
Concept explainers
1.
Find the value of point-biserial
1.
Answer to Problem 28CAP
The value of point-biserial
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The given information is that, the researcher is interested to determine the relation between the factors recycle (X) and attitude of Eco friendly (Y).
Point-biserial correlation coefficient:
When the one factor is continuous that is measured on either interval scale or ratio scale and other is dichotomous that is measured on nominal scale, then the strength and direction of the linear relationship between the two factors can be measured by Point-biserial correlation coefficient. It is denoted by
In the formula, p and q are the proportion of scores for the dichotomous factor at each level,
The Point-biserial correlation for recycle and attitude of Eco friendly is to be calculated. The factor ‘recycle’ has to be coded with 1 and 2. Code the value 1 for ‘No’ and 2 for ‘Yes’ for dichotomous factor ‘recycle’.
The coded data is,
| Recycle |
Attitude toward Eco friendly |
| 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 3 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 7 |
| 2 | 6 |
| 2 | 5 |
| 2 | 6 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 2 | 6 |
| 2 | 5 |
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain test statistic valuefor recycle and attitude of Eco friendly using SPSS software is given as,
- Choose Variable view.
- Under the name, enter the name as X, Y.
- Choose Data view, enter the data.
- Choose Analyze>Correlate>Bivariate.
- In variables, enter the X, and Y.
- Click OK.
Output using SPSS software is given below:
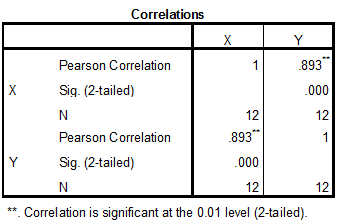
The correlation coefficient value is 0.893.
2.
Determine the decision for the null hypothesis using two-tailed test at a 0.05 level of significance
2.
Answer to Problem 28CAP
The decision is to reject the null hypothesis.
The point-biserial correlation coefficient between recycle and attitude of Eco friendly is significant.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The given information is that, the correlation coefficient value is –0.893 and degrees of freedom is 10.
Test statistic:
The coefficient of determination for the point-serial correlation and the effect size of the two-independent-sample t test are similar and hence for significance test of point-biserial correlation, t test is used.
The formula for converting the r to a t statistic is,
In the formula, r denotes the correlation coefficient and df is the degrees of freedom for correlation coefficient.
Degrees of freedom:
The formula is.
In formula, n denotes the
Decision rules:
- If the positive test statistic value is greater than the critical value, then reject the null hypothesis and test is significant, or else retains the null hypothesis.
- If the negative test statistic value is less than negative critical value, then reject the null hypothesis and test is significant, or else retains the null hypothesis.
The correlation between recycle and attitude of Eco friendly is to be tested. Let
Null hypothesis:
That is, the point-biserialcorrelation coefficient between recycle and attitude of Eco friendly is not significant.
Alternative hypothesis:
That is, the point-biserial correlation coefficient between recycle and attitude of Eco friendly is significant.
Degrees of freedom:
A sample of 12 participants is taken. The degrees of freedom are,
Test statistic:
Substitute,
The value of t is,
Critical value:
The given significance level is
The test is two tailed, the degrees of freedom are 10, and the alpha level is 0.05.
From the Appendix C: Table C.2 the t Distribution:
- Locate the value 10 in the degrees of freedom (df) column.
- Locate the 0.05 in the proportion in two tails combined row.
- The intersecting value that corresponds to the 10 with level of significance 0.05 is 2.228.
Thus, the critical value for
Conclusion:
The value of test statistic is 6.283.
The critical value is 2.228.
The test statistic value is greater than the critical value.
The test statistic value falls under critical region.
Hence the null hypothesis is rejected and test is significant.
The point-biserial correlation coefficient between recycle and attitude of Eco friendly is significant.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences
- For context, the image provided below is a quesion from a Sepetember, 2024 past paper in statistical modelingarrow_forwardFor context, the images attached below (the question and the related figure) is from a january 2024 past paperarrow_forwardFor context, the image attached below is a question from a June 2024 past paper in statisical modelingarrow_forward
- For context, the images attached below are a question from a June, 2024 past paper in statistical modelingarrow_forwardFor context, the images attached below (question and related graph) are from a February 2024 past paper in statistical modelingarrow_forwardFor context, the images attached below are from a February 2024 past paper in statistical modelingarrow_forward
- For context, the image provided below is a question from a September, 2024 past paper in statistical modelingarrow_forwardFor context, the image below is from a January 2024 past paper in statistical modelingarrow_forwardFor context, the image provided below is a question from a September, 2024 past paper in statistical modelingarrow_forward
- Section 2.2 Subsets 71 Exercise Set 2.2 Practice Exercises In Exercises 1-18, write or in each blank so that the resulting statement is true. 1. {1, 2, 5} {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7} 2. {2, 3, 7} {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7} 3. {-3, 0, 3} {-4,-3,-1, 1, 3, 4} 4. {-4, 0, 4} 5. {Monday, Friday} {-3, -1, 1, 3} {Saturday, Sunday, Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday} 6. {Mercury, Venus, Earth} {Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter} 7. {x/x is a cat} {xx is a black cat} {x|x is a pure-bred dog} ibrary mbers, ause the entire sual 8. {xx is a dog} 9. (c, o, n, v, e, r, s, a, t, i, o, n} {v, o, i, c, e, s, r, a, n, t, o, n} 10. [r, e, v, o, l, u, t, i, o, n} {t, o, l, o, v, e, r, u, i, n} 33. A = {x|x E N and 5 < x < 12} B = {x|x E N and 2 ≤ x ≤ 11} A_ B 34. A = {x|x = N and 3 < x < 10} B = A. {x|x = N and 2 ≤ x ≤ 8} B 35. Ø {7, 8, 9,..., 100} 36. Ø _{101, 102, 103, . . ., 200} 37. [7, 8, 9,...} 38. [101, 102, 103, ...} 39. Ø 40. { } { } e In Exercises 41-54, determine whether each statement is true or false. If…arrow_forwardA = 5.8271 ± 0.1497 = B 1.77872 ± 0.01133 C=0.57729 ± 0.00908 1. Find the relative uncertainty of A, B, and C 2. Find A-3 3. Find 7B 4. Find A + B 5. Find A B-B - 6. Find A * B 7. Find C/B 8. Find 3/A 9. Find A 0.3B - 10. Find C/T 11. Find 1/√A 12. Find AB²arrow_forwardWhy charts,graphs,table??? difference between regression and correlation analysis.arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL


