
Concept explainers
Matt Kenseth won the 2012 Daytona 500, the most important race of the NASCAR season. His win was no surprise because for the 2011 season he finished fourth in the point standings with 2330 points, behind Tony Stewart (2403 points), Carl Edwards (2403 points), and Kevin Harvick (2345 points). In 2011 he earned $6,183,580 by winning three Poles (fastest driver in qualifying), winning three races, finishing in the top five 12 times, and finishing in the top ten 20 times. NASCAR’s point system in 2011 allocated 43 points to the driver who finished first, 42 points to the driver who finished second, and so on down to 1 point for the driver who finished in the 43rd position. In addition any driver who led a lap received 1 bonus point, the driver who led the most laps received an additional bonus point, and the race winner was awarded 3 bonus points. But, the maximum number of points a driver could earn in any race was 48. Table 15.13 shows data for the 2011 season for the top 35 drivers (NASCAR website).
Managerial Report
- 1. Suppose you wanted to predict Winnings ($) using only the number of poles won (Poles), the number of wins (Wins), the number of top five finishes (Top 5), or the number of top ten finishes (Top 10). Which of these four variables provides the best single predictor of winnings?
- 2. Develop an estimated regression equation that can be used to predict Winnings ($) given the number of poles won (Poles), the number of wins (Wins), the number of top five finishes (Top 5), and the number of top ten (Top 10) finishes. Test for individual significance and discuss your findings and conclusions.
- 3. Create two new independent variables: Top 2–5 and Top 6–10. Top 2–5 represents the number of times the driver finished between second and fifth place and Top 6–10 represents the number of times the driver finished between sixth and tenth place. Develop an estimated regression equation that can be used to predict Winnings ($) using Poles, Wins, Top 2–5, and Top 6–10. Test for individual significance and discuss your findings and conclusions.
TABLE 15.13 Nascar Results for the 2011 Season
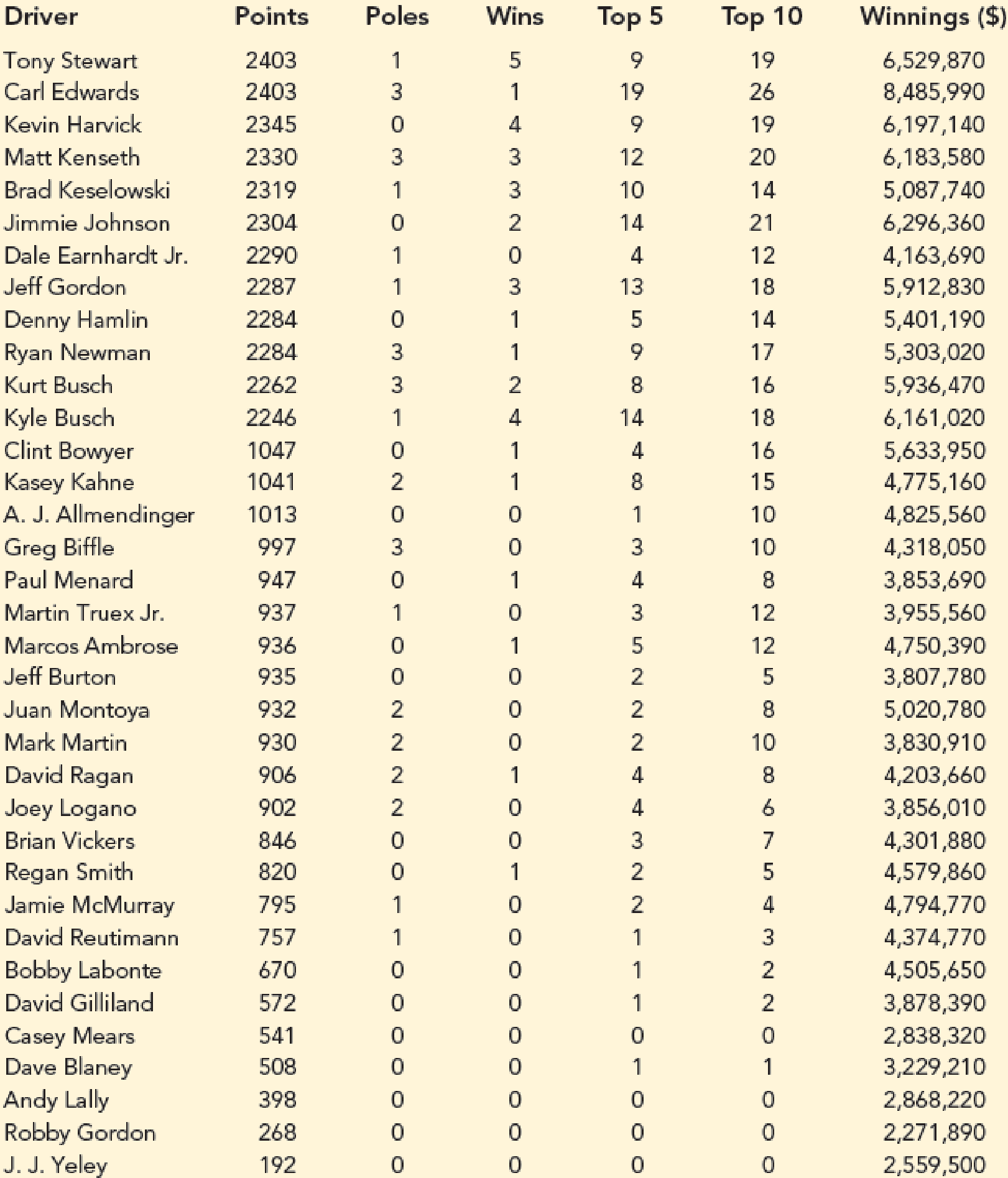
Source: NASCAR website, February 28, 2011. (https://www.nascar.com/)
- 4. Based upon the results of your analysis, what estimated regression equation would you recommend using to predict Winnings ($)? Provide an interpretation of the estimated regression coefficients for this equation.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 15 Solutions
MindTap Business Statistics, 1 term (6 months) Printed Access Card for Anderson/Sweeney/Williams/Camm/Cochran's Essentials of Statistics for Business and Economics, 8th
- Bob scores 80 on both his math exam (which has a mean of 70 and standard deviation of 10) and his English exam (which has a mean of 85 and standard deviation of 5). Find and interpret Bob's Z-scores on both exams to let him know which exam (if either) he did bet- ter on. Don't, however, let his parents know; let them think he's just as good at both subjects. algas 70) sering digarrow_forwardSue's math class exam has a mean of 70 with a standard deviation of 5. Her standard score is-2. What's her original exam score?arrow_forwardClint sleeps an average of 8 hours per night with a standard deviation of 15 minutes. What's the chance he will sleep less than 7.5 hours tonight? nut bow visarrow_forward
- Suppose that your score on an exam is directly at the mean. What's your standard score?arrow_forwardOne state's annual rainfall has a normal dis- tribution with a mean of 100 inches and standard deviation of 25 inches. Suppose that corn grows best when the annual rainfall is between 100 and 150 inches. What's the chance of achieving this amount of rainfall? wved now of sociarrow_forward13 Suppose that your exam score has a standard score of 0.90. Does this mean that 90 percent of the other exam scores are lower than yours?arrow_forward
- Bob's commuting times to work have a nor- mal distribution with a mean of 45 minutes and standard deviation of 10 minutes. How often does Bob get to work in 30 to 45 minutes?arrow_forwardBob's commuting times to work have a nor- mal distribution with a mean of 45 minutes and standard deviation of 10 minutes. a. What percentage of the time does Bob get to work in 30 minutes or less? b. Bob's workday starts at 9 a.m. If he leaves at 8 a.m., how often is he late?arrow_forwardSuppose that you want to put fat Fido on a weight-loss program. Before the program, his weight had a standard score of +2 com- pared to dogs of his breed/age, and after the program, his weight has a standard score of -2. His weight before the program was 150 pounds, and the standard deviation for the breed is 5 pounds. a. What's the mean weight for Fido's breed/ age? b. What's his weight after the weight-loss program?arrow_forward
- Weights have a normal distribution with a mean of 100 and standard deviation of 10. What weight has 60 percent of the values lying below it?arrow_forwardThe times it takes to complete a statistics exam have a normal distribution with a mean of 40 minutes and standard deviation of 6 minutes. Deshawn's time falls at the 42nd percentile. How long does Deshawn take to finish her exam? bad boy wod abbed a le signe ne tolgikiwo (ezonipuo brit of heen ugy shies von no rep on ud af vt to into Or festes e a (92) 00arrow_forwardJimmy walks a mile, and his previous times have a normal distribution with a mean of 8 minutes and standard deviation of 1 minute. What time does he have to make to get into his own top 10 percent of his fastest times?arrow_forward
 Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell Algebra for College StudentsAlgebraISBN:9781285195780Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra for College StudentsAlgebraISBN:9781285195780Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781285195728Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781285195728Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning


