
Concept explainers
Calculation of annual lease payments; residual value
• LO15–2, LO15–6
Each of the four independent situations below describes a finance lease in which annual lease payments are payable at the beginning of each year. The lessee is aware of the lessor’s implicit
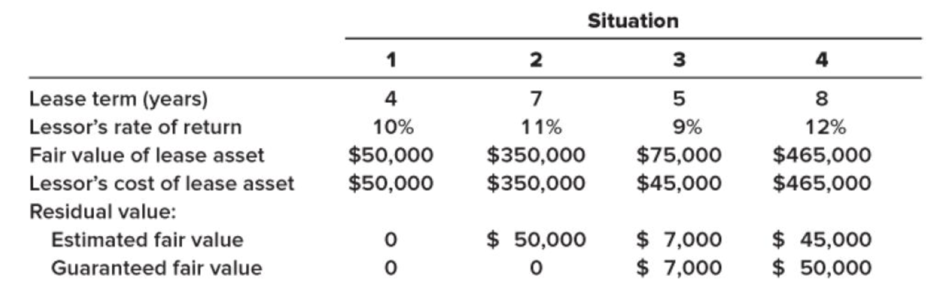
Required:
For each situation, determine:
a. The amount of the annual lease payments as calculated by the lessor.
b. The amount the lessee would record as a right-of-use asset and a lease liability.
(Situation 1) (a)
Lease
Lease is a contractual agreement whereby the right to use an asset for a particular period of time is provided by the owner of the asset to the user of the asset. The owner, who possesses the asset, is termed as ‘Lessor’ and user, to whom the right is transferred to, is termed as ‘Lessee’.
To Determine: the annual lease payments as calculated by the lessor.
Explanation of Solution
The lease payments at the beginning of each year is calculated by dividing fair value of the leased asset by present value of annuity for 4 years at the rate of 10%.
Therefore, annual lease payment as calculated by lessor is $14,340.
(Situation 1) (b)
Explanation of Solution
The lessor cost of lease asset is reported by the lessee as right-of-use asset$50,000.
Therefore, amount the lessee would record as right-of-use and lease liability is $50,000.
(Situation 2) (a)
Explanation of Solution
Working notes:
Calculate the present value of residual value
Calculate the amount to be recovered through periodic lease payments
| Particulars | Amounts ($) |
| Amount to be recovered (Fair value) | 350,000 |
| Less: Present value of residual value (1) | 24,083 |
| Amount to be recovered through periodic lease payments | 325,917 |
(2)
In case of lessor, even if the residual value is not guaranteed, the lessor is expected to receive. So, the lessor will assess the residual asset as contributing to amount needed to recover its investment causing the lessee’s lease payments to be lower.
Therefore, annual lease payment as calculated by lessor is $62,310.
(Situation 2) (b)
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the lessee would record as right-of-use asset and lease liability
Therefore, amount the lessee would record as right-of-use and lease liability is $325,917.
(Situation 3) (a)
Explanation of Solution
Working notes:
Calculate the present value of residual value
Calculate the amount to be recovered through periodic lease payments
| Particulars | Amounts ($) |
| Amount to be recovered (Fair value) | 75,000 |
| Less: Present value of residual value (4) | 4,550 |
| Amount to be recovered through periodic lease payments | 70,450 |
(5)
In case of lessor, even if the residual value is not guaranteed, the lessor is expected to receive. So, the lessor will assess the residual asset as contributing to amount needed to recover its investment causing the lessee’s lease payments to be lower.
Therefore, annual lease payment as calculated by lessor is $16,617.
(Situation 3) (b)
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the lessee would record as right-of-use asset and lease liability
Therefore, amount the lessee would record as right-of-use and lease liability is $70,450.
(Situation 4) (a)
Explanation of Solution
Working notes:
Calculate the present value of excess guaranteed residual value
Calculate the present value of residual value
Calculate the amount to be recovered through periodic lease payments
| Particulars | Amounts ($) |
| Amount to be recovered (Fair value) | 465,000 |
| Less: Present value of excess guaranteed residual value (7) | 2,019 |
| Less: Present value of residual value (8) | 18,175 |
| Amount to be recovered through periodic lease payments | 444,806 |
(9)
If a lessee guaranteed residual value is expected, the present value of the payments is added to the present value of lease payments which the lessee records as right-of-use of asset and lease liability. In case of a finance lease, the lessor records it as lease receivable.
Therefore, annual lease payment as calculated by lessor is $79,947.
(Situation 4) (b)
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the lessee would record as right-of-use asset and lease liability
Therefore, amount the lessee would record as right-of-use and lease liability is $446,825.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting
- Kindly help me with this General accounting questions not use chart gpt please fast given solutionarrow_forwardPlease provide the correct answer to this general accounting problem using accurate calculations.arrow_forwardI am looking for help with this financial accounting question using proper accounting standards.arrow_forward
- I need the correct answer to this financial accounting problem using the standard accounting approach.arrow_forwardCan you explain the correct approach to solve this general accounting question?arrow_forwardPlease given correct answer for General accounting question I need step by step explanationarrow_forward
- Can you solve this financial accounting question using valid financial methods?arrow_forwardPlease provide the correct answer to this financial accounting problem using accurate calculations.arrow_forwardPlease help me solve this general accounting problem with the correct financial process.arrow_forward
- Please provide the solution to this financial accounting question using proper accounting principles.arrow_forwardPlease explain this financial accounting problem with accurate financial standards.arrow_forwardI am searching for the correct answer to this general accounting problem with proper accounting rules.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





