
Concept explainers
Draw the plot for
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The specific gravity of the loessial soil is
The liquid limit of the soil is
The dry density of the soil is
Calculation:
Refer to the Equation (11.5) in the textbook.
Consider the density of water is
Consider the liquid limit of 10.
Find the natural dry unit weight
Substitute
Tabulate the remaining calculated values as in Table 1.
| LL | |
| 10 | 133.434 |
| 15 | 120.545 |
| 20 | 109.927 |
| 25 | 101.029 |
| 30 | 93.4626 |
| 35 | 86.9508 |
| 40 | 81.2874 |
Table 1
Draw the graph between liquid limit versus the natural dry unit weight as in Figure 1.
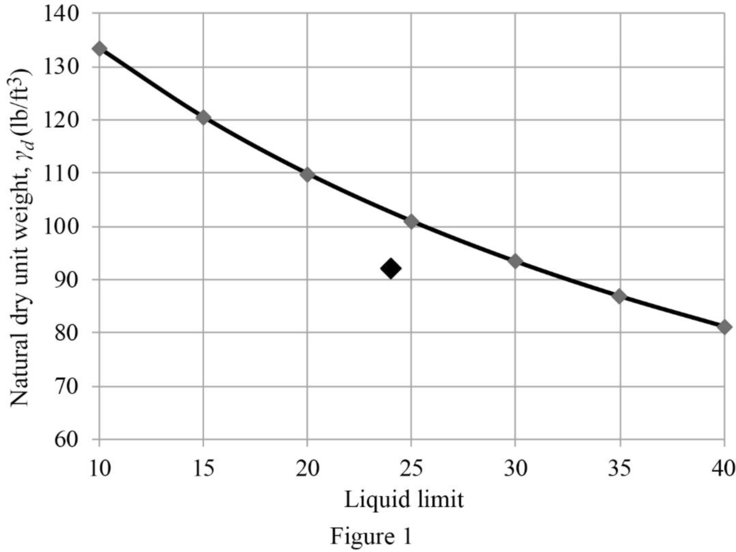
Mark the liquid limit of 24 corresponding to the dry unit weight of
Thus, collapse will occur.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Course List)
- For an reinforced concrete two-way slab shown in figure under the load (P). (the slab continuous over all edges - all sides are fixed), Determine (By using yield line theory): A- Draw the Yield line Pattern B- Determine the moment m C- Find The required flexural steel to resist the loads causing the slab to collapse if P = 200 KN, f=28 MPa, fy = 420 MPa d = 120 mm. Use 10 mm bars. Draw the yield line and (Qmin = 0.002) 2m solve PO 6 m 3 m -8 marrow_forwardFind the internal torques for segments AB, BC, and CD (in N-m) by drawing the internal torque diagram, the maximum torsional shear on the shaft in MPa, and the relative rotation of section A with respect to section D in degrees.arrow_forwardFor an reinforced concrete two-way slab shown in figure under the load (P). (the slab continuous over all edges - all sides are fixed), Solve by using equilibrium method A- Draw the Yield line Pattern B- Determine the moment m C- Find The required flexural steel to resist the loads causing the slab to collapse if P = 200 kN, f=28 MPa, fy = 420 MPa d = 120 mm. Use 10 mm bars. (Pmin = 0.002) 2 m 6 m -8 m 3 marrow_forward
- A double-T simply supported concrete beam its cross section is shown in Figure, is prestressed with 2 tendons each 400 mm². Determine the allowable service load. Use span 12 m, fse = 1300 MPa, fe = 40 MPa, y = 25 kN/m³. = 1200 mm >09 *100* As = 400 +100+ As = 400 400 1400+arrow_forwardA double-T simply supported concrete beam its cross section is shown in Figure, is prestressed with 2 tendons each 400 mm². Determine the allowable service load. Use span 12 m, fse = 1300 MPa, fc = 40 MPa, y = 25 kN/m³. = 1200 mm >09< *100* As = 400 +100+ As = 400 400 1400+arrow_forwardA prestressed simply supported 15 m span beam with rectangular box section is post-tensioned by straight high tensile steel wires as shown in Figure. The prestressing wires are placed at the center line of the flanges and initially stressed to 850 N/mm². The beam is required to carry a uniformly distributed superimposed load of 4.5 kN/m in addition to its weight. If the concrete stresses are not to exceed 17 MPa in compression and 1 MPa in tension at service stage, calculate the range of the total prestressing wires area required. Ignore prestressing force losses in your answer. (Ye kN/m³). = 24 2As 400 As 80 80; 750arrow_forward
- A simply supported rectangular prestressed concrete beam, of span 13 m and its cross section as shown in figure, is carrying a live load equals to 30 kN/m in addition to its weight, compute the following stresses and compare it with ACI allowable stress: a) Bottom fiber stress at support in initial stage. b) Top fiber stress at mid span in final stage. Use y = 24 kN/m³, As = 600 mm², initial stress of the prestressed steel = 1200 MPa, total losses is 20%, fci = 22 MPa, and fo' = 28 MPa 800 mm 3 As 400 mm As 340 mm 340 mmarrow_forwardA study of the properties of metal plate-connected trusses used for roof support yielded the following observations on axial stiffness index (kips/in.) for plate lengths 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12 in: 4: 320.2 409.5 311.0 326.5 316.8 349.8 309.7 6: 401.1 347.2 361.0 404.5 331.0 348.9 381.7 8: 395.4 366.2 351.0 357.1 409.9 367.3 382.0 10: 356.7 452.9 461.4 433.1 410.6 384.2 362.6 12: 415.4 441.8 419.9 410.7 473.4 441.2 465.8 USE SALT Does variation in plate length have any effect on true average axial stiffness? State the relevant hypotheses using analysis of variance. O Ho M1 M2 M3 = μ4=μ5 Ha all five μ's are unequal Ho: M1 M2 M3 #44 #μ5 Ha all five μ's are equal Ho: M₁ μ2 43 #44 #μ5 H₁: at least two μ,'s are equal O Ho M1 M2 M3 = μ4=μ5 Ha at least two μ's are unequal Test the relevant hypotheses using analysis of variance with a = 0.01. Display your results in an ANOVA table. (Round your answers to two decimal places.) Degrees of Sum of Mean Source Squares Squares f freedom Treatments Error…arrow_forward1-Define a cartesion system 2 identify the structure's supports and the type of structure (2D) or 3D 3-If the structure has more than one element dismember the structure and draw free body diagram(show all actions and reactions) on each element independently 4- Determine the type of suports 5- show the unkown supports reactions with any assumed direction but you cannot change the assumed force direction once you dicede 6-In a common joint, you can dicide on the force direction in one element, however, in the other one you need to follow the Newton'ns 3rd law and shoe the opposite direction 7- if you have multiple actions forces in the system, find force components for each foce independently use Sin/Cos/Tan functions to find forces components in two perpendicular directions 8- Add forces in each direction since they are paralled forces Rx=fx Ry=fy Rz= fyarrow_forward
- Physical properties of six flame-retardant fabric samples were investigated in an article. Use the accompanying data and a 0.05 significance level to determine whether a linear relationship exists between stiffness x (mg-cm) and thickness y (mm). x y 8.08 24.33 12.39 6.99 23.97 35.64 0.25 0.68 0.30 0.28 0.82 0.57 State the appropriate null and alternative hypotheses. ○ Ho: p = 0 H₂: pO ○ Hop = 0 Hap #0 Compute the value of the sample correlation coefficient, r. Round your answer to four decimal places. Calculate the test statistic and determine the P-value. (Round your test statistic to two decimal places and your P-value to three decimal places.) P-value = State the conclusion in the problem context. O Fail to reject Ho. The data indicates that the population correlation coefficient differs from 0. Fail to reject Ho. The data does not indicate that the population correlation coefficient differs from 0. Reject Ho. The data indicates that the population correlation coefficient differs…arrow_forward1-Define a cartesion system 2 identify the structure's supports and the type of structure (2D) or 3D 3-If the structure has more than one element dismember the structure and draw free body diagram(show all actions and reactions) on each element independently 4- Determine the type of suports 5- show the unkown supports reactions with any assumed direction but you cannot change the assumed force direction once you dicede 6-In a common joint, you can dicide on the force direction in one element, however, in the other one you need to follow the Newton'ns 3rd law and shoe the opposite direction 7- if you have multiple actions forces in the system, find force components for each foce independently use Sin/Cos/Tan functions to find forces components in two perpendicular directions 8- Add forces in each direction since they are paralled forces Rx=fx Ry=fy Rz= fyarrow_forward- - A study reports data on the effects of the drug tamoxifen on change in the level of cortisol-binding globulin (CBG) of patients during treatment. With age = x and ACBG = y, summary values are n = 26, Ex, = 1613, Σ(x, x)² = 3756.96, Ey, = 281.9, (y, v)² = 465.34, and Exy, = 16,709. (a) Compute a 90% CI for the true correlation coefficient p. (Round your answers to four decimal places.) (b) Test Ho: p =-0.5 versus Ha: p< -0.5 at level 0.05. Calculate the test statistic and determine the P-value. (Round your test statistic to two decimal places and your P-value to four decimal places.) P-value = State the conclusion in the problem context. Fail to reject Ho. There is evidence that p < -0.5. Reject Ho. There is no evidence that p < -0.5. Reject Ho. There is evidence that p < -0.5. Fail to reject Ho. There is no evidence that p < -0.5. (c) In a regression analysis of y on x, what proportion of variation in change of cortisol-binding globulin level could be explained by variation in…arrow_forward
 Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning



