
Concept explainers
To describe: The comparison and differences between Haeckel’s and Von Baer’s ways of thinking about changes in development over the course of animal evolution.
Introduction: Biologists from the nineteenth and twentieth centuries compared and described embryonic development of a diverse group of animals. They also described the ways in which the various morphogenetic processes in different groups of organisms result in different adult forms.
Explanation of Solution
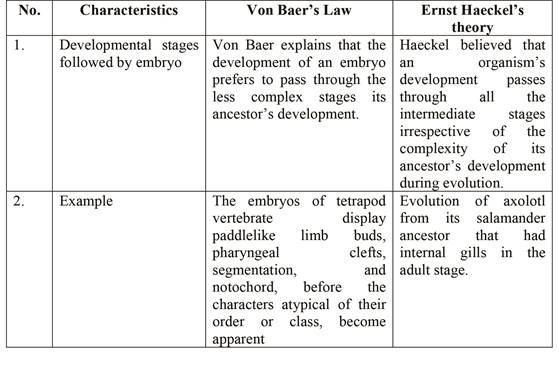
Among the many first things, the biologists who were studying developmental biology learned that the embryos of many species are more often similar than the adults. Both Karl Von Baer and Ernst Haeckel studied embryo development to know more about the developmental pattern of organisms. In 1882, Karl von Baer noted that those features that are common to higher taxon appear early than those characters of lower tax such as families or order. According to Baer’s law, embryo development passes through the developmental stages of their adults. Haeckel also explained that the development of an organism, during the course of evolution, pass through all its adult form’s developmental stages.
Following are some differences in the way of thinking of these two biologists about changes in an organism’s development over the course of evolution:
To explain: The learning about phylogeny from development, even though Haeckel’s dictum seldom holds.
Introduction: Biologists from the nineteenth and twentieth century compared and described embryonic development of a diverse group of animals. They also described the ways in which the various morphogenetic processes in different groups of organisms result in different adult forms.
Explanation of Solution
Ernst Haeckel, a German biologist, interpreted developmental patterns to mean that an individual organism’s development repeats the evolutionary history of adult forms of their ancestors. It is known as “ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny”.
However, by the end of the 19th century, it was clear that Haeckel’s dictum seldom holds. For example, embryos of mammal and reptile go through a development stage where they have pharyngeal clefts and branchial arches identical to fish supporting that they share a common ancestor with fish. However, mammals and reptiles never acquire the characters of typical adult fish.
Nevertheless, these developmental studies provided information about the evolutionary relationship between different organisms. By studying embryo development, biologists identified many common developmental difference patterns among species.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- please fill in missing parts , thank youarrow_forwardplease draw in the answers, thank youarrow_forwarda. On this first grid, assume that the DNA and RNA templates are read left to right. DNA DNA mRNA codon tRNA anticodon polypeptide _strand strand C с A T G A U G C A TRP b. Now do this AGAIN assuming that the DNA and RNA templates are read right to left. DNA DNA strand strand C mRNA codon tRNA anticodon polypeptide 0 A T G A U G с A TRParrow_forward
- Please identify the curve shown below. What does this curve represent? Please identify A, B, C, D, and E (the orange oval). What is occurring in these regions?arrow_forwardPlease identify the test shown here. 1) What is the test? 2) What does the test indicate? How is it performed? What is CX? 3) Why might the test be performed in a clinical setting? GEN CZ CX CPZ PTZ CACarrow_forwardDetermine how much ATP would a cell produce when using fermentation of a 50 mM glucose solution?arrow_forward
- Determine how much ATP would a cell produce when using aerobic respiration of a 7 mM glucose solution?arrow_forwardDetermine how much ATP would a cell produce when using aerobic respiration to degrade one small protein molecule into 12 molecules of malic acid, how many ATP would that cell make? Malic acid is an intermediate in the Krebs cycle. Assume there is no other carbon source and no acetyl-CoA.arrow_forwardIdentify each of the major endocrine glandsarrow_forward
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning





