Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133915426
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
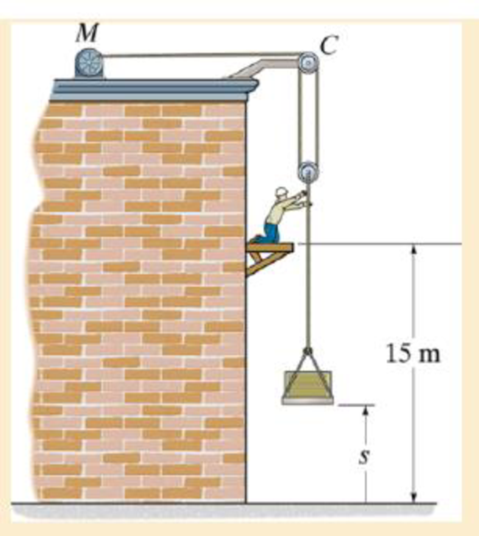
Chapter 14.3, Problem 3FP
If the motor exerts a force of F = (600 + 2s2) N on the cable, determine the speed of the 1 00-kg crate when it rises to s = 15 m. The crate is initially at rest on the ground.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Quick solution required.
My request, Don't use Ai.
Mechanical engineering
Please give handwritten solution, don't use chatgpt.
Fbd should be included
(I) [40 Points] Using centered finite difference approximations as done in class, solve the equation for O:
d20
dx²
+ 0.010+ Q=0
subject to the boundary conditions shown in the stencil below. Do this for two values of Q: (a) Q = 0.3,
and (b) Q= √(0.5 + 2x)e-sinx (cos(5x)+x-0.5√1.006-x| + e −43*|1+.001+x* | * sin (1.5 − x) +
(cosx+0.001 + ex-1250+ sin (1-0.9x)|) * x - 4.68x4. For Case (a) (that is, Q = 0.3), use the stencil in Fig.
1. For Case (b), calculate with both the stencils in Fig. 1 and Fig 2. For all the three cases, show a table as
well as a plot of O versus x. Discuss your results. Use MATLAB and hand in the MATLAB codes.
1
0=0
x=0
2
3
4
0=1
x=1
Fig 1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
11
0=0
x=0
0=1
x=1
Fig 2
Chapter 14 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
Ch. 14.3 - Determine the work of the force when it displaces...Ch. 14.3 - Determine the kinetic energy of the 10-kg block.Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 1FPCh. 14.3 - If the motor exerts a constant force of 300 N on...Ch. 14.3 - If the motor exerts a force of F = (600 + 2s2) N...Ch. 14.3 - The 1.8-Mg dragster is traveling at 125 m/s when...Ch. 14.3 - When s = 0.5 m, the spring is unstretched and the...Ch. 14.3 - The 5-lb collar is pulled by a cord that passes...Ch. 14.3 - The 20-kg crate is subjected to a force having a...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 2P
Ch. 14.3 - The crate, which has a mass of 100 kg, is...Ch. 14.3 - The 100-kg crate is subjected to the forces shown....Ch. 14.3 - Determine the required height h of the roller...Ch. 14.3 - When the driver applies the brakes of a light...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 7PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 8PCh. 14.3 - The air spring A is used to protect the support B...Ch. 14.3 - The force F, acting in a constant direction on the...Ch. 14.3 - The force of F= 50 N is applied to the cord when s...Ch. 14.3 - Design considerations for the bumper B on the 5-Mg...Ch. 14.3 - The 2-lb brick slides down a smooth roof, such...Ch. 14.3 - Block A has a weight of 60 lb and block B has a...Ch. 14.3 - The two blocks A and B have weights WA = 60 lb and...Ch. 14.3 - A small box of mass m is given a speed of v=14gr...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 17PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 18PCh. 14.3 - If the cord is subjected to a constant force of F=...Ch. 14.3 - The crash cushion for a highway barrier consists...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 21PCh. 14.3 - The 25-lb block has an initial speed of v0 = 10...Ch. 14.3 - The 8-Kg block is moving with an initial speed of...Ch. 14.3 - At a given instant the 10-lb block A is moving...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 25PCh. 14.3 - The catapulting mechanism is used to propel the...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 27PCh. 14.3 - The 1 0-lb box falls off the conveyor belt at...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 29PCh. 14.3 - The 30-lb box A is released from rest and slides...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 31PCh. 14.3 - The block has a mass of 0.8 kg and moves within...Ch. 14.3 - The 10-lb block is pressed against the spring so...Ch. 14.3 - The spring bumper is used to arrest the motion of...Ch. 14.3 - When the 150-lb skier is at point A he has a speed...Ch. 14.3 - The spring has a stiffness k = 50 lb/ ft and an...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 37PCh. 14.3 - If the 60-kg skier passes point A with a speed of...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 39PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 40PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 41PCh. 14.4 - If the contact surface between the 20-kg block and...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 8FPCh. 14.4 - Prob. 9FPCh. 14.4 - Prob. 10FPCh. 14.4 - Prob. 11FPCh. 14.4 - Prob. 12FPCh. 14.4 - The jeep has a weight of 2500 lb and an engine...Ch. 14.4 - Determine the power Input for a motor necessary to...Ch. 14.4 - An automobile having a mass of 2 Mg travels up a 7...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 45PCh. 14.4 - To dramatize the loss of energy in an automobile,...Ch. 14.4 - Escalator steps move with a constant speed of 0.6...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 48PCh. 14.4 - Prob. 49PCh. 14.4 - Determine the power output of the draw-works motor...Ch. 14.4 - The 1000-lb elevator is hoisted by the pulley...Ch. 14.4 - The 50-lb crate is given a speed of 10ft/s in t =...Ch. 14.4 - The sports car has a mass of 2.3 Mg, and while it...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 54PCh. 14.4 - Prob. 55PCh. 14.4 - The 10-lb collar starts from rest at A and is...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 57PCh. 14.4 - The 50-lb block rests on the rough surface for...Ch. 14.4 - The escalator steps move with a constant speed of...Ch. 14.4 - If the escalator in Prob.14-46 is not moving,...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 61PCh. 14.4 - Prob. 62PCh. 14.4 - Prob. 63PCh. 14.4 - Prob. 64PCh. 14.5 - The block has a mass of 150 kg and rests on a...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 3PPCh. 14.5 - Prob. 4PPCh. 14.5 - The 2-kg pendulum bob is released from rest when...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 14FPCh. 14.5 - Prob. 15FPCh. 14.5 - Prob. 16FPCh. 14.5 - The 75-lb block is released from rest 5 ft above...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 18FPCh. 14.5 - The girl has a mass of 40 kg and center of mass at...Ch. 14.5 - The 30-lb block A is placed on top of two nested...Ch. 14.5 - The 5-kg collar has a velocity of 5 m/s to the...Ch. 14.5 - The 5-kg collar has a velocity of 5 m/s to the...Ch. 14.5 - The ball has a weight of 15 lb and is fixed to a...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 71PCh. 14.5 - The roller coaster car has a mass of 700 kg,...Ch. 14.5 - The roller coaster car has a mass of 700 kg,...Ch. 14.5 - The assembly consists of two blocks A and B which...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 75PCh. 14.5 - Prob. 76PCh. 14.5 - The roller coaster car having a mass m is released...Ch. 14.5 - The spring has a stiffness k = 200 N/m and an...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 79PCh. 14.5 - Prob. 80PCh. 14.5 - When s = 0, the spring on the firing mechanism is...Ch. 14.5 - If the mass of the earth is Me, show that the...Ch. 14.5 - A rocket of mass m is fired vertically from the...Ch. 14.5 - The 4-kg smooth collar has a speed of 3 m/s when...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 85PCh. 14.5 - The skier starts from rest at A and travels down...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 87PCh. 14.5 - Prob. 88PCh. 14.5 - When the 6-kg box reaches point A it has a speed...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 90PCh. 14.5 - Prob. 91PCh. 14.5 - The roller coaster car has a speed of 15 ft/s when...Ch. 14.5 - The 10-kg sphere C is released from rest when =...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 94PCh. 14.5 - The cylinder has a mass of 20 kg and is released...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 96PCh. 14.5 - A pan of negligible mass is attached to two...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 1CPCh. 14.5 - Prob. 1RPCh. 14.5 - The small 2-lb collar starting from rest at A...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 3RPCh. 14.5 - Prob. 4RPCh. 14.5 - Prob. 5RPCh. 14.5 - Prob. 6RPCh. 14.5 - Prob. 7RPCh. 14.5 - Prob. 8RP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Fig 2 (II) [60 Points] Using centered finite difference approximation as done in class, solve the equation: 020 020 + მx2 მy2 +0.0150+Q=0 subject to the boundary conditions shown in the stencils below. Do this for two values of Q: (a) Q = 0.3, and (b) Q = 10.5x² + 1.26 * 1.5 x 0.002 0.008. For Case (a) (that is, Q = 0.3) use Fig 3. For Case (b), use both Fig. 3 and Fig 4. For all the three cases, show a table as well as the contour plots of versus (x, y), and the (x, y) heat flux values at all the nodes on the boundaries x = 1 and y = 1. Discuss your results. Use MATLAB and hand in the MATLAB codes. (Note that the domain is (x, y)e[0,1] x [0,1].) 0=0 0=0 4 8 12 16 10 Ꮎ0 15 25 9 14 19 24 3 11 15 0=0 8-0 0=0 3 8 13 18 23 2 6 сл 5 0=0 10 14 6 12 17 22 1 6 11 16 21 13 e=0 Fig 3 Fig 4 Textbook: Numerical Methods for Engineers, Steven C. Chapra and Raymond P. Canale, McGraw-Hill, Eighth Edition (2021).arrow_forwardShip construction question. Sketch and describe the forward arrangements of a ship. Include componets of the structure and a explanation of each part/ term. Ive attached a general fore end arrangement. Simplfy construction and give a brief describion of the terms.arrow_forwardProblem 1 Consider R has a functional relationship with variables in the form R = K xq xx using show that n ✓ - (OR 1.) = i=1 2 Их Ux2 Ихэ 2 (177)² = ² (1)² + b² (12)² + c² (1)² 2 UR R x2 x3arrow_forward
- 4. Figure 3 shows a crank loaded by a force F = 1000 N and Mx = 40 Nm. a. Draw a free-body diagram of arm 2 showing the values of all forces, moments, and torques that act due to force F. Label the directions of the coordinate axes on this diagram. b. Draw a free-body diagram of arm 2 showing the values of all forces, moments, and torques that act due to moment Mr. Label the directions of the coordinate axes on this diagram. Draw a free body diagram of the wall plane showing all the forces, torques, and moments acting there. d. Locate a stress element on the top surface of the shaft at A and calculate all the stress components that act upon this element. e. Determine the principal stresses and maximum shear stresses at this point at A.arrow_forward3. Given a heat treated 6061 aluminum, solid, elliptical column with 200 mm length, 200 N concentric load, and a safety factor of 1.2, design a suitable column if its boundary conditions are fixed-free and the ratio of major to minor axis is 2.5:1. (Use AISC recommended values and round the ellipse dimensions so that both axes are whole millimeters in the correct 2.5:1 ratio.)arrow_forward1. A simply supported shaft is shown in Figure 1 with w₁ = 25 N/cm and M = 20 N cm. Use singularity functions to determine the reactions at the supports. Assume El = 1000 kN cm². Wo M 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 cm Figure 1 - Problem 1arrow_forward
- Please AnswerSteam enters a nozzle at 400°C and 800 kPa with a velocity of 10 m/s and leaves at 375°C and 400 kPa while losing heat at a rate of 26.5 kW. For an inlet area of 800 cm2, determine the velocity and the volume flow rate of the steam at the nozzle exit. Use steam tables. The velocity of the steam at the nozzle exit is m/s. The volume flow rate of the steam at the nozzle exit is m3/s.arrow_forward2. A support hook was formed from a rectangular bar. Find the stresses at the inner and outer surfaces at sections just above and just below O-B. -210 mm 120 mm 160 mm 400 N B thickness 8 mm = Figure 2 - Problem 2arrow_forwardSteam flows steadily through a turbine at a rate of 45,000 lbm/h, entering at 1000 psia and 900°F and leaving at 5 psia as saturated vapor. If the power generated by the turbine is 4.1 MW, determine the rate of heat loss from the steam. The enthalpies are h1 = 1448.6 Btu/lbm and h2 = 1130.7 Btu/lbm. The rate of heat loss from the steam is Btu/s.arrow_forward
- The A/D converter wit the specifications listed below is planned to be used in an environment in which the A/D converter temperature may change by ± 10 °C. Estimate the contributions of conversion and quantization errors to the uncertainty in the digital representation of an analog voltage by the converter. FSO N Linearity error Temperature drift error Analog to Digital (A/D) Converter 0-10 V 12 bits ± 3 bits 1 bit/5 °Carrow_forward6-13. A smooth tube in the form of a circle of radius r rotates in its vertical plane with a constant angular velocity w. The position of a particle of mass m that slides inside the tube is given by the relative coordinate p. Find the differential equation for . e О E g ω Figure P6-13arrow_forwardProblem 2 Consider the power drawn by a resistance load in a DC circuit. The power is calculated as P = VI or P = 1²R. It is given that the normalized uncertainty or % percentage uncertainty in measurements of I, R, and V are the same. Find the uncertainty in P using the two different expressions for power. Is the uncertainty using the two methods the same? If not, WHY, explain?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Introduction To Engg Mechanics - Newton's Laws of motion - Kinetics - Kinematics; Author: EzEd Channel;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ksmsp9OzAsI;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY