How does the voltmeter reading compare to the potential difference across the electrodes? Explain.
If the sliding lead from electrode A were connected at point C along the resistor, would the voltmeter reading be positive, negative, or zero? Explain.
(Hint: Imagine disconnecting the ammeter and evacuated tube from the rest of the circuit, and answering the same question.)
How would you adjust the sliding connection from electrode A in order to make the potential difference across the electrodes
The potential difference reading in the voltmeter.
Voltmeter reading positive, negative or zero.
To adjustment to be made for the Voltmeter reading as positive and negative.
Answer to Problem 1aT
The potential across the electrodes is equal to the potential difference reading in the voltmeter.
Voltmeter reading will be positive.
By reversing the direction of the connection of the variable battery voltmeter can read negative potential.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
Photoelectric effect: Electrons from a metal surface are ejected when a light of an appropriate frequency is incident on it.The ejected electrons are called photoelectrons and the whole phenomenon is called photoelectric effect. This effect was explained by The Albert Einstein.
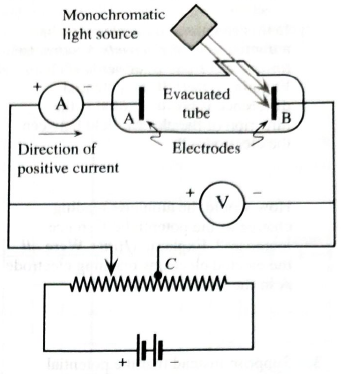
Figure 1 shows the circuit diagram to study the Photoelectric effect (PE).
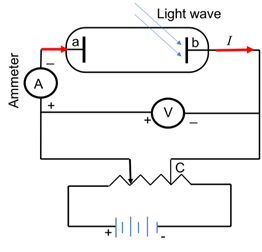
Figure 1: Set up to study photoelectric effect
A monochromatic is incident on one of the electrodes ‘b’ . Electron bonded to a metal requires a minimum energy just to leave the surface of metal is called binding energy of electron, also known as work function of the electron and denoted as
Current is flowing from positive to negative terminal of the battery (shown as red arrows in Figure 1).Therefore, the voltmeter will show the potential across electrode positive as electrons are flowing from high potential to lower potential.
Figure 2 shows the circuit diagram to study the Photoelectric effect (PE). In order to obtain the positive potentialdifference, read by voltmeter, figure 2(1) is applicable, as the electrode ‘b’ exposed to light is connected to negative terminal and other electrode ‘a’to the positive terminal of the battery. To make it more positive, one need to increase the potential of the variable battery that will make the electrode ‘a’more positive, hence will result in more positive potential across the electrodes.
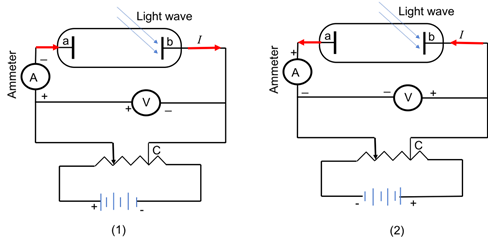
Figure 2: Set up to study photoelectric effect
In order to obtain the negative potential difference,read by voltmeter, figure 2(2) is applicable, as the electrode ‘b’ exposed to light is connected to positive terminal and other electrode ‘a’to the negative terminal of the battery.
Conclusion:
The potential across the electrodes is equal to the potential difference reading in the voltmeter.Voltmeter reading will be positive.By reversing the direction of the connection of the variable battery voltmeter can read negative potential.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Tutorials In Introductory Physics: Homework
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
- please answer this asap!!!!arrow_forwardRT = 4.7E-30 18V IT = 2.3E-3A+ 12 38Ω ли 56Ω ли r5 27Ω ли r3 28Ω r4 > 75Ω r6 600 0.343V 75.8A Now figure out how much current in going through the r4 resistor. |4 = unit And then use that current to find the voltage drop across the r resistor. V4 = unitarrow_forward7 Find the volume inside the cone z² = x²+y², above the (x, y) plane, and between the spheres x²+y²+z² = 1 and x² + y²+z² = 4. Hint: use spherical polar coordinates.arrow_forward
- ганм Two long, straight wires are oriented perpendicular to the page, as shown in the figure(Figure 1). The current in one wire is I₁ = 3.0 A, pointing into the page, and the current in the other wire is 12 4.0 A, pointing out of the page. = Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at point P. Express your answer using two significant figures. VO ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ? Figure P 5.0 cm 5.0 cm ₁ = 3.0 A 12 = 4.0 A B: μΤ You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again. Submit Previous Answers Request Answer 1 of 1 Part B X Express your answer using two significant figures. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ 0 = 0 ? below the dashed line to the right P You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again.arrow_forwardAn infinitely long conducting cylindrical rod with a positive charge λ per unit length is surrounded by a conducting cylindrical shell (which is also infinitely long) with a charge per unit length of −2λ and radius r1, as shown in the figure. What is σinner, the surface charge density (charge per unit area) on the inner surface of the conducting shell? What is σouter, the surface charge density on the outside of the conducting shell? (Recall from the problem statement that the conducting shell has a total charge per unit length given by −2λ.)arrow_forwardA small conducting spherical shell with inner radius aa and outer radius b is concentric with a larger conducting spherical shell with inner radius c and outer radius d (Figure 1). The inner shell has total charge +2q, and the outer shell has charge −2q. What's the total charge on the inner surface of the small shell? What's the total charge on the outer surface of the small shell? What's the total charge on the inner surface of the large shell? What's the total charge on the outer surface of the large shell?arrow_forward

 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning





