
a)
Whether the purchase of palm trees creates a negative externality, a positive externality, or no externality.
a)
Explanation of Solution
The purchase of palm trees creates a positive externality because, with the plantation of trees, all people on the island will get the benefits of shelter, beauty, and erosion control. Therefore, planting the cost of trees can be bear by one person but it will provide benefits to the whole society which shows a positive externality.
Introduction: The benefits which are obtained by the third party who is not buying, selling, or consuming the good are called external benefits such as using a vehicle to travel that reduces the congestion on the road because it provides benefit to other drivers so that they can drive quickly and safely.
b)
The marginal
b)
Explanation of Solution
The marginal social cost and the marginal social benefit of palm trees on the graph are as follows:
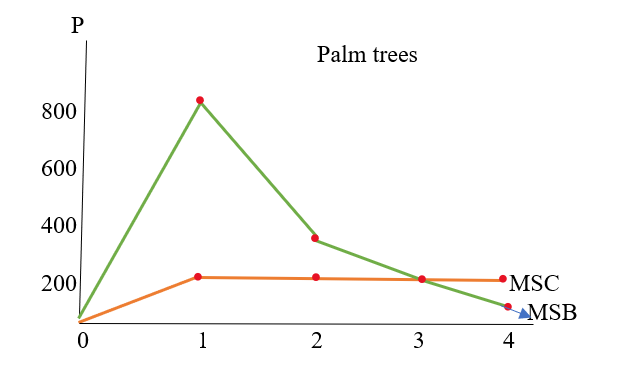
Green curve represents the marginal social benefit curve and the orange curve shows the marginal social cost.
The data of the graph is obtained from the following table:
| Q of palm trees | Total social cost (total private cost) | Marginal social cost | Total private benefit or total social benefit | Marginal social benefit or marginal private benefit |
| 0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| 1 | $200 | $200 | 8 | 800 |
| 2 | $400 | $200 | 12 | 400 |
| 3 | $600 | $200 | 14 | 200 |
| 4 | $800 | $200 | 15 | 100 |
As the number of residents is 100, then marginal social benefit:
Introduction: Marginal private benefit is the benefit that is obtained by an individual by using an extra unit of the product. And, the marginal social benefit is the benefit that is obtained by the whole society as well as the individual by producing an extra unit of a product.
Marginal private cost is the cost that is incurred by an individual by using an extra unit of the product. And, the marginal social cost is the expense which is incurred by the whole society due to the production of an extra unit of a product.
c)
The number of palm trees that would be purchased if they were sold in a private market
c)
Explanation of Solution
In the private market, no tree would be sold at a price less than the cost and people will prefer to purchase where the price is minimum. And, for a quantity of 3 palm trees, the marginal social cost is equal to the marginal social benefit, which means 3 palm trees would be purchased if they were sold in a private market because after that cost will increase more than the benefit.
Introduction: Private market considers investments from individuals or companies which are non-government and it runs for profit where the state does not have any control over the companies.
d)
The socially optimal quantity of palm trees.
d)
Explanation of Solution
Social marginal cost and social marginal benefit are equal at the quantity of 3 palm trees which means 3 palm trees is the socially optimal quantity.
Introduction: The quantity where all the costs and benefits are accounted for is called socially optimal quantity.
e)
Whether palm trees are a private good, a public good, or a common resource
e)
Explanation of Solution
In this case, the palm tree is a public good because every person or resident of the island can benefit from these trees as they can enjoy shade, beauty, and erosion control. Moreover, palm tree, in this case, is not rival in consumption. Therefore, the palm tree is a public good.
Introduction: A public good covers both non-excludable as well as non-rival. And, a private good is excludable and rival in consumption which may prevent people from consuming when one person consumes the same good.
f)
The appropriate governmental policy response to this situation.
f)
Explanation of Solution
To increase social benefits and lower private costs, the government will use a policy that subsidizes palm trees because it will increase the number of trees to be purchased. This policy will provide more benefits to the whole residents of the island.
Introduction: Government policies are made to control the exploitation of resources and provide equal benefits to all citizens of the country at affordable costs.
Chapter 14R Solutions
Krugman's Economics For The Ap® Course
- Thanks in advance!arrow_forwardI need help figuring this out. I'm pretty sure this is correct?If Zambia is open to international trade in oranges without any restrictions, it will import 180 tons of oranges.I can't figure these two out: 1) Suppose the Zambian government wants to reduce imports to exactly 60 tons of oranges to help domestic producers. A tariff of ???? per ton will achieve this. 2) A tariff set at this level would raise ????in revenue for the Zambian government.arrow_forward16:10 ← BEC 3701 - Assignments-... KWAME NKRUMAH UNIVERSITY TEACHING FOR EXCELLENCE SCHOOL OF BUSINESS STUDIES DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS AND FINANCE ADVANCED MICRO-ECONOMICS (BEC 3701) Assignments INSTRUCTIONS: Check instructions below: LTE 1) Let u(q1,q2) = ln q₁ + q2 be the (direct) utility function, where q₁ and q2the two goods. Denote P₁ and P2 as the prices of those two goods and let M be per period money income. Derive each of the following: a) the ordinary or Marshallian demand functions q₁ = d₂ (P₁, P₂, M) for i = 1,2 [3 Marks] b) the compensated or Hicksian demand functions q₁ = h₂ (P₁, P2, M) for i = 1,2 [3 Marks] c) the Indirect Utility Function uº = v(P₁, P2, M) [3 Marks] d) the Expenditure Function E(P1, P2, U°) [3 Marks] e) Draw a diagram of the solution. There should be two graphs, one above the other; the first containing the indifference curves and budget constraint that characterize the solution to the consumer's choice problem; the second characterizing the demand…arrow_forward
- How would you answer the question in the News Wire “Future Living Standards”? Why?arrow_forwardal Problems (v) T (ix) F 1. Out of total number of 2807 women, who were interviewed for employment in a textile factory, 912 were from textile areas and the rest from non-textile areas. Amongst the married women, who belonged to textile areas, 347 were having some work experience and 173 did not have work experience, while for non-textile areas the corresponding figures were 199 and 670 respectively. The total number of women having no experience was 1841 of whom 311 resided in textile areas. Of the total number of women, 1418 were unmarried and of these the number of women having experience in the textile and non-textile areas was 254 and 166 respectively. Tabulate the above information. [CA. (Foundation), May 2000 Exactly (14) of the total employees of a sugar mill were these were married and one-halfarrow_forwardHow did Jennifer Lopez use free enterprise to become successful ?arrow_forward
- An actuary analyzes a company’s annual personal auto claims, M and annual commercialauto claims, N . The analysis reveals that V ar(M ) = 1600, V ar(N ) = 900, and thecorrelation between M and N is ρ = 0.64. Compute V ar(M + N ).arrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forwardAnswer in step by step with explanation. Don't use Ai.arrow_forward
- Use the figure below to answer the following question. Let I represent Income when healthy, let I represent income when ill. Let E [I] represent expected income for a given probability (p) of falling ill. Utility у в ULI income Is есте IM The actuarially fair & partial contract is represented by Point X × OB A Yarrow_forwardSuppose that there is a 25% chance Riju is injured and earns $180,000, and a 75% chance she stays healthy and will earn $900,000. Suppose further that her utility function is the following: U = (Income) ³. Riju's utility if she earns $180,000 is _ and her utility if she earns $900,000 is. X 56.46; 169.38 56.46; 96.55 96.55; 56.46 40.00; 200.00 169.38; 56.46arrow_forwardUse the figure below to answer the following question. Let là represent Income when healthy, let Is represent income when ill. Let E[I], represent expected income for a given probability (p) of falling ill. Utility & B естве IH S Point D represents ☑ actuarially fair & full contract actuarially fair & partial contract O actuarially unfair & full contract uninsurance incomearrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





