
Concept explainers
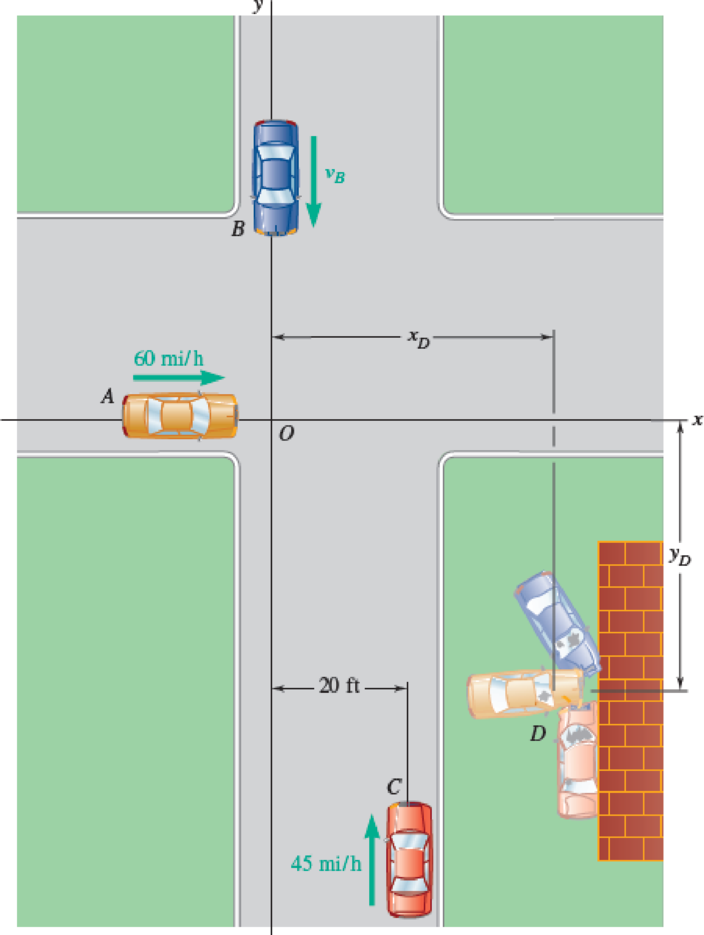
14.19 and 14.20 Cruiser A was traveling east at 60 mi/h on a police emergency call when it was hit at an intersection by car B, which was traveling south at high speed. After sliding together on the wet pavement, the two cars hit cruiser C, which was traveling north at 45 mi/h and was 63 ft from the intersection at the time of the first collision. Stuck together, the three cars hit a wall and came to a stop at D. Knowing that car B weighs 3600 lb and that each of the cruisers weighs 3000 lb, solve the problems below neglecting the forces exerted on the cars by the wet pavement and treating the cars as point masses.
14.19 Knowing that the coordinates of point D are xD = 42 ft and yD = 46.5 ft, determine (a) the time elapsed from the first collision to the stop at D, (b) the speed of car B.
Fig. P14.19 and P14.20
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
<LCPO> VECTOR MECH,STAT+DYNAMICS
- applied mechanics 2arrow_forward10 m/s 5° A 5 m 10 m/s PROBLEM 13.15 Car B is towing car A with a 5-m cable at a constant speed of 10 m/s on an uphill grade when the brakes of car B are fully applied causing it to skid to a stop. Car A, whose driver had not observed that car B was slowing down, then strikes the rear of car B. Neglecting air resistance and rolling resistance and assuming a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.9, determine the speed of car A just before the collision. VA : 9.09 m/s =arrow_forward13.21 Car B is towing car A at a constant speed of 10 m/s on an uphill grade when the brakes of car A are fully applied causing all four wheels to skid. The driver of car B does not change the throttle set- ting or change gears. The masses of the cars A and B are 1400 kg and 1200 kg, respectively, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.8. Neglecting air resistance and rolling resistance, determine (a) the dis- tance traveled by the cars before they come to a stop, (b) the tension in the cable. 5° 10 m/s A Fig. P13.21 5 m 10 m/s Barrow_forward
- applied mechanics 2arrow_forwardCar A with a constant velocity of 6.1 ft/s is heading east and in an instant that Car B with an initial velocity of 2.75 ft/s is traveling southwest at a constant rate of 0.05 ft/s2. The bearing of Car B from Car A is 30 deg north of east and the distance between them is 4800 ft. (a) Prove whether or not both Cars will collide in 5 mins. (b) What is the distance between the two cars in 10 mins? Show free body diagram.arrow_forwardA Fig. P11.140 150 m B -100 m Carrow_forward
- 11.20 A spring AB is attached to a support at A and to a collar. The unstretched length of the spring is 1. Knowing that the collar is released from rest at x = xo and has an acceleration defined by the relation a = -100(x- Ix/yR +x²), determine the velocity of the collar as it passes through point C.arrow_forwardTwo cars A and B start travelling at different times. Car A travelled 2 hours ahead of car B. Initially, car A is located at a distance 50 north of the location of car B. Car A travels towards the southeast direction in a straight line that deviates at an angle of 18 with respect to the east direction, while car B travels towards the northeast direction in a straight line that deviates at an angle of 20 with respect to the east direction as well. a. If the two cars meet after 6 hours, calculate the speed of both cars. b. Using the data from the first question, calculate the horizontal distance between the meeting point of the cars and the vertical line initially separating the two cars.arrow_forwardSAMPLE PROBLEM A motorist is traveling on a curved section of highway of radius 2500 ft at the speed of 60 mi/h. The motorist suddenly applies the brakes, causing the automobile to slow down at a constant rate. Knowing that after 8 s the speed has been reduced to 45 mi/h, determine the acceleration of the automobile immediately after the brakes have been applied. V= 60 mi /h 2500 ftarrow_forward
- RELATIVE MOTION Please show your neat and complete solution to this problem. ASAP! Thanks.arrow_forwardi need the answer quicklyarrow_forwardQuestion 6 Mohammed is driving his car at 80 km/hr speed from Alaya and Ahmed is driving his car at 60 km/hr from Thapti. If both start at the same time, with Ahmed 200 m ahead, the time in which Mohammed catches Ahmed will be a. 360.36 s b. 18.018 s c. 36.036 s d. 3.6036 sarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





