
(a)
Interpretation:
The name of the given compound has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
The hydrocarbons which contain only single bonds are said to be
The Alkanes are named following some rules:
- The name of the alkane is given by the number of carbon atoms present in the chain. It is said to be Root of the alkane.
Root = number of carbon atoms in chain.
- To name the root, for one carbon atom, the root name use is meth-. For two carbon atoms, the root name is eth-, for three carbon atoms, it is prop-, for four carbon atoms, it is but-, for five carbon atoms, it is pent- and so on.
- The root name is followed by Suffix. Suffix indicates the
functional group present in the compound. It is placed after the root name.
Suffix = name of the functional group present in the compound.
- The root name also contains Prefix. Prefix is the groups attached to the root. It indicates the branched carbon atoms on the root chain and name according to the root specifying the carbon number on which it is placed. It contains –yl in name end. The prefix is placed before the root name.
Prefix = name of the branched carbon atoms on chain.
- The name of the alkane is given in the form
Prefix + Root + Suffix
(a)
Explanation of Solution
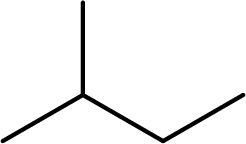
The given compound is
To give the compound a systematic name, first the root has to be identified. The root consists of number of carbon atoms present in the longest chain. In the given compound, the longest chain contains four carbon atoms. Hence, the name but- is used as the root. The carbon chain is numbered in the way that the substituents get the lowest number.
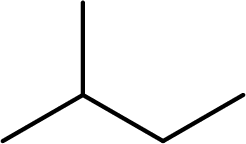
As the given compound contains only single bonds, it is an alkane. For alkanes, the suffix used is –ane. The suffix is added to the root name.
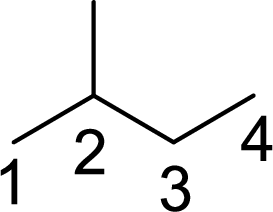
The given compound contains branched carbon atom. It contains one carbon atom (
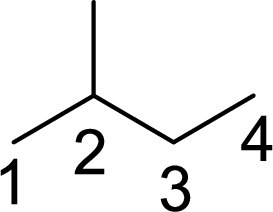
The systematic name of the given compound is
Root = but-
Suffix = -ane
Prefix = 2-methyl-
The name of the given compound is given as 2-methylbutane.
(b)
Interpretation:
The name of the given compound has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
The hydrocarbons which contain only single bonds are said to be cycloalkanes. The general formula for alkanes can be given as
The cycloalkanes are named following some rules:
- The name of the alkane is given by the number of carbon atoms present in the ring. It is said to be Root of the alkane.
Root = number of carbon atoms in ring.
- To name the root, for one carbon atom, the root name use is meth-. For two carbon atoms, the root name is eth-, for three carbon atoms, it is prop-, for four carbon atoms, it is but-, for five carbon atoms, it is pent- and so on.
- The root name is followed by Suffix. Suffix indicates the functional group present in the compound. It is placed after the root name.
Suffix = name of the functional group present in the compound.
- The root name also contains Prefix. Prefix is the groups attached to the root. It indicates the branched carbon atoms on the root chain and name according to the root specifying the carbon number on which it is placed. It contains –yl in name end. The prefix is placed before the root name.
Prefix = name of the branched carbon atoms on chain.
- The name of the alkane is given in the form
Prefix + Root + Suffix
(b)
Explanation of Solution
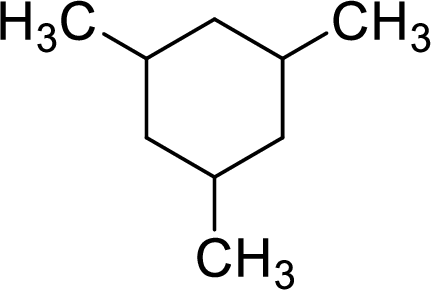
The given compound is
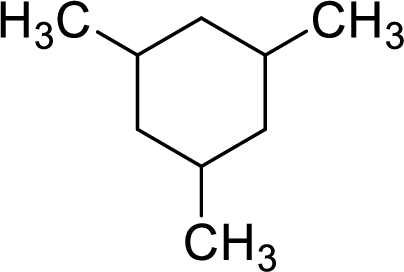
To give the compound a systematic name, first the root has to be identified. The root consists of number of carbon atoms present in the ring. In the given compound, the ring contains six carbon atoms. Hence, the name hex- is used as the root. The carbon ring is numbered in the way that the substituents get the lowest number.
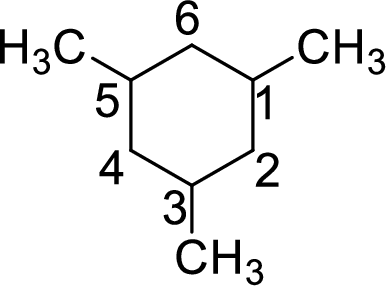
As the given compound contains only single bonds, it is an alkane. For alkanes, the suffix used is –ane. The suffix is added to the root name.
The given compound contains branched carbon atoms. It contains one carbon atom (
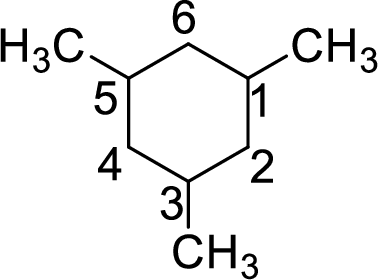
The systematic name of the given compound is
Root = cyclohex-
Suffix = -ane
Prefix = 1,3,5-trimethyl-
The name of the given compound is given as 1,3.5-trimethylcyclohexane.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given compound (1,2-diethylcyclopentane) has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The structure of the compound is given by its systematic name.
To give the structure from the name of the compound, the root name has to be identified. The root name indicates the number of carbon atoms present in the longest chain.
Then the functional group (suffix) has to be identified. It indicates whether any functional groups are present in the compound, it also gives whether the compound is an alkane or
The prefix of the name indicates the branched groups and their positions on the carbon chain.
The name of the compound is in the form
Prefix + Root + Suffix
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The compound given is 1,2-diethylcyclopentane.
To give the structure of 1,2-diethylcyclopentane, first the root name has to be identified. The root name indicates carbon atoms in ring. In the given compound, the root name is cyclopentane. As the suffix is –ane, it is an alkane and contains only single bonds. Cyclopentane consists of five carbon atoms in ring.
As the name is 1,2-diethylcyclopentane, it contains prefix 1,2-diethyl. The ethyl group contains two carbon atoms (
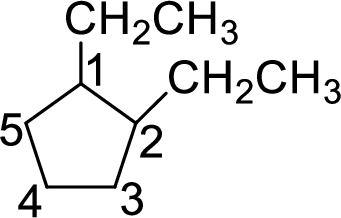
The structure of 1,2-diethylcyclopentane is given as
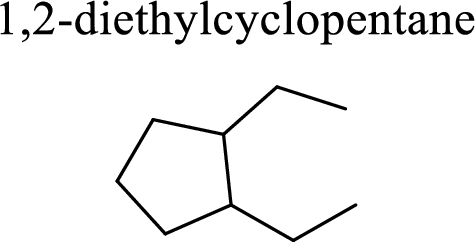
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given compound (2,4,5-trimethylnonane) has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The structure of the compound is given by its systematic name.
To give the structure from the name of the compound, the root name has to be identified. The root name indicates the number of carbon atoms present in the longest chain.
Then the functional group (suffix) has to be identified. It indicates whether any functional groups are present in the compound, it also gives whether the compound is an alkane or alkene or alkyne.
The prefix of the name indicates the branched groups and their positions on the carbon chain.
The name of the compound is in the form
Prefix + Root + Suffix
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The compound given is 2,4,5-trimethylnonane.
To give the structure of 2,4,5-trimethylnonane, first the root name has to be identified. The root name indicates carbon atoms in longest chain. In the given compound, the root name is nonane. In nonane, nine carbon atoms are present in the chain. As the suffix is –ane, it is an alkane and contains only single bonds. The structure of nonane is given as
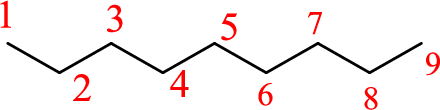
As the name is 2,4,5-trimethylnonane, it contains prefix 2,4,5-trimethyl. It indicates that the carbon chain is substituted at three positions. The substituent groups are methyl (
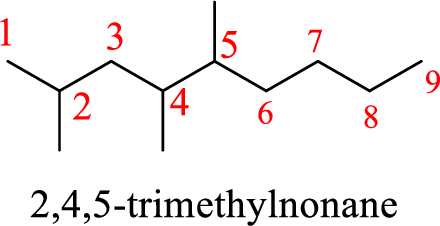
The structure of 2,4,5-trimethylnonane is given as
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Student Study Guide for Silberberg Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change
- 20.33 Think-Pair-Share (a) Rank the following dienes and dienophiles in order of increasing reactivity in the Diels-Alder reaction. (i) CO₂Et (ii) COEt || CO₂Et MeO MeO (b) Draw the product that results from the most reactive diene and most reactive dienophile shown in part (a). (c) Draw a depiction of the orbital overlap involved in the pericyclic reaction that oc- curs between the diene and dienophile in part (b). (d) Is the major product formed in part (b) the endo or exo configuration? Explain your reasoning.arrow_forward20.40 The following compound undergoes an intramolecular Diels-Alder reaction to give a tricyclic product. Propose a structural formula for the product. CN heat An intramolecular Diels-Alder adductarrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forward
- What is the reaction mechanism for this?arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. + Drawing Arrows CH3ONA, CH3OH heat : Br:O Na → H H Br Na + H H H H H :0: .H + Undo Reset Done Q CH3 Drag To Pan +arrow_forwardWhat is the reaction mechanism for this?arrow_forward
- 20.19 Predict the structure of the major 1,2-addition product formed by reaction of one mole of Cl₂ with 3-methylenecyclohexene. Also predict the structure of the 1,4-addition product formed under these conditions. 20.20 Which of the two molecules shown do you expect to be the major product formed by 1,2-addition of HCI to cyclopentadiene? Explain. Cyclopentadiene + HC 3-Chlorocyclopentene (racemic) or 4-Chlorocyclopentene (racemic)arrow_forward20.35 Propose structural formulas for compounds A and B and specify the configuration of compound B. EtO₂C 250°C C14H2004 CO₂Et 1. Oso, then NaHSO3 2. HIO4 C14H2006 A Barrow_forward20.21 Predict the major product formed by 1,4-addition of HCI to cyclopentadiene. 20.22 Draw structural formulas for the two constitutional isomers with the molecular for- mula C₂H,Br, formed by adding one mole of Br, to cyclopentadiene.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





