
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The
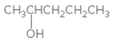
Concept Introduction:
When H2O is lost from a material it is called dehydration. When an alcohol is treated with a strong acid such as H2SO4, a water molecule is lost by breaking two adjacent bonds C-OH and C-H and forming a new double bond, producing an alkene. This is an elimination reaction.
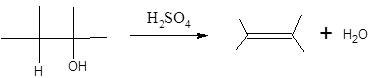
In this reaction more than one type of alkene may produce. But one of them is the major product.
According to Zaitsev rule, the major product alkene formed by elimination, is that which possess more alkyl groups bonded to it
(b)
Interpretation:
The alkene formed when the given alcohol is treated with H2SO4 should be determined. The major product should be predicted using Zaitsev rule.
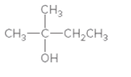
Concept Introduction:
When H2O is lost from a material it is called dehydration. When an alcohol is treated with a strong acid such as H2SO4, a water molecule is lost by breaking two adjacent bonds C-OH and C-H and forming a new double bond, producing an alkene. This is an elimination reaction.
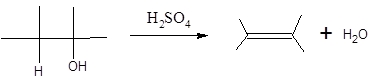
In this reaction more than one type of alkene may produce. But one of them is the major product.
According to Zaitsev rule, the major product alkene formed by elimination, is that which possess more alkyl groups bonded to it
(c)
Interpretation:
The alkene formed when the given alcohol is treated with H2SO4 should be determined. The major product should be predicted using Zaitsev rule.
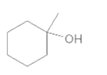
Concept Introduction:
When H2O is lost from a material it is called dehydration. When an alcohol is treated with a strong acid such as H2SO4, a water molecule is lost by breaking two adjacent bonds C-OH and C-H and forming a new double bond, producing an alkene. This is an elimination reaction.
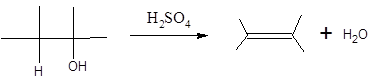
In this reaction more than one type of alkene may produce. But one of them is the major product.
According to Zaitsev rule, the major product alkene formed by elimination, is that which possess more alkyl groups bonded to it
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
Loose Leaf for General, Organic and Biological Chemistry with Connect 2 Year Access Card
- Show the mechanism steps to obtain the lowerenergy intermediate: *see imagearrow_forwardSoap is made by the previous reaction *see image. The main difference between one soap and another soap isthe length (number of carbons) of the carboxylic acid. However, if a soap irritates your skin, they mostlikely used too much lye.Detergents have the same chemical structure as soaps except for the functional group. Detergentshave sulfate (R-SO4H) and phosphate (R-PO4H2) functional groups. Draw the above carboxylic acidcarbon chain but as the two variants of detergents. *see imagearrow_forwardWhat are the reactions or reagents used? *see imagearrow_forward
- The two pKa values of oxalic acid are 1.25 and 3.81. Why are they not the same value? Show the protontransfer as part of your explanation. *see imagearrow_forwardасть Identify all the bonds that gauche interact with C-OMe in the most stable conformation of the above compound.arrow_forwardPredict the reactants used in the formation of the following compounds using Acid-Catalyzed dehydration reactionarrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this?arrow_forward.. Give the major organic product(s) for each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show ll relevant stereochemistry [3 ONLY]. A H Br 1. NaCN 2 NaOH, H₂O, heat 3. H3O+ B. CH₂COOH 19000 1. LiAlH4 THF, heat 2 H₂O* C. CH Br 1. NaCN, acetone 2 H3O+, heat D. Br 1. Mg. ether 3. H₂O+ 2 CO₂ E. CN 1. (CH) CHMgBr, ether 2 H₂O+arrow_forwardAssign this COSY spectrumarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
