
The bromination of acetone is acid-catalyzed:
The rate of disappearance of bromine was measured for several different concentrations of acetone, bromine, and
|
|
|
Rate of Disappearance of
|
|
(1) |
0.30 |
0.050 |
0.050 |
|
(2) |
0.30 |
0.10 |
0.050 |
|
(3) |
0.30 |
0.050 |
0.10 |
|
(4) |
0.40 |
0.050 |
0.20 |
|
(5) |
0.40 |
0.050 |
0.050 |
|
(a) What is the rate law for the reaction? (b) Determine the rate constant. (c) The following mechanism has been proposed for the reaction:
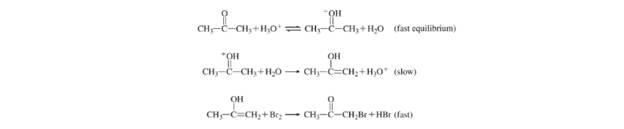
Show that the rate law deduced from the mechanism is consistent with that shown in part (a).
Interpretation:
The rate law and rate constant for the reaction are to be determined. The rate law is consistent with the mechanism shown in part (a), is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The rate of reaction in terms of concentration is called the rate law.
The step-by-step reaction is called the reaction mechanism. The reaction that takes place in a single step is called an elementary reaction.
Answer to Problem 85AP
Solution:
(a)
(b)
(c) The rate law deduced from the mechanism is consistent.
Explanation of Solution
a)The rate law for the reaction
For the determination of rate law, calculate the exponents as follows:
Based on
Based on
Based on
Based on
Hence, the rate law for the reaction is:
b)The rate constant
According to rate law, the rate constant for the reaction is:
Rearrange the above equation for
Here,
From experiment 1,
The rate law is
The concentration of
Substitute,
The rate constant for the reaction is
c) The rate law deduced from the given following mechanism is consistent or not with
The proposed mechanism for the reaction is:
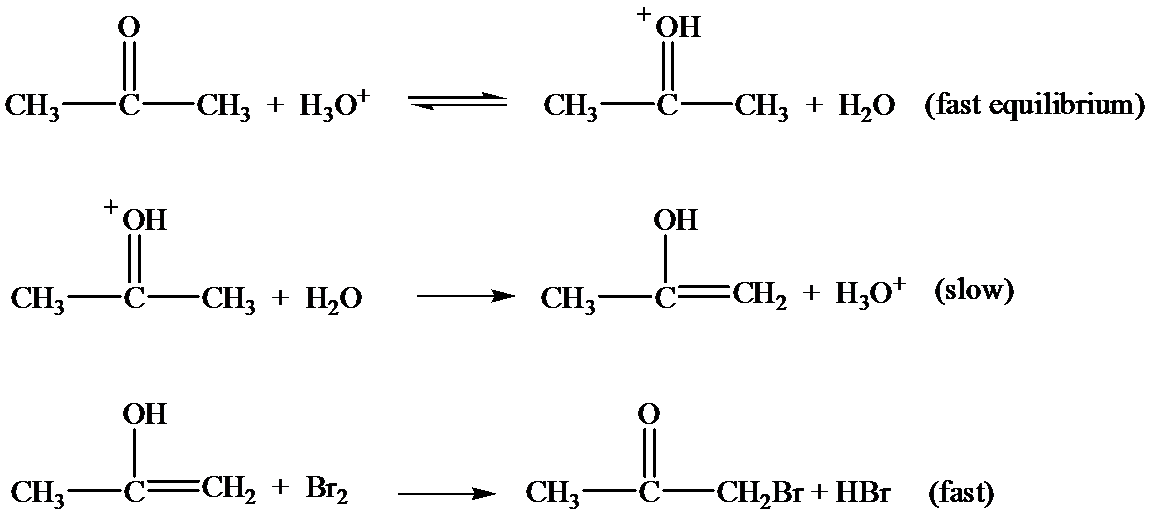
Let the rate constant for the slow step be
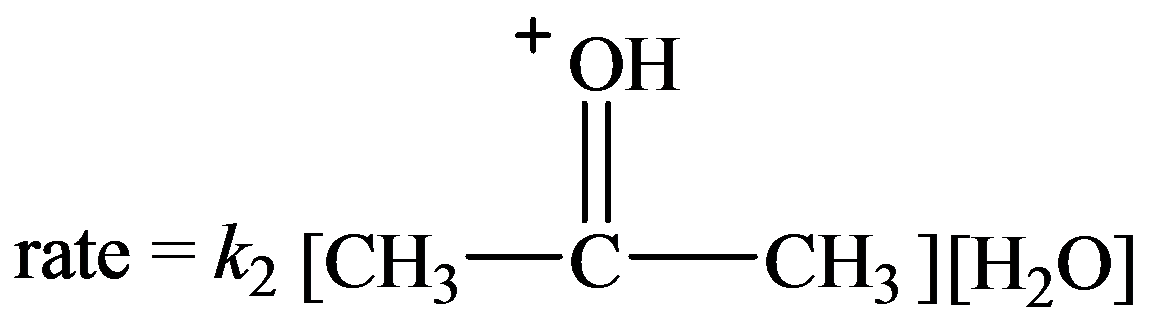 …… (1)
…… (1)
The rate constants for the forward and reverse steps in the fast equilibrium are
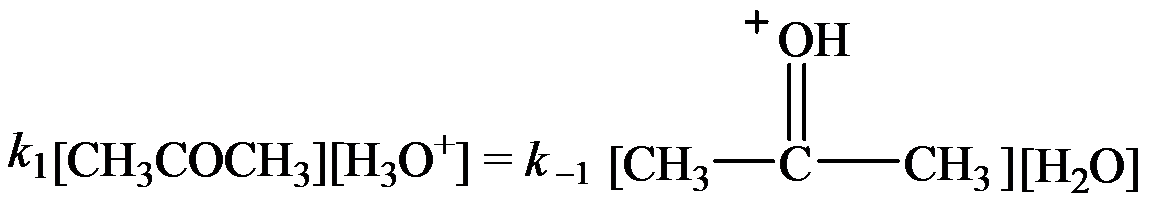 …… (2)
…… (2)
So, equation (1) becomes
The overall equation from part (a) is:
From equation (3) and (4),
So, the rate law is consistent with the mechanism shown in part (a).
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
EBK CHEMISTRY
- For questions 1-4, consider the following complexes: [Co(CN)6]+, [CoCl4]², [Cr(H2O)6]²+ 2. Draw the corresponding d-orbital splitting for each of the complexes; predict the spin- state (low-spin/high spin) for each of the complexes (if applicable); explain your arguments. Calculate the crystal field stabilization energy for each complex (in Ao or At). (6 points)arrow_forwardFor questions 1-4, consider the following complexes: [Co(CN)6]4, [COC14]², [Cr(H2O)6]²+ 1. Assign oxidation number to the metal, then indicate d-electron count. (3 points)arrow_forwardUsing iodometry I want to titrate a sodium thiosulfate solution and I use 15 mL. If I have 50 mL of a 0.90 M copper solution and KI, what will be the molarity of sodium thiosulfate?arrow_forward
- For Raman spectroscopy/imaging, which statement is not true regarding its disadvantages? a) Limited spatial resolution. b) Short integration time. c) A one-dimensional technique. d) Weak signal, only 1 in 108 incident photons is Raman scattered. e) Fluorescence interference.arrow_forwardUsing a cell of known pathlength b = 1.25115 x 10-3 cm, a water absorption spectrum was measured. The band at 1645 cm-1, assigned to the O-H bending, showed an absorbance, A, of 1.40. a) Assuming that water density is 1.00 g/mL, calculate the water molar concentration c (hint: M= mole/L) b) Calculate the molar absorptivity, a, of the 1645 cm-1 band c) The transmitted light, I, can be written as I= Ioexp(-xb), where x is the absorption coefficient (sometimes designated as alpha), Io is the input light, and b is the cell pathlength. Prove that x= (ln10)*x*c. (Please provide a full derivation of the equation for x from the equation for I). d) Calculate x for the 1645 cm-1 bandarrow_forwardI need help with the follloaingarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781285199023Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781285199023Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





