
To match: The structures of the eye with the terms.
Introduction: Eyes are the organs of the visual system. They detect light and convert it into electro-chemical impulses present in the neurons. They provide vision and the ability to receive and process visual detail to the organism.
Answer to Problem 1P
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 shows the structure of eye:
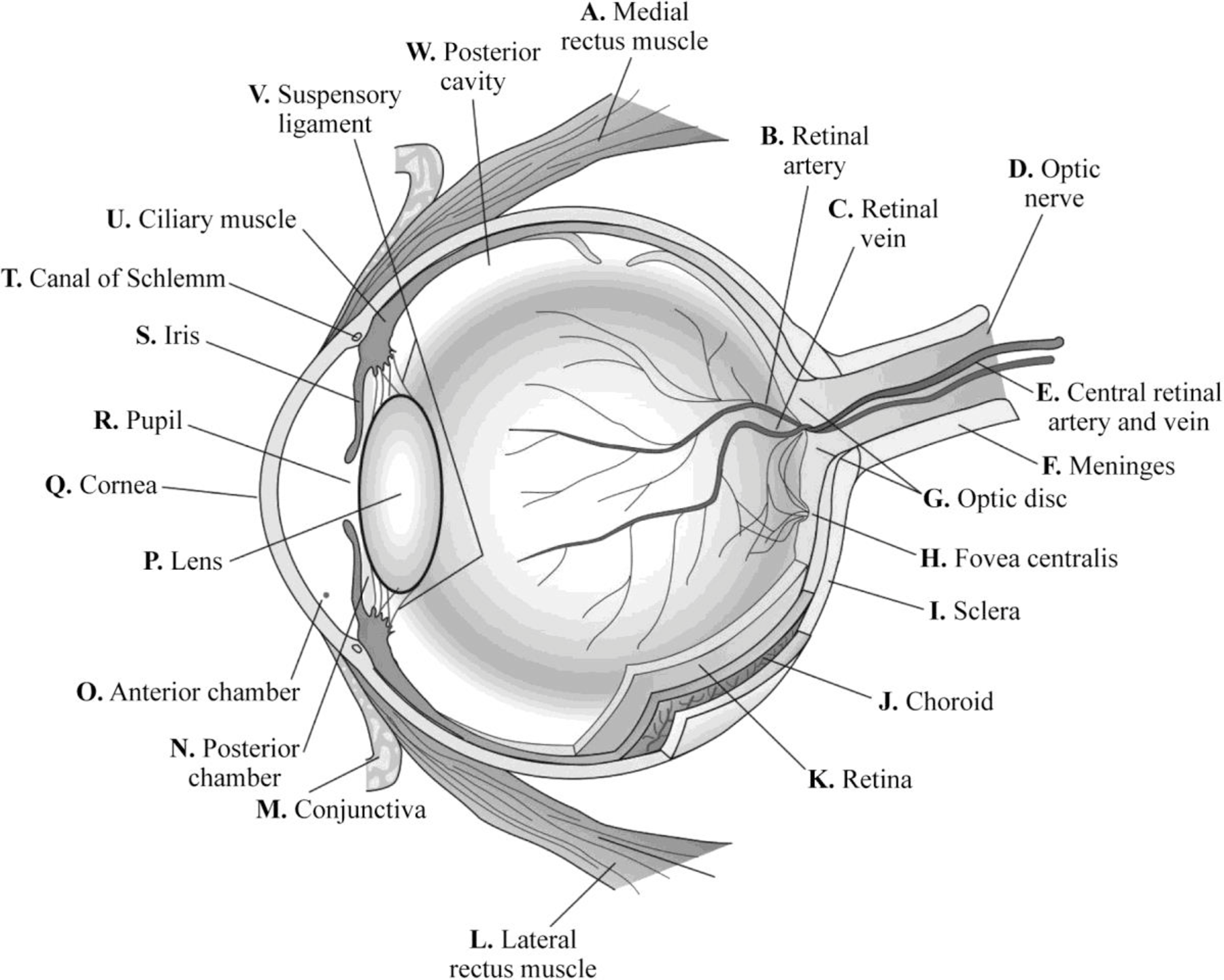
Fig.1: Structure of eye
Explanation of Solution
A. Medial rectus muscle:
Medial rectus muscle is a muscle present in the orbit. It is the largest of the extraocular muscles. The medial rectus muscle helps to move the eye up and down and from side to side.
B. Retinal artery:
Retinal arteries carry the blood to the parts of eye.
C. Retinal vein:
Retinal veins carry the blood from the eye back to the heart.
D. Optic nerve
Optic nerve fibers are layer of tissues that are present on the retina. They are made of ganglion cells. Its main function is to carry the electrical impulses from retina to the brain. Thus, it carries visual information to the brain from the eye.
E. Central retinal artery and vein:
The central retinal artery provides nutrients and oxygen to the inner retina and surface of the optic nerve. The central retinal vein is a short vein that runs through the optic nerve. It drains the blood from the capillaries of retina either to cavernous sinus directly or superior ophthalmic vein.
F. Meninges:
Meninges surround the optic nerve.
G. Optic disc:
The optic disc is an oval spot at the back of the eye. Optic disc is the point at which the ganglion cells exit the eye and carries visual information to the brain.
H. Fovea centralis:
The fovea centralis is a small pit or depression that is composed of closely packed cones in the eye. It is responsible for the clearest vision. Fovea centralis is located at the center of macula region in the retina.
I. Sclera:
The white, protective layer of the eye is called sclera. It contains collagen and some elastic fibers. Sclera is covered by conjunctiva that lubricates the eye.
J. Choroid:
Choroid is the vascular layer of eye that contains connective tissues. It is present between retina and sclera. It is a part of uvea that supplies nutrients to the inner parts of the eye.
K. Retina:
Retina is a thin layer of tissues that is located near the optic nerve. The main function of retina is to convert the received light signal to neural signal that is transmitted to brain for visual recognition.
L. Lateral rectus muscle:
The lateral rectus muscle is located in the lateral side of the eyeball in the orbit.
M. Conjunctiva:
It is the thin membrane that covers the inner surface of the eyelid and sclera.
N. Posterior chamber:
Posterior chamber is a narrow space in the eye behind the iris and in front of the lens. The posterior chamber is filled with water fluid called aqueous humor.
O. Anterior chamber:
The anterior chamber is a region located between the iris and endothelium. The anterior chamber is filled with the fluid called aqueous humor.
P. Lens:
Lens is a biconvex, transparent structure present in eye and suspended behind the iris. It is made of an unusual elongated cell that does not contain blood supply but obtains nutrients from the surrounding fluids.
Q. Cornea:
Cornea is the transparent, front layer that covers the iris, pupil, anterior chamber, and lens. It acts as a barrier against dirt, germs, and other factors that cause damage.
R. Pupil:
Pupil is the opening at the center of the iris by which light enters and reaches the retina. Its main function is to regulate the amount of light that enters the eye.
S. Iris:
Iris is the pigmented muscular layer that is present between the cornea and lens. This controls the amount of light that enters into the eye.
T. Canal of schlemm:
Canal of schlemm is a circular lymphatic-like vessel in the eye. It collects the aqueous humor from the anterior chamber and delivers it into the episcleral blood vessels through the aqueous veins.
U. Ciliary muscle:
Ciliary body is the part of eye, which contains ciliary muscles that control the shape of the lens. The ciliary epithelium in ciliary body produces aqueous humor that maintains intra-ocular pressure and refracts light. The non-pigmented part of cornea produces vitreous humor that maintains intra-ocular pressure, refracts light, and maintains shape.
V. Suspensory ligament:
Suspensory ligament is a ligament that supports a body part. The suspensory ligament of the eyeball is also called Lockwood’s ligament. The suspensory ligament of lens is also called zonular fiber.
W. Posterior cavity:
The posterior cavity is the back two-thirds of the eye that consists of the anterior hyaloid membrane and all the optical structures behind it.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Professions
- how is mental health nursing independent from general nursing?arrow_forwardThe importance of monitoring resident's wound healing (bed sores, cuts, and scrapes, etc.) and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forwardThe importance of seeing how it is to work as a chief in a nursing home and how they accommodate for special diets (low sodium, low sugar, heart healthy, etc.) and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forward
- The importance of dealing with work confrontation (different healthcare departments fighting; diet aide and CNA) as a manager of a kitchen and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forwardQuestion 1: You are the Community Dietitian for the local public health agency. Recent news coverage has highlighted the state of food insecurity and child hunger in your county. Initial reports indicate that 15% of the population is food insecure. Of this group, 28.4% are children. It is estimated that 86% of the food insecure population is eligible for federal nutrition assistance. You are asked to conduct a community needs assessment and, ultimately, develop an appropriate intervention aimed at reducing hunger. First, however, you must submit a plan for the needs assessment. Complete the following: 1. State the nutritional problem (10 pts) 2. Set the parameters of the assessment (20 pts, 5 pts per bullet) A. State the purpose of the assessment B. Identify the community and target population for this assessment C. Develop 2 goals and 2 SMART objectives for each goal D. Discuss the major categories of community data and target population data E. Specify the types of data you might…arrow_forwardAssignment Instructions: Nursing Research Essay Objective: Select a specific area of nursing that captivates your interest. Compose a comprehensive essay, ranging from 300 to 500 words, that delves into the intricacies of nursing research within your chosen area. It is recommended that you consider the topic carefully as this topic, should be the topic for your course research project: see week 4 assignments. Your essay should elucidate the following points: The Significance of Nursing Research: Explore how nursing research in your selected area contributes to advancements in applied medicine. Discuss the potential achievements and innovations that can arise from dedicated nursing research in this field. Articulate the value and impact of such research on patient care, healthcare practices, and overall medical knowledge. Research Methods and Approaches: Identify the most effective methods for conducting nursing research in your chosen area. Highlight specific topics or research…arrow_forward
- The importance of understanding low meal consumption of residents in a nursing home and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forwardThe importance of accommodating special diets (diabetic, low sodium, etc.) in a nursing home and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forwardThe importance of making a weekly clean list for kitchen staff in a nursing home and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forward
- The importance of keeping a clean food pantry in a nursing home and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forwardI’m finding it a bit difficult to understand the Arrhenius equation and how shelf life relates to pH and temperature. Also in the question that says ‘this solution maintains 80% potency at 30C’, am I correct in thinking the formula would be:t = ln(0.8)/ -karrow_forward4.24 mmmarrow_forward
 Phlebotomy EssentialsNursingISBN:9781451194524Author:Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)Publisher:JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC.
Phlebotomy EssentialsNursingISBN:9781451194524Author:Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)Publisher:JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC. Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Profession...NursingISBN:9780323414425Author:Robert J Hubert BSPublisher:Saunders
Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Profession...NursingISBN:9780323414425Author:Robert J Hubert BSPublisher:Saunders Fundamentals Of NursingNursingISBN:9781496362179Author:Taylor, Carol (carol R.), LYNN, Pamela (pamela Barbara), Bartlett, Jennifer L.Publisher:Wolters Kluwer,
Fundamentals Of NursingNursingISBN:9781496362179Author:Taylor, Carol (carol R.), LYNN, Pamela (pamela Barbara), Bartlett, Jennifer L.Publisher:Wolters Kluwer, Fundamentals of Nursing, 9eNursingISBN:9780323327404Author:Patricia A. Potter RN MSN PhD FAAN, Anne Griffin Perry RN EdD FAAN, Patricia Stockert RN BSN MS PhD, Amy Hall RN BSN MS PhD CNEPublisher:Elsevier Science
Fundamentals of Nursing, 9eNursingISBN:9780323327404Author:Patricia A. Potter RN MSN PhD FAAN, Anne Griffin Perry RN EdD FAAN, Patricia Stockert RN BSN MS PhD, Amy Hall RN BSN MS PhD CNEPublisher:Elsevier Science Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the H...NursingISBN:9780323414142Author:Hubert BS, Robert J; VanMeter PhD, Karin C.Publisher:Saunders
Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the H...NursingISBN:9780323414142Author:Hubert BS, Robert J; VanMeter PhD, Karin C.Publisher:Saunders Issues and Ethics in the Helping Professions (Min...NursingISBN:9781337406291Author:Gerald Corey, Marianne Schneider Corey, Cindy CoreyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Issues and Ethics in the Helping Professions (Min...NursingISBN:9781337406291Author:Gerald Corey, Marianne Schneider Corey, Cindy CoreyPublisher:Cengage Learning





