’s stock.
Prepare journal entry for sale of 600 shares of Company AP, at $32, with a brokerage of $100.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Year 1 | |||||
| June | 1 | Cash | 19,100 | ||
| Gain on Sale of Investments | 3,476 | ||||
| Investments–Company AP Stock | 15,624 | ||||
| (To record sale of shares) | |||||
Table (3)
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Loss on Sale of Investments is a loss or expense account. Since losses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Investments–Company AP Stock is an asset account. Since stock investments are sold, asset value decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working Notes:
Calculate the realized gain (loss) on sale of stock.
Step 1: Compute cash received from sale proceeds.
Step 2: Compute cost of stock investment sold.
Step 3: Compute realized gain (loss) on sale of stock.
Note: Refer to Steps 1 and 2 for value and computation of cash received and cost of stock investment sold.
Prepare journal entry for the dividend received from Company AP for 4,200 shares.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Year 1 | |||||
| June | 27 | Cash | 840 | ||
| Dividend Revenue | 840 | ||||
| (To record receipt of dividend revenue) | |||||
Table (4)
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Dividend Revenue is a revenue account. Since revenues increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of dividend received on Company AP’s stock.
Prepare adjusting entry for valuation of trading securities transaction.
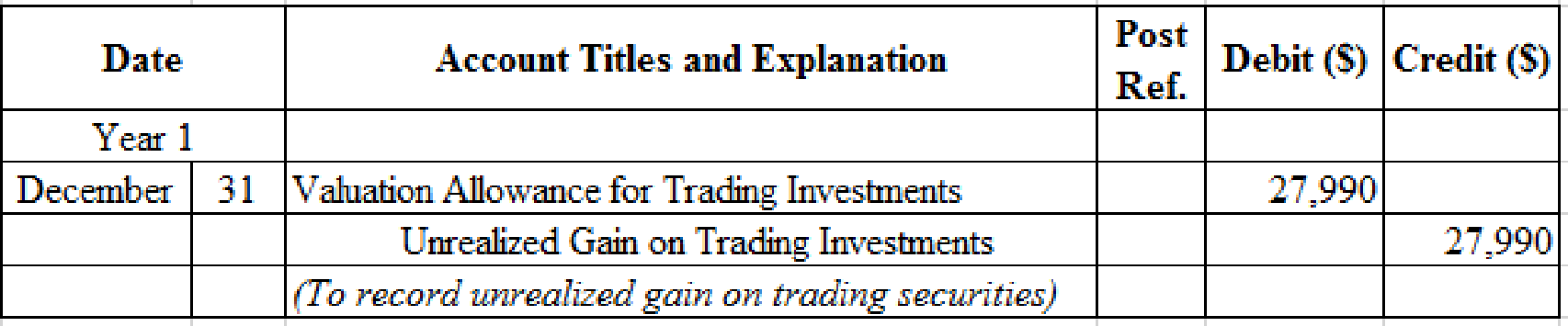
Table (5)
- Valuation Allowance for Trading Investments is a contra-asset account. The account is credited because the market price was increased (gain) to $181,150 from the cost of $153,160.
- Unrealized Gain on Trading Investments is an adjustment account used to report gain or loss on adjusting cost of investment at fair market value. Since gain has occurred and increase stockholders’ equity value, and an increase in stockholders’ equity value is debited.
Working Notes:
Compute the unrealized gain (loss) as on December 31.
Step 1: Compute the fair value of the portfolio of the trading investment.
| Security | Number of Shares | Fair Market Value | = | Fair Market Value of Investment | |
| Company AP | 4,200 shares | $33.00 | = | $138,600 | |
| Company AR | 2,300 shares | 18.50 | = | 42,550 | |
| Total | $181,150 | ||||
Table (6)
Step 2: Compute the cost per share of Company AP.
Step 3: Compute the cost per share of Company AR.
Step 4: Compute the cost of the portfolio of the trading investment, as on December 31.
| Security | Number of Shares | Cost per Share | = | Cost of Investment | |
| Company AP | 4,200 shares | $26.04 | = | $109,368 | |
| Company AR | 2,300 shares | 19.04 | = | 43,792 | |
| Total | $153,160 | ||||
Table (7)
Note: Refer to Steps 3 and 4 for cost per share of Company AP and Company AR.
Step 5: Compute the unrealized gain (loss) as on December 31.
| Details | Amount ($) |
| Trading investments at fair value, December 31 (From Table-6) | $181,150 |
| Less: Trading investments at cost, December 31 (From Table-7) | (153,160) |
| Unrealized loss on trading investments | $27,990 |
Table (8)
Prepare journal entry for the purchase of 1,200 shares of Company AT, at $65 per share, and a brokerage commission of $120.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Year 2 | |||||
| March | 14 | Investments–Company AT Stock | 78,120 | ||
| Cash | 78,120 | ||||
| (To record purchase of shares for cash) | |||||
Table (9)
- Investments–Company AT Stock is an asset account. Since stock investments are purchased, asset value increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of cash paid to purchase Company AT’s stock.
Prepare journal entry for the dividend received from Company AP for 4,200 shares.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Year 2 | |||||
| June | 26 | Cash | 882 | ||
| Dividend Revenue | 882 | ||||
| (To record receipt of dividend revenue) | |||||
Table (10)
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Dividend Revenue is a revenue account. Since revenues increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of dividend received on Company AP’s stock.
Prepare journal entry for sale of 480 shares of Company AT at $60, with a brokerage of $50.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Year 2 | |||||
| July | 30 | Cash | 28,750 | ||
| Loss on Sale of Investments | 2,498 | ||||
| Investments–Company AT Stock | 31,248 | ||||
| (To record sale of shares) | |||||
Table (11)
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Loss on Sale of Investments is an expense account. Since expenses and losses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Investments–Company AT Stock is an asset account. Since stock investments are sold, asset value decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working Notes:
Calculate the realized gain (loss) on sale of stock.
Step 1: Compute cash received from sale proceeds.
Step 2: Compute cost of stock investment sold.
Step 3: Compute realized gain (loss) on sale of stock.
Note: Refer to Steps 1 and 2 for value and computation of cash received and cost of stock investment sold.
Prepare adjusting entry for valuation of trading securities transaction.
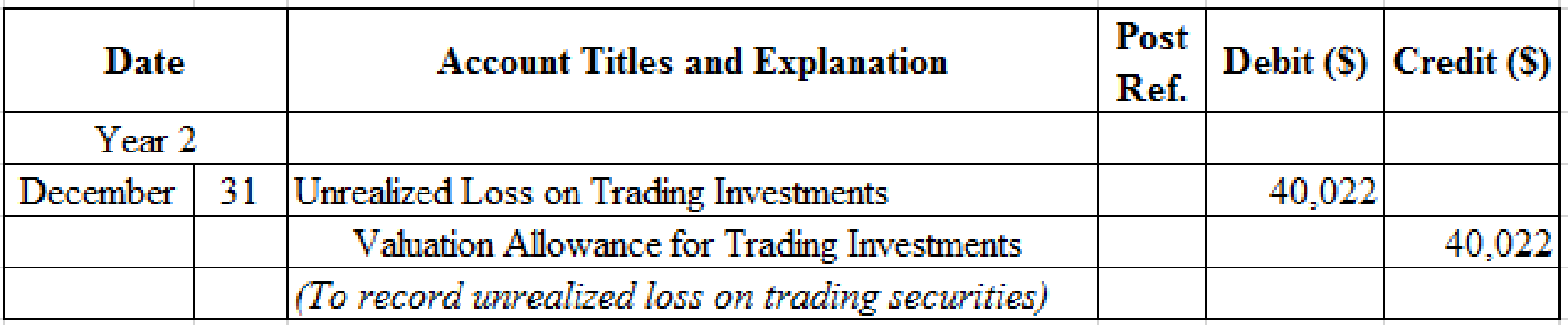
Table (12)
- Unrealized Loss on Trading Investments is an adjustment account used to report gain or loss on adjusting cost of investment at fair market value. Since loss has occurred and losses decrease stockholders’ equity value, and a decrease in stockholders’ equity value is debited.
- Valuation Allowance for Trading Investments is a contra-asset account. The account is credited because the market price was decreased (loss).
Working Notes:
Compute the unrealized gain (loss) as on December 31.
| Details | Amount ($) |
| Unrealized loss as on December 31, Year 2 | $12,032 |
| Add: Unrealized gain as on December 31, Year 1 (From Table-8) | 27,990 |
| Unrealized loss on trading investments | $40,022 |
Table (13)
(2)
Indicate the presentation of trading investments on the current assets section of the
(2)
Explanation of Solution
Balance sheet presentation:
| Company Z | ||
| Balance Sheet (Partial) | ||
| December 31, Year 2 | ||
| Assets | ||
| Current assets: | ||
| Trading investments (at cost) | $200,032 | |
| Less valuation allowance for trading investments | (12,032) | |
| Trading investments (at fair value) | $188,000 | |
Table (14)
(3)
Discuss the reporting of trading investments on the financial statements.
(3)
Explanation of Solution
Unrealized gain or loss is the result of change in trading investments cost and fair values, and reported as Other Revenues (Losses) on the income statement. The unrealized gain will be added to the net income and unrealized loss will be deducted from the net income. In the Year 1, Company Z would report $27,990 of unrealized gain as Other Income on the income statement. In the Year 2, Company Z would report $40,022 of unrealized loss as Other Losses on the income statement.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
- Evergreen Corporation (calendar-year-end) acquired the following assets during the current year: (Use MACRS Table 1 and Table 2.) Date Placed in Asset Machinery Service October 25 Original Basis $ 120,000 Computer equipment February 3 47,500 Used delivery truck* August 17 Furniture April 22 60,500 212,500 The delivery truck is not a luxury automobile. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest whole dollar amount. a. What is the allowable depreciation on Evergreen's property in the current year, assuming Evergreen does not elect §179 expense and elects out of bonus depreciation?arrow_forwardAssume that TDW Corporation (calendar-year-end) has 2024 taxable income of $952,000 for purposes of computing the §179 expense. The company acquired the following assets during 2024: (Use MACRS Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table 4, and Table 5.) Asset Machinery Computer equipment Furniture Total Placed in Service September 12 February 10 April 2 Basis $ 2,270,250 263,325 880,425 $ 3,414,000 a. What is the maximum amount of §179 expense TDW may deduct for 2024? Maximum §179 expense deductiblearrow_forwardhelparrow_forward
- Identify and discuss at least 7 problems with the Jamaican tax system and then provide recommendations to alleviate the problems.arrow_forwardOn 17-Feb of year 1, Javier purchased a building, including the land it was on, to assemble his new equipment. The total cost of the purchase was $1,302,500; $295,000 was allocated to the basis of the land and the remaining $1,007,500 was allocated to the basis of the building. (Use MACRS Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5.) Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest whole dollar amount. d. Assume the building was purchased and placed in service on 17-Feb of year 1 and is residential property. Depreciation Expense Year 1 Year 2 $ 36,632 Year 3 $ 36,632arrow_forwardOn 17-Feb of year 1, Javier purchased a building, including the land it was on, to assemble his new equipment. The total cost of the purchase was $1,302,500; $295,000 was allocated to the basis of the land and the remaining $1,007,500 was allocated to the basis of the building. (Use MACRS Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5.) Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest whole dollar amount. a. Using MACRS, what is Javier's depreciation deduction on the building for years 1 through 3? Year 1 Depreciation Expense Year 2 Year 3arrow_forward
- On 17-Feb of year 1, Javier purchased a building, including the land it was on, to assemble his new equipment. The total cost of the purchase was $1,302,500; $295,000 was allocated to the basis of the land and the remaining $1,007,500 was allocated to the basis of the building. (Use MACRS Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5.) Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest whole dollar amount. c. Assume the building was purchased and placed in service on 22-Nov instead of 17-Feb. Using MACRS, what is Javier's depreciation deduction on the building for years 1 through 3? Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Depreciation Deductionarrow_forward1) Evaluate the progress and challenges in achieving a single set of global accounting standards. 2) Discuss the benefits and drawbacks of globalization in accounting, providing relevant examples.arrow_forwardWanting to finalize a sale before year-end, on December 29, WR Outfitters sold to Bob a warehouse and the land for $140,000. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answers to the nearest whole dollar amount. a. What is Bob's basis in the warehouse and in the land if the appraised value of the warehouse was $100,750 and the appraised value of the land was $115,000? Bob's Basis Warehouse Landarrow_forward
- On 17-Feb of year 1, Javier purchased a building, including the land it was on, to assemble his new equipment. The total cost of the purchase was $1,302,500; $295,000 was allocated to the basis of the land and the remaining $1,007,500 was allocated to the basis of the building. (Use MACRS Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5.) Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest whole dollar amount. e. What would be the depreciation for 2024, 2025, and 2026 if the property were nonresidential property purchased and placed in service 17-Feb, 2007 (assume the same original basis)? Depreciation Year Expense 2024 2025 2026arrow_forwardWhat percentage of RBC’s total assets is held in investments (at October 31, 2020 and 2019)? refer to the 2020 financial statements and accompanying notes of Royal Bank of Canada (RBC). Note that RBC also holds a significant loan portfolio. What is the business reason for holding loans versus securities? Comment on how the investments are classified and presented on the balance sheet. What percentage of total interest income comes from securities (2020 and 2019)? Are there any other lines on the income statement or in OCI) relating to the securities? What percentage of net income (include any relevant OCI items) relates to securities (2020 versus 2019)? Calculate an approximate return on the investments in securities.arrow_forwardYou are the partner-in-charge of a large metropolitan office of a regional public accounting firm. Two members of your professional staff have come to you to discuss problems that may affect the firm's independence. Neither of these situations has been specifically answered by the AICPA Professional Ethics Division. Case 1: Don Moore, a partner in the firm, has recently moved into a condominium that he shares with his girlfriend, Joan Scott. Moore owns the condominium and pays all the expenses relating to its maintenance. Otherwise, the two are self-supporting. Scott is a stockbroker, and recently she has started acquiring shares in one of the audit clients of this office of the public accounting firm. The shares are held in Scott's name. At present, the shares are not material in relation to her net worth. 1. What arguments would indicating that the firm's independence has not been impaired? 2. What arguments would indicating that the firm's independence has been impaired? 3. Which…arrow_forward
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning



