
(a)
Interpretation:
The molecular geometry, polarity and the strongest intermolecular force present in
Concept introduction:
Geometry of a molecule is the arrangement of atoms of a molecule in space. Geometry is dependent on the number of bond pairs, lone pairs and valence electrons of central atom. Polarity is defined as the tendency of atoms of a molecule to attract the electrons of the bond pairs towards itself.
Answer to Problem 15.3TC
The geometry, polarity and intermolecular force present in
Geometry is tetrahedral.
Polarity of methane is zero. It means
The strongest intermolecular force present is induced dipole.
Explanation of Solution
Methane,
Structure of methane is shown below.
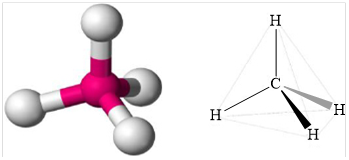
Figure 1
Therefore, methane is tetrahedral, non-polar and strongest intermolecular forces are induced dipole.
Geometry of methane is tetrahedral methane is non polar and the strongest intermolecular force present in methane is induced dipole.
(b)
Interpretation:
The geometry, polarity and the strongest intermolecular force present in
Concept introduction:
Geometry of a molecule of a molecule is the arrangements of atoms of a molecule in space. Geometry is depends on the number of bond pairs, lone pairs and valence electrons of central atom. Polarity is defined as the tendency of atoms of a molecule to attract the bond pairs towards itself.
Answer to Problem 15.3TC
The geometry, polarity and the strongest intermolecular force present in
Geometry is linear.
Polarity of carbon dioxide is zero. It means
Strongest intermolecular force present is induced dipole.
Explanation of Solution
Carbon dioxide
Structure of carbon dioxie is shown below.
![]()
Figure 2
Therefore, carbon dioxide is linear, non-polar and the strongest intermolecular force present is induced dipole.
Geometry of carbon dioxide is linear, polarity is zero means non polar molecule and the strongest intermolecular force present is induced dipole.
(c)
Interpretation:
The geometry, polarity and the strongest intermolecular force present in
Concept introduction:
Geometry of a molecule of a molecule is the arrangements of atoms of a molecule in space. Geometry is depends on the number of bond pairs, lone pairs and valence electrons of central atom. Polarity is defined as the tendency of atoms of a molecule to attract the bond pairs towards itself.
Answer to Problem 15.3TC
The geometry, polarity and intermolecular force present in
Geometry is bent.
Polarity of
Strongest intermolecular force present in
Explanation of Solution
Oxygen difluoride
Structure of oxygen difluoride is shown below.
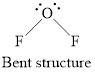
Figure 3
Therefore, oxygen difluoride is bent, polar, and the strongest intermolecular force present is dipole-dipole.
Geometry of oxygen difluoride is bent, polarity is non-zero means polar molecule and the strongest intermolecular force present is dipole dipole interaction.
(d)
Interpretation:
The geometry, polarity and the strongest intermolecular force present in
Concept introduction:
Geometry of a molecule of a molecule is the arrangements of atoms of a molecule in space. Geometry is depends on the number of bond pairs, lone pairs and valence electrons of central atom. Polarity is defined as the tendency of atoms of a molecule to attract the bond pairs towards itself.
Answer to Problem 15.3TC
The geometry, polarity and intermolecular force present in
Geometry is bent.
Polarity of
The strongest intermolecular force present is hydrogen bonding.
Explanation of Solution
Chloric acid
Structure of chloric acid is shown below.
![]()
Figure 4
Therefore, chloric acid is bent, polar and the strongest force present is hydrogen bonding.
Geometry of chloric acid is bent, polarity is non-zero means polar molecule and the strongest intermolecular force present is hydrogen bonding.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Bundle: Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach, 6th + OWLv2, 1 term (6 months) Printed Access Card
- b. ὋΗ CH3CH2OH H2SO4arrow_forwardFor the reaction A (g) → 3 B (g), Kp = 0.379 at 298 K. What is the value of ∆G for this reaction at 298 K when the partial pressures of A and B are 5.70 atm and 0.250 atm?arrow_forward14. Calculate the concentrations of Ag+, Ag(S2O3), and Ag(S2O3)23- in a solution prepared by mixing 150.0 mL of 1.00×10-3 M AgNO3 with 200.0 mL of 5.00 M Na2S2O3 Ag+ + S20 Ag(S203)¯ K₁ = 7.4 × 108 Ag(S203)¯ + S20¯ = Ag(S203) K₂ = 3.9 x 104arrow_forward
- ΗΝ, cyclohexanone pH 4-5 Draw Enamine I I CH3CH2Br THF, reflux H3O+ I Drawing Draw Iminium Ionarrow_forward:0: :0: Select to Add Arrows :0: (CH3)2NH :0: ■ Select to Add Arrows :0: :0: (CH3)2NH ■ Select to Add Arrowsarrow_forwardDraw the product of the following H action sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CH3Br Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings H Charges ㅁarrow_forward
- Please help me with this the problem is so confusingarrow_forward14 Question (1 point) Disiamylborane adds to a triple bond to give an alkenylborane. Upon oxidation with OH, H2O2, the alkenylborane will form an enol that tautomerizes to an aldehyde. In the first box below, draw the mechanism arrows for the reaction of disiamylborane with the alkyne, and in the last box draw the structure of the aldehyde. 4th attempt Feedback i > 3rd attempt OH, H2O2 i See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forwardanswer with mechanisms and steps. handwritten please!arrow_forward
- Hello I need some help with Smartwork. For drawing structure B, I know the correct answer is CH₃B₂, but when I try to type it in, it keeps giving me CH₄BH₃ instead. Do you know how I should write it properly? Should I use a bond or something else?arrow_forwardTrue or false, chemistryarrow_forwardanswer thse questions with mechanisms and steps. handwritten please!arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning





