
(1)
Trading securities: These are short-term investments in debt and equity securities with an intention of trading and earning profits due to changes in market prices.
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in
stockholders’ equity accounts. - Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
To journalize: The stock investment transactions in the books of Company SF.
(1)
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry for the purchase of 5,000 shares of Company W, at $40 per share, and a brokerage commission of $500.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2016 | |||||
| March | 14 | Investments–Company W Stock | 200,500 | ||
| Cash | 200,500 | ||||
| (To record purchase of shares for cash) | |||||
Table (1)
- Investments–Company W Stock is an asset account. Since stock investments are purchased, asset value increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of cash paid to purchase Company W’s stock.
Prepare journal entry for the purchase of 1,800 shares of Company M, at $50 per share, and a brokerage commission of $198.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2016 | |||||
| April | 24 | Investments–Company M Stock | 90,198 | ||
| Cash | 90,198 | ||||
| (To record purchase of shares for cash) | |||||
Table (2)
- Investments–Company M Stock is an asset account. Since stock investments are purchased, asset value increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of cash paid to purchase Company M’s stock.
Prepare journal entry for sale of 2,600 shares of Company W, at $38, with a brokerage of $100.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2016 | |||||
| June | 1 | Cash | 98,700 | ||
| Loss on Sale of Investments | 5,560 | ||||
| Investments–Company W Stock | 104,260 | ||||
| (To record sale of shares) | |||||
Table (3)
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Loss on Sale of Investments is a loss or expense account. Since losses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Investments–Company W Stock is an asset account. Since stock investments are sold, asset value decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working Notes:
Calculate the realized gain (loss) on sale of stock.
Step 1: Compute cash received from sale proceeds.
Step 2: Compute cost of stock investment sold.
Step 3: Compute realized gain (loss) on sale of stock.
Note: Refer to Steps 1 and 2 for value and computation of cash received and cost of stock investment sold.
Prepare journal entry for the dividend received from Company W shares.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2016 | |||||
| June | 30 | Cash | 840 | ||
| Dividend Revenue | 840 | ||||
| (To record receipt of dividend revenue) | |||||
Table (4)
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Dividend Revenue is a revenue account. Since revenues increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of dividend received on Company W’s stock.
Prepare adjusting entry for valuation of trading securities transaction.
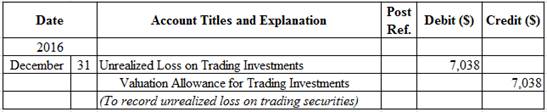
Figure (1)
- Unrealized Loss on Trading Investments is an adjustment account used to report gain or loss on adjusting cost of investment at fair market value. Since loss has occurred and losses reduce stockholders’ equity value, and a decrease in stockholders’ equity value is debited.
- Valuation Allowance for Trading Investments is a contra-asset account. The account is credited because the market price was decreased (loss) to $179,400 from the cost of $136,438.
Working Notes:
Compute the unrealized gain (loss) as on December 31, 2016.
Step 1: Compute the fair value of the portfolio of the trading investment.
| Security | Number of Shares | Fair Market Value | = | Fair Market Value of Investment | |
| Company W | 2,400 shares | $38 | = | $91,200 | |
| Company M | 1,800 shares | 49 | = | 88,200 | |
| Total | $179,400 | ||||
Table (5)
Step 2: Compute the cost per share of Company W.
Step 3: Compute the cost per share of Company M.
Step 4: Compute the cost of the portfolio of the trading investment, as on December 31.
| Security | Number of Shares | Cost per Share | = | Cost of Investment | |
| Company W | 2,400 shares | $40.10 | = | $96,240 | |
| Company M | 1,800 shares | 50.11 | = | 90,198 | |
| Total | $186,438 | ||||
Table (6)
Note: Refer to Steps 3 and 4 for cost per share of Company W and Company M.
Step 5: Compute the unrealized gain (loss) as on December 31, 2016.
| Details | Amount ($) |
| Trading investments at fair value, December 31 (From Table-5) | $179,400 |
| Less: Trading investments at cost, December 31 (From Table-6) | (186,438) |
| Unrealized loss on trading investments | $(7,038) |
Table (7)
Prepare journal entry for the purchase of 3,500 shares of Company D, at $30 per share, and a brokerage commission of $175.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2017 | |||||
| April | 4 | Investments–Company D Stock | 105,715 | ||
| Cash | 105,715 | ||||
| (To record purchase of shares for cash) | |||||
Table (8)
:
- Investments–Company D Stock is an asset account. Since stock investments are purchased, asset value increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of cash paid to purchase Company D’s stock.
Prepare journal entry for the dividend received from Company W shares.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2017 | |||||
| June | 28 | Cash | 960 | ||
| Dividend Revenue | 960 | ||||
| (To record receipt of dividend revenue) | |||||
Table (9)
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Dividend Revenue is a revenue account. Since revenues increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of dividend received on Company W’s stock.
Prepare journal entry for sale of 700 shares of Company D at $32, with a brokerage of $50.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2017 | |||||
| September | 9 | Cash | 22,350 | ||
| Gain on Sale of Investments | 1,315 | ||||
| Investments–Company D Stock | 21,035 | ||||
| (To record sale of shares) | |||||
Table (10)
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Gain on Sale of Investments is a revenue account. Since revenues increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
- Investments–Company D Stock is an asset account. Since stock investments are sold, asset value decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working Notes:
Calculate the realized gain (loss) on sale of stock.
Step 1: Compute cash received from sale proceeds.
Step 2: Compute cost of stock investment sold.
Step 3: Compute realized gain (loss) on sale of stock.
Note: Refer to Steps 1 and 2 for value and computation of cash received and cost of stock investment sold.
Prepare adjusting entry for valuation of trading securities transaction.
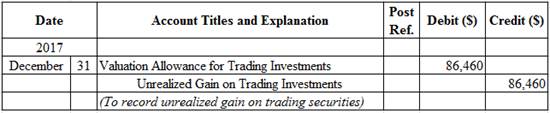
Figure (2)
- Valuation Allowance for Trading Investments is a contra-asset account. The account is debited because the market price was increased (gain).
- Unrealized Gain on Trading Investments is an adjustment account used to report gain or loss on adjusting cost of investment at fair market value. Since gain has occurred and gains increase stockholders’ equity value, and an increase in stockholders’ equity value is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute the unrealized gain (loss) as on December 31, 2017.
| Details | Amount ($) |
| Unrealized gain as on December 31, 2017 | $79,422 |
| Add: Unrealized loss as on December 31, 2016 (From Table-8) | 7,038 |
| Unrealized gain on trading investments | $86,460 |
Table (11)
(2)
To indicate: The presentation of trading investments on the current assets section of the balance sheet.
(2)
Explanation of Solution
Solution:
Balance sheet presentation:
| Company S | ||
| Balance Sheet (Partial) | ||
| December 31, 2017 | ||
| Assets | ||
| Current assets: | ||
| Trading investments (at cost) | $270,578 | |
| Add valuation allowance for trading investments | 79,422 | |
| Trading investments (at fair value) | $350,000 | |
Table (12)
(3)
To discuss: The reporting of trading investments on the financial statements.
(3)
Explanation of Solution
Unrealized gain or loss is the result of change in trading investments cost and fair values, and reported as Other Revenues (Losses) on the income statement. The unrealized gain will be added to the net income and unrealized loss will be deducted from the net income. In 2016, Company S would report $7,038 of unrealized loss as Other Losses on the income statement. In 2017, Company S would report $86,460 of unrealized gain as Other Income on the income statement.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Bundle: Accounting, Chapters 1-13, 26th + Working Papers, Chapters 1-17 For Warren/reeve/duchac's Accounting, 26th And Financial Accounting, 14th + ... For Warren/reeve/duchac's Accounting, 26th
- I am looking for the correct answer to this general accounting question with appropriate explanations.arrow_forwardCould you help me solve this financial accounting question using appropriate calculation techniques?arrow_forwardSubject General Accounting: Exxon Company has a DSO of 22 days. The company's average daily sales are $45,000. What is the level of its accounts receivable? Assume there are 365 days in a year.arrow_forward
- I am searching for the correct answer to this financial accounting problem with proper accounting rules.arrow_forwardI am searching for the correct answer to this financial accounting problem with proper accounting rules.arrow_forwardZephyr Products produces a product that has a variable cost of $20 per unit. The company's fixed costs are $72,000. The product sells for $35 a unit and the company desires to earn a $48,000 profit. What is the volume of sales in units required to achieve the target profit?arrow_forward
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning





