Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133915426
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 14.3, Problem 1PP
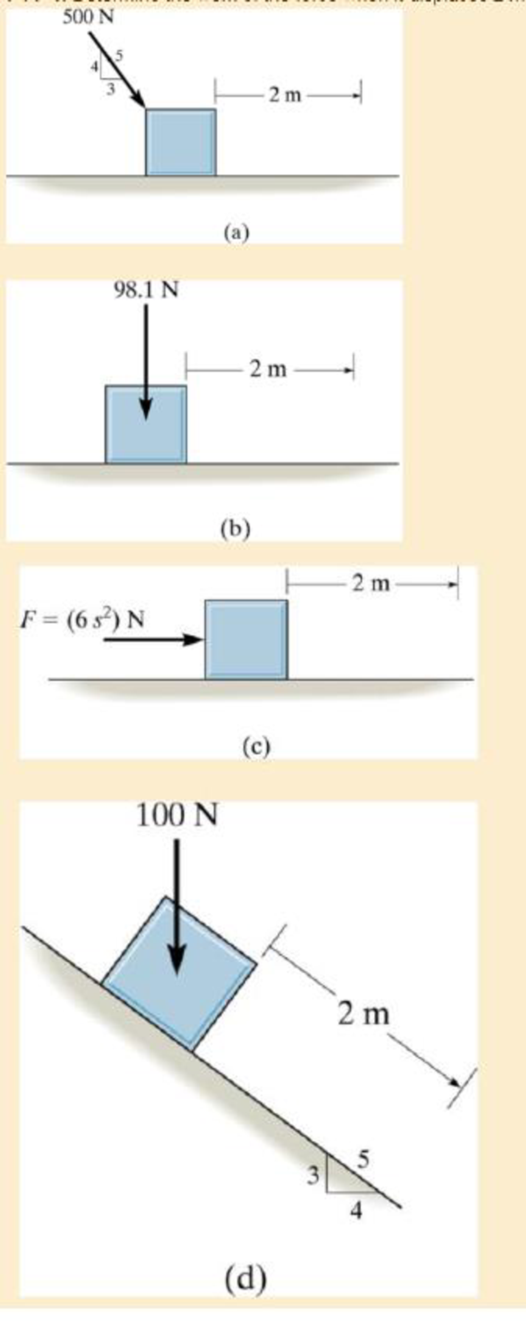
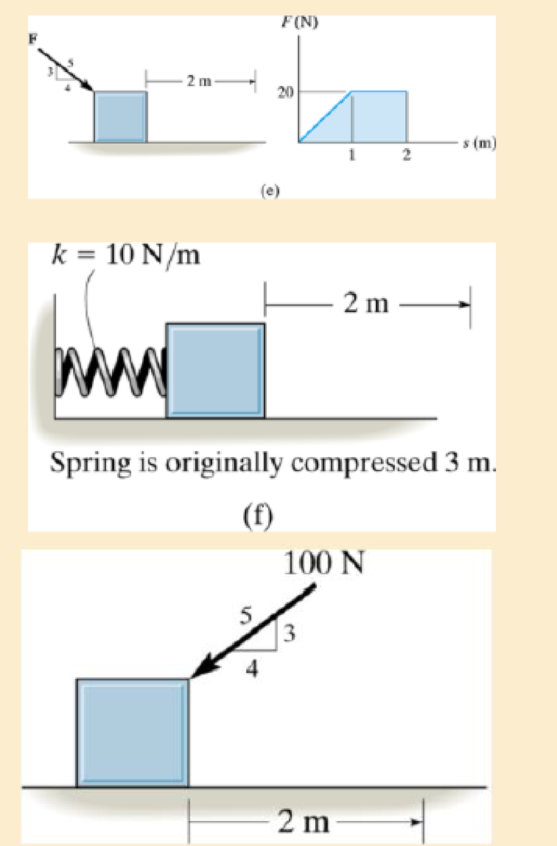
Determine the work of the force when it displaces 2 m.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
PROBLEM 3.46
The solid cylindrical rod BC of length L = 600
mm is attached to the rigid lever AB of length a
= 380 mm and to the support at C. When a 500
N force P is applied at A, design specifications
require that the displacement of A not exceed
25 mm when a 500 N force P is applied at A
For the material indicated determine the
required diameter of the rod.
Aluminium: Tall = 65 MPa, G = 27 GPa.
A
Find the equivalent mass of the rocker arm assembly with respect to the x coordinate.
k₁
mi
m2
k₁
2. Figure below shows a U-tube manometer open at both ends and containing a column of liquid
mercury of length l and specific weight y. Considering a small displacement x of the manometer
meniscus from its equilibrium position (or datum), determine the equivalent spring constant associated
with the restoring force.
Datum
Area, A
Chapter 14 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
Ch. 14.3 - Determine the work of the force when it displaces...Ch. 14.3 - Determine the kinetic energy of the 10-kg block.Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 1FPCh. 14.3 - If the motor exerts a constant force of 300 N on...Ch. 14.3 - If the motor exerts a force of F = (600 + 2s2) N...Ch. 14.3 - The 1.8-Mg dragster is traveling at 125 m/s when...Ch. 14.3 - When s = 0.5 m, the spring is unstretched and the...Ch. 14.3 - The 5-lb collar is pulled by a cord that passes...Ch. 14.3 - The 20-kg crate is subjected to a force having a...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 2P
Ch. 14.3 - The crate, which has a mass of 100 kg, is...Ch. 14.3 - The 100-kg crate is subjected to the forces shown....Ch. 14.3 - Determine the required height h of the roller...Ch. 14.3 - When the driver applies the brakes of a light...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 7PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 8PCh. 14.3 - The air spring A is used to protect the support B...Ch. 14.3 - The force F, acting in a constant direction on the...Ch. 14.3 - The force of F= 50 N is applied to the cord when s...Ch. 14.3 - Design considerations for the bumper B on the 5-Mg...Ch. 14.3 - The 2-lb brick slides down a smooth roof, such...Ch. 14.3 - Block A has a weight of 60 lb and block B has a...Ch. 14.3 - The two blocks A and B have weights WA = 60 lb and...Ch. 14.3 - A small box of mass m is given a speed of v=14gr...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 17PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 18PCh. 14.3 - If the cord is subjected to a constant force of F=...Ch. 14.3 - The crash cushion for a highway barrier consists...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 21PCh. 14.3 - The 25-lb block has an initial speed of v0 = 10...Ch. 14.3 - The 8-Kg block is moving with an initial speed of...Ch. 14.3 - At a given instant the 10-lb block A is moving...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 25PCh. 14.3 - The catapulting mechanism is used to propel the...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 27PCh. 14.3 - The 1 0-lb box falls off the conveyor belt at...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 29PCh. 14.3 - The 30-lb box A is released from rest and slides...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 31PCh. 14.3 - The block has a mass of 0.8 kg and moves within...Ch. 14.3 - The 10-lb block is pressed against the spring so...Ch. 14.3 - The spring bumper is used to arrest the motion of...Ch. 14.3 - When the 150-lb skier is at point A he has a speed...Ch. 14.3 - The spring has a stiffness k = 50 lb/ ft and an...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 37PCh. 14.3 - If the 60-kg skier passes point A with a speed of...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 39PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 40PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 41PCh. 14.4 - If the contact surface between the 20-kg block and...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 8FPCh. 14.4 - Prob. 9FPCh. 14.4 - Prob. 10FPCh. 14.4 - Prob. 11FPCh. 14.4 - Prob. 12FPCh. 14.4 - The jeep has a weight of 2500 lb and an engine...Ch. 14.4 - Determine the power Input for a motor necessary to...Ch. 14.4 - An automobile having a mass of 2 Mg travels up a 7...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 45PCh. 14.4 - To dramatize the loss of energy in an automobile,...Ch. 14.4 - Escalator steps move with a constant speed of 0.6...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 48PCh. 14.4 - Prob. 49PCh. 14.4 - Determine the power output of the draw-works motor...Ch. 14.4 - The 1000-lb elevator is hoisted by the pulley...Ch. 14.4 - The 50-lb crate is given a speed of 10ft/s in t =...Ch. 14.4 - The sports car has a mass of 2.3 Mg, and while it...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 54PCh. 14.4 - Prob. 55PCh. 14.4 - The 10-lb collar starts from rest at A and is...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 57PCh. 14.4 - The 50-lb block rests on the rough surface for...Ch. 14.4 - The escalator steps move with a constant speed of...Ch. 14.4 - If the escalator in Prob.14-46 is not moving,...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 61PCh. 14.4 - Prob. 62PCh. 14.4 - Prob. 63PCh. 14.4 - Prob. 64PCh. 14.5 - The block has a mass of 150 kg and rests on a...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 3PPCh. 14.5 - Prob. 4PPCh. 14.5 - The 2-kg pendulum bob is released from rest when...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 14FPCh. 14.5 - Prob. 15FPCh. 14.5 - Prob. 16FPCh. 14.5 - The 75-lb block is released from rest 5 ft above...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 18FPCh. 14.5 - The girl has a mass of 40 kg and center of mass at...Ch. 14.5 - The 30-lb block A is placed on top of two nested...Ch. 14.5 - The 5-kg collar has a velocity of 5 m/s to the...Ch. 14.5 - The 5-kg collar has a velocity of 5 m/s to the...Ch. 14.5 - The ball has a weight of 15 lb and is fixed to a...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 71PCh. 14.5 - The roller coaster car has a mass of 700 kg,...Ch. 14.5 - The roller coaster car has a mass of 700 kg,...Ch. 14.5 - The assembly consists of two blocks A and B which...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 75PCh. 14.5 - Prob. 76PCh. 14.5 - The roller coaster car having a mass m is released...Ch. 14.5 - The spring has a stiffness k = 200 N/m and an...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 79PCh. 14.5 - Prob. 80PCh. 14.5 - When s = 0, the spring on the firing mechanism is...Ch. 14.5 - If the mass of the earth is Me, show that the...Ch. 14.5 - A rocket of mass m is fired vertically from the...Ch. 14.5 - The 4-kg smooth collar has a speed of 3 m/s when...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 85PCh. 14.5 - The skier starts from rest at A and travels down...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 87PCh. 14.5 - Prob. 88PCh. 14.5 - When the 6-kg box reaches point A it has a speed...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 90PCh. 14.5 - Prob. 91PCh. 14.5 - The roller coaster car has a speed of 15 ft/s when...Ch. 14.5 - The 10-kg sphere C is released from rest when =...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 94PCh. 14.5 - The cylinder has a mass of 20 kg and is released...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 96PCh. 14.5 - A pan of negligible mass is attached to two...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 1CPCh. 14.5 - Prob. 1RPCh. 14.5 - The small 2-lb collar starting from rest at A...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 3RPCh. 14.5 - Prob. 4RPCh. 14.5 - Prob. 5RPCh. 14.5 - Prob. 6RPCh. 14.5 - Prob. 7RPCh. 14.5 - Prob. 8RP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. The consequences of a head-on collision of two automobiles can be studied by considering the impact of the automobile on a barrier, as shown in figure below. Construct a mathematical model (i.e., draw the diagram) by considering the masses of the automobile body, engine, transmission, and suspension and the elasticity of the bumpers, radiator, sheet metal body, driveline, and engine mounts.arrow_forward3.) 15.40 – Collar B moves up at constant velocity vB = 1.5 m/s. Rod AB has length = 1.2 m. The incline is at angle = 25°. Compute an expression for the angular velocity of rod AB, ė and the velocity of end A of the rod (✓✓) as a function of v₂,1,0,0. Then compute numerical answers for ȧ & y_ with 0 = 50°.arrow_forward2.) 15.12 The assembly shown consists of the straight rod ABC which passes through and is welded to the grectangular plate DEFH. The assembly rotates about the axis AC with a constant angular velocity of 9 rad/s. Knowing that the motion when viewed from C is counterclockwise, determine the velocity and acceleration of corner F.arrow_forward
- 500 Q3: The attachment shown in Fig.3 is made of 1040 HR. The static force is 30 kN. Specify the weldment (give the pattern, electrode number, type of weld, length of weld, and leg size). Fig. 3 All dimension in mm 30 kN 100 (10 Marks)arrow_forward(read image) (answer given)arrow_forwardA cylinder and a disk are used as pulleys, as shown in the figure. Using the data given in the figure, if a body of mass m = 3 kg is released from rest after falling a height h 1.5 m, find: a) The velocity of the body. b) The angular velocity of the disk. c) The number of revolutions the cylinder has made. T₁ F Rd = 0.2 m md = 2 kg T T₂1 Rc = 0.4 m mc = 5 kg ☐ m = 3 kgarrow_forward
- (read image) (answer given)arrow_forward11-5. Compute all the dimensional changes for the steel bar when subjected to the loads shown. The proportional limit of the steel is 230 MPa. 265 kN 100 mm 600 kN 25 mm thickness X Z 600 kN 450 mm E=207×103 MPa; μ= 0.25 265 kNarrow_forwardT₁ F Rd = 0.2 m md = 2 kg T₂ Tz1 Rc = 0.4 m mc = 5 kg m = 3 kgarrow_forward
- 2. Find a basis of solutions by the Frobenius method. Try to identify the series as expansions of known functions. (x + 2)²y" + (x + 2)y' - y = 0 ; Hint: Let: z = x+2arrow_forward1. Find a power series solution in powers of x. y" - y' + x²y = 0arrow_forward3. Find a basis of solutions by the Frobenius method. Try to identify the series as expansions of known functions. 8x2y" +10xy' + (x 1)y = 0 -arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Power Transmission; Author: Terry Brown Mechanical Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YVm4LNVp1vA;License: Standard Youtube License