
Concept explainers
(a)
Sketch the domain of the function
Answer to Problem 1CRE
Solution:Domain of the function is
Explanation of Solution
Domain: The domain of the function is defined as the set of complete possible values which will make the function work and gives output as real values.
Given: A function as
Formula:
a. Domain of Square root function, is given as
b. The expression in the denominator can never be zero.
Calculation:
Given function is
Domain of the function:
To find the domain, set the expression the expression inside the square root greater than equal to zero and the expression in the denominator not equal to zero.
And
And
Thus, domain of the function is
Graph is as follows:
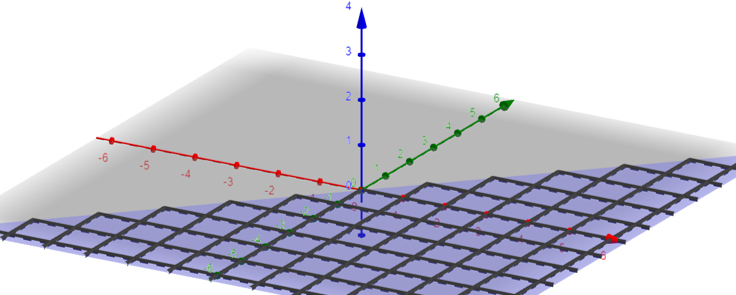
Conclusion: Domain of the function is
(b)
The value of and for the function
Answer to Problem 1CRE
Solution: The value of and
Explanation of Solution
Domain: The domain of the function is defined as the set of complete possible values which will make the function work and gives output as real values.
Given: A function as
Calculation:
Given function is
Conclusion: The value of and
(c)
A point such that for the function
Answer to Problem 1CRE
Solution: The point such that for the function Are and
Explanation of Solution
Domain: The domain of the function is defined as the set of complete possible values which will make the function work and gives output as real values.
Given: A function as
Calculation:
Given function is
Also,
Squaring both the sides, we get
Let ,
Then
Thus,
Points are and
Conclusion: The point such that for the function are and
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
CALCULUS (CLOTH)
- A 20 foot ladder rests on level ground; its head (top) is against a vertical wall. The bottom of the ladder begins by being 12 feet from the wall but begins moving away at the rate of 0.1 feet per second. At what rate is the top of the ladder slipping down the wall? You may use a calculator.arrow_forwardExplain the focus and reasons for establishment of 12.4.1(root test) and 12.4.2(ratio test)arrow_forwarduse Integration by Parts to derive 12.6.1arrow_forward
- Explain the relationship between 12.3.6, (case A of 12.3.6) and 12.3.7arrow_forwardExplain the key points and reasons for the establishment of 12.3.2(integral Test)arrow_forwardUse 12.4.2 to determine whether the infinite series on the right side of equation 12.6.5, 12.6.6 and 12.6.7 converges for every real number x.arrow_forward
- use Corollary 12.6.2 and 12.6.3 to derive 12.6.4,12.6.5, 12.6.6 and 12.6.7arrow_forwardExplain the focus and reasons for establishment of 12.5.1(lim(n->infinite) and sigma of k=0 to n)arrow_forwardExplain the focus and reasons for establishment of 12.5.3 about alternating series. and explain the reason why (sigma k=1 to infinite)(-1)k+1/k = 1/1 - 1/2 + 1/3 - 1/4 + .... converges.arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning

